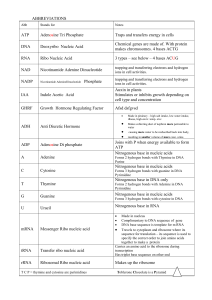
abbreviations - Spanish Point Biology
... Complimentary to DNA sequence of gene DNA base sequence is template for m RNA Travels to cytoplasm and ribosome where its sequence for translation – its sequence is used to specify the correct order to join amino acids together to make a protein Carries an amino acid to the ribosome during transcr ...
... Complimentary to DNA sequence of gene DNA base sequence is template for m RNA Travels to cytoplasm and ribosome where its sequence for translation – its sequence is used to specify the correct order to join amino acids together to make a protein Carries an amino acid to the ribosome during transcr ...
The Story of DNA vs. RNA
... § Proteins help to determine the size, shape and many other traits of an organism. ...
... § Proteins help to determine the size, shape and many other traits of an organism. ...
Nucleic Acids Placemat
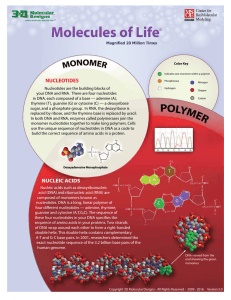
... Nucleic acids such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are composed of monomers known as nucleotides. DNA is a long, linear polymer of four different nucleotides — adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine (A,T,G,C). The sequence of these four nucleotides in your DNA specifies the ...
... Nucleic acids such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are composed of monomers known as nucleotides. DNA is a long, linear polymer of four different nucleotides — adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine (A,T,G,C). The sequence of these four nucleotides in your DNA specifies the ...
Use the diagram to match the letter (A-C) to the correct term(1
... 4. ______ Complementary base pair. 5. ______ Hydrogen bond. 6. ______ Individual nitrogen base. 7. ______ Sugar-phosphate backbone. 8. In DNA, which of the following determines the traits of an organism? a. Amount of adenine b. Number of sugars c. Sequence of nitrogen bases d. Strength of hydrogen b ...
... 4. ______ Complementary base pair. 5. ______ Hydrogen bond. 6. ______ Individual nitrogen base. 7. ______ Sugar-phosphate backbone. 8. In DNA, which of the following determines the traits of an organism? a. Amount of adenine b. Number of sugars c. Sequence of nitrogen bases d. Strength of hydrogen b ...
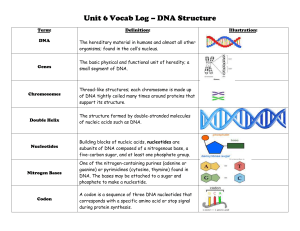
Unit 6 Vocab Log – DNA Structure Term: DNA Definition: The
... Thread-like structures; each chromosome is made up of DNA tightly coiled many times around proteins that support its structure. ...
... Thread-like structures; each chromosome is made up of DNA tightly coiled many times around proteins that support its structure. ...
DNA-notes
... nucleus of a cell *Genes within the chromosomes are considered the basic unit of heredity (Each gene has its own specific location called a LOCUS) *Double stranded, double helix shape ...
... nucleus of a cell *Genes within the chromosomes are considered the basic unit of heredity (Each gene has its own specific location called a LOCUS) *Double stranded, double helix shape ...
NA stabilization
... Other kind of pairings do occur in certain DNA and RNA structures. Watson Crick Base pairs are most stable as demonstrated by Lord and Rich by IR spectroscopy. ...
... Other kind of pairings do occur in certain DNA and RNA structures. Watson Crick Base pairs are most stable as demonstrated by Lord and Rich by IR spectroscopy. ...
the nucleic acids - This is MySchool
... The sister strands of the DNA molecule run in opposite directions (antiparallel) They are joined by the bases Each base is paired with a specific partner: A is always paired with T G is always paired with C Purine with Pyrimidine This the sister strands are complementary but not identical Th ...
... The sister strands of the DNA molecule run in opposite directions (antiparallel) They are joined by the bases Each base is paired with a specific partner: A is always paired with T G is always paired with C Purine with Pyrimidine This the sister strands are complementary but not identical Th ...
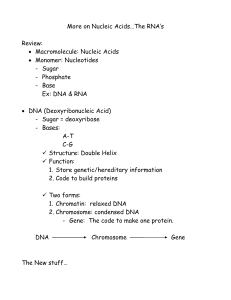
Notes: More on Nucleic Acids
... 1. Store genetic/hereditary information 2. Code to build proteins Two forms: 1. Chromatin: relaxed DNA 2. Chromosome: condensed DNA - Gene: The code to make one protein. DNA ...
... 1. Store genetic/hereditary information 2. Code to build proteins Two forms: 1. Chromatin: relaxed DNA 2. Chromosome: condensed DNA - Gene: The code to make one protein. DNA ...
Study_Guide
... State that deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a polynucleotide, usually double-stranded, made up of nucleotides containing the bases adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). State that ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polynucleotide, usually single-stranded, made up of nucleotides containi ...
... State that deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a polynucleotide, usually double-stranded, made up of nucleotides containing the bases adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). State that ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polynucleotide, usually single-stranded, made up of nucleotides containi ...
DNA Structure and Function Vocabulary
... Base pair • To form the DNA molecule, bases pair together across the double helix structure. Adenine (A) always pairs with Thymine (T), and Cytosine (C) always pairs with Guanine (G). These are the only pairs possible. ...
... Base pair • To form the DNA molecule, bases pair together across the double helix structure. Adenine (A) always pairs with Thymine (T), and Cytosine (C) always pairs with Guanine (G). These are the only pairs possible. ...
Objectives 2
... 1) List the types and principal functions of the nucleic acids. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is found in the cell nucleus and in the mitochondria and functions to store genetic information used for the synthesis of proteins and enzymes. Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is found in the nucleus, in the cytosol, ...
... 1) List the types and principal functions of the nucleic acids. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is found in the cell nucleus and in the mitochondria and functions to store genetic information used for the synthesis of proteins and enzymes. Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is found in the nucleus, in the cytosol, ...
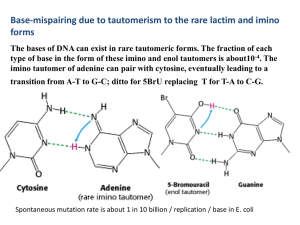
Guanine – Cytosine
... If you unraveled all your chromosomes from all of your cells and laid out the DNA end to end, the strands would stretch from the Earth to the Moon about 6,000 times. ...
... If you unraveled all your chromosomes from all of your cells and laid out the DNA end to end, the strands would stretch from the Earth to the Moon about 6,000 times. ...
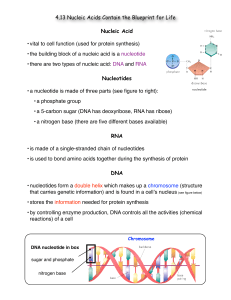
4.13 notes
... • there are two types of nucleic acid: DNA and RNA Nucleotides • a nucleotide is made of three parts (see figure to right): • a phosphate group • a 5-carbon sugar (DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose) • a nitrogen base (there are five different bases available) RNA • is made of a single-stranded cha ...
... • there are two types of nucleic acid: DNA and RNA Nucleotides • a nucleotide is made of three parts (see figure to right): • a phosphate group • a 5-carbon sugar (DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose) • a nitrogen base (there are five different bases available) RNA • is made of a single-stranded cha ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.