DNA - PBworks
... DNA Structure DNA consists of two molecules that are arranged into a ladder-like structure called a Double Helix. A molecule of DNA is made up of millions of ...
... DNA Structure DNA consists of two molecules that are arranged into a ladder-like structure called a Double Helix. A molecule of DNA is made up of millions of ...
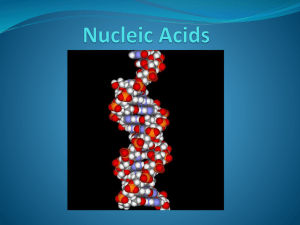
DNA – The Double Helix
... within the cell; which proteins are made is determined by the sequence of the DNA. Proteins are the building blocks of an organism. How you look is largely determined by the proteins that are made. ...
... within the cell; which proteins are made is determined by the sequence of the DNA. Proteins are the building blocks of an organism. How you look is largely determined by the proteins that are made. ...
Nucleic Acids
... DNA molecule • Double helix – H bonds between bases join the 2 strands • A :: T • C :: G ...
... DNA molecule • Double helix – H bonds between bases join the 2 strands • A :: T • C :: G ...
Introduction to Nucleic Acids
... messenger RNA and transfer RNA, respectively. You may even hear about rRNA which stands for ribosomal RNA. They are called nucleic acids because scientists first found them in the nucleus of cells. Now that we have better equipment, nucleic acids have been found in mitochondria, chloroplasts, and ce ...
... messenger RNA and transfer RNA, respectively. You may even hear about rRNA which stands for ribosomal RNA. They are called nucleic acids because scientists first found them in the nucleus of cells. Now that we have better equipment, nucleic acids have been found in mitochondria, chloroplasts, and ce ...
Nucleic Acids and DNA Replication
... • Dehydration reactions link nucleotides together • Phosphodiester linkages are the bonds between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of the next • New nucleotides can only be added to the 3’ end where there is an exposed hydroxyl group (from the sugar) • This is why we say that DNA is bui ...
... • Dehydration reactions link nucleotides together • Phosphodiester linkages are the bonds between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of the next • New nucleotides can only be added to the 3’ end where there is an exposed hydroxyl group (from the sugar) • This is why we say that DNA is bui ...
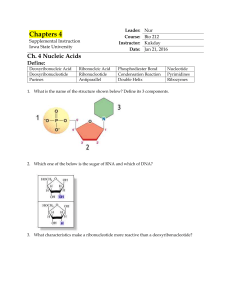
Ch. 4 Nucleic Acids Define
... 1. What is the name of the structure shown below? Define its 3 components. ...
... 1. What is the name of the structure shown below? Define its 3 components. ...
Quiz 2
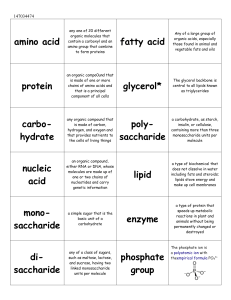
... 1. Nucleic Acids are informational macromolecules. Explain what they are and why this is. - Polymers that store, transmit, and express genetic information: this information is stored in sequences of monomers of nucleic acids - Two types of Nucleic acids: Deoxyribonucleic acid and Ribonucleic acid - ...
... 1. Nucleic Acids are informational macromolecules. Explain what they are and why this is. - Polymers that store, transmit, and express genetic information: this information is stored in sequences of monomers of nucleic acids - Two types of Nucleic acids: Deoxyribonucleic acid and Ribonucleic acid - ...
Nucleic Acids - cpprashanths Chemistry
... P = Phosphate Group S= 5 Carbon Sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) B= Nitrogen Base ...
... P = Phosphate Group S= 5 Carbon Sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) B= Nitrogen Base ...
Biology: Protein Synthesis, Extra Credit Name: Place these
... Place these events in the correct order defining protein synthesis. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. m. n. o. ...
... Place these events in the correct order defining protein synthesis. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. m. n. o. ...
Creation of a novel unnatural base pair system for the expansion of
... Creation of a novel unnatural base pair system for the expansion of the genetic alphabet toward future biotechnology Creation of a novel unnatural base pair system for the expansion of the genetic alphabet toward future biotechnology In nature, all organisms store genetic information within sequence ...
... Creation of a novel unnatural base pair system for the expansion of the genetic alphabet toward future biotechnology Creation of a novel unnatural base pair system for the expansion of the genetic alphabet toward future biotechnology In nature, all organisms store genetic information within sequence ...
CS4030: Tutorial 1- Biological Issues (from Bioinformatics ch 1)
... the nitrogenous base uracil in place of DNA’s thymine, and (2) the hydroxyl (OH) group attached to the 2’ carbon of the deoxyribose sugar of RNA is replaced with just a hydrogen (H) in DNA. Sketch the chemical structure of the deoxyribose sugar used by DNA in the ribose sugar used in RNA. 2. Diagram ...
... the nitrogenous base uracil in place of DNA’s thymine, and (2) the hydroxyl (OH) group attached to the 2’ carbon of the deoxyribose sugar of RNA is replaced with just a hydrogen (H) in DNA. Sketch the chemical structure of the deoxyribose sugar used by DNA in the ribose sugar used in RNA. 2. Diagram ...
August 31, 2016 - Iowa State University
... Ribonucleic Acid Thymine Watson-Crick pairing Glycosidic linkage Peptide Dehydration ...
... Ribonucleic Acid Thymine Watson-Crick pairing Glycosidic linkage Peptide Dehydration ...
nucleic acids - onlinebiosurgery
... One phosphate group; One sugar molecule ; One organic nitrogenous base. These subunits are joined by covalent bonds to form a nucleotide molecule. ...
... One phosphate group; One sugar molecule ; One organic nitrogenous base. These subunits are joined by covalent bonds to form a nucleotide molecule. ...
DNA and RNA
... the phosphate group of one nucleotide to the sugar of an adjacent nucleotide along the side of the double helix. The nitrogenous bases are held together by hydrogen bonds across a rung. ...
... the phosphate group of one nucleotide to the sugar of an adjacent nucleotide along the side of the double helix. The nitrogenous bases are held together by hydrogen bonds across a rung. ...
Genetic Information
... will only bond with their complementary base like a lock and a key o adenine + thymine o guanine + cytosine if you know one strand you can figure out the other strand o CGTTAACGTA o GCAATTGCAT DNA Replication o Occurs during interphase, right before cell enters prophase (mitosis and mitosis I) ...
... will only bond with their complementary base like a lock and a key o adenine + thymine o guanine + cytosine if you know one strand you can figure out the other strand o CGTTAACGTA o GCAATTGCAT DNA Replication o Occurs during interphase, right before cell enters prophase (mitosis and mitosis I) ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.