File - Mrs. Badger`s Honors Biology Class
... _____ 2. The main function of tRNA is to a. carry a message that, when translated, forms proteins. b. form a portion of ribosomes, a cell’s protein factories. c. string together complementary RNA and DNA strands. d. bring amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. _____ 3. What is the term for ...
... _____ 2. The main function of tRNA is to a. carry a message that, when translated, forms proteins. b. form a portion of ribosomes, a cell’s protein factories. c. string together complementary RNA and DNA strands. d. bring amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. _____ 3. What is the term for ...
So You Think
... won the Nobel Prize for discovering the shape of DNA. ________________ 5. DNA is said to have a ___________ ___________ ________________ shape. ________________ 6. Weak _________________ bonds allow the DNA ________________ molecule to “unzip”. ________________ 7. RNA contains three of the same nucl ...
... won the Nobel Prize for discovering the shape of DNA. ________________ 5. DNA is said to have a ___________ ___________ ________________ shape. ________________ 6. Weak _________________ bonds allow the DNA ________________ molecule to “unzip”. ________________ 7. RNA contains three of the same nucl ...
Unit 1 Rev 2 - Mr. Lesiuk
... ___ 1. List two specific examples of your cells making proteins. ___ 2. Name the three main nutrient groups/chemicals used by cells. ___ 3. What are the basic building blocks that make up a protein molecule? ___ 4. Many of the proteins/enzymes that a cell makes are crucial for the cell to properly w ...
... ___ 1. List two specific examples of your cells making proteins. ___ 2. Name the three main nutrient groups/chemicals used by cells. ___ 3. What are the basic building blocks that make up a protein molecule? ___ 4. Many of the proteins/enzymes that a cell makes are crucial for the cell to properly w ...
Nucleic Acids - Biology Innovation
... be once of five different bases. The pyrimidine bases are thymine, cytosine and uracil. The Purine bases are adenine and guanine. There are also two different types of pentose sugar which differ between DNA and RNA, the pentose sugar in DNA is deoxyribose and in RNA it is ribose. Shown below is a si ...
... be once of five different bases. The pyrimidine bases are thymine, cytosine and uracil. The Purine bases are adenine and guanine. There are also two different types of pentose sugar which differ between DNA and RNA, the pentose sugar in DNA is deoxyribose and in RNA it is ribose. Shown below is a si ...
DNA Connection
... DNA is made up of 4 nitrogen bases. Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) ...
... DNA is made up of 4 nitrogen bases. Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) ...
lecture 1
... Different DNA molecules differ only in the identities of the nitrogenous bases at any given position – they have different DNA sequences. A simple way to represent this strand of DNA is: 5’-TACG-3’ ...
... Different DNA molecules differ only in the identities of the nitrogenous bases at any given position – they have different DNA sequences. A simple way to represent this strand of DNA is: 5’-TACG-3’ ...
Players in the protein game
... microscope but in order to see the DNA you have to have a high powered mircroscope ...
... microscope but in order to see the DNA you have to have a high powered mircroscope ...
Chapter 24
... and cytosine, while RNA substitutes uracil for thymine. You aren’t responsible for the structures of the individual bases, but you should remember which bases are associated with which nucleic acid. The base always attaches at the aldol carbon. You should know the difference between ribose and deox ...
... and cytosine, while RNA substitutes uracil for thymine. You aren’t responsible for the structures of the individual bases, but you should remember which bases are associated with which nucleic acid. The base always attaches at the aldol carbon. You should know the difference between ribose and deox ...
Chapter 11 Concept Check Questions
... 3. Desribe the experimental design that allowed Hershey and Chase to distinguish between the two options for genetic material. ...
... 3. Desribe the experimental design that allowed Hershey and Chase to distinguish between the two options for genetic material. ...
BIO_Protein_Synthesis_Outline - Cole Camp R-1
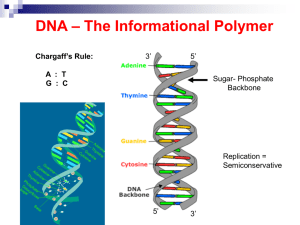
... ▸Describe the DNA molecule as being Spiral in Shape with the BASES on the inside and the Sugar- Phosphate Groups on the outside. ...
... ▸Describe the DNA molecule as being Spiral in Shape with the BASES on the inside and the Sugar- Phosphate Groups on the outside. ...
Isolating the Material of Heredity (Page 568
... acidic molecular part. Phoebus Levene did further work on nucleic acids... 1. Isolated 2 types... - have different sugars as part of their structures One has a five carbon sugar molecule in it ( ribose ), Levene called it ribonucleic acid, or RNA. ( 1909) One has the same five carbon sugar, with one ...
... acidic molecular part. Phoebus Levene did further work on nucleic acids... 1. Isolated 2 types... - have different sugars as part of their structures One has a five carbon sugar molecule in it ( ribose ), Levene called it ribonucleic acid, or RNA. ( 1909) One has the same five carbon sugar, with one ...
10 DNA Vocabulary - Petal School District
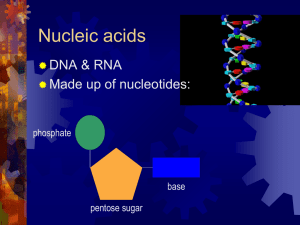
... 1. DNA—deoxyribonucleic acid 2. RNA—ribonucleic acid 3. nucleotide—the monomer for nucleic acids; made of a phosphate, sugar, and nitrogen base 4. hydrogen bonds—hold nitrogen base pairs together 5. genetic code—the sequence of the nitrogen bases (nucleotides) on DNA 6. DNA replication—process that ...
... 1. DNA—deoxyribonucleic acid 2. RNA—ribonucleic acid 3. nucleotide—the monomer for nucleic acids; made of a phosphate, sugar, and nitrogen base 4. hydrogen bonds—hold nitrogen base pairs together 5. genetic code—the sequence of the nitrogen bases (nucleotides) on DNA 6. DNA replication—process that ...
Application Sheet: DNA - NETZSCH Thermal Analysis
... DNA is a long polymer of simple units called nucleotides, which are held together by a backbone made of sugars and phosphate groups. This backbone carries four types of molecules called bases and it is the sequence of these ...
... DNA is a long polymer of simple units called nucleotides, which are held together by a backbone made of sugars and phosphate groups. This backbone carries four types of molecules called bases and it is the sequence of these ...
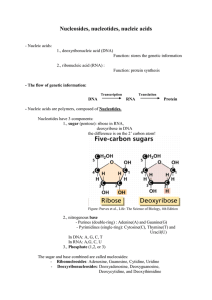
Nucleosides, nucleotides, nucleic acids
... Figure: Purves et al., Life: The Science of Biology, 4th Edition ...
... Figure: Purves et al., Life: The Science of Biology, 4th Edition ...
Mentor: James A. MacKay Students: Amanda Williams, Holly Sofka
... Project Description: Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is believed to be an important molecule in the evolution of life and has functionally taken on many important biological roles. Given the many functions of RNA, molecular recognition of RNA represents an attractive goal for practical applications in biotec ...
... Project Description: Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is believed to be an important molecule in the evolution of life and has functionally taken on many important biological roles. Given the many functions of RNA, molecular recognition of RNA represents an attractive goal for practical applications in biotec ...
Scientific Miracles of the Q
... of these ‘pairs’ of nucleotides control the genetic information carried by the DNA. A chromosome consists of different types of protein bound tightly with a single DNA molecule chain. The DNA is a large long (up to 1 meter long) amino acid chain. It consists of a ‘pair’ of spiral strands, connected ...
... of these ‘pairs’ of nucleotides control the genetic information carried by the DNA. A chromosome consists of different types of protein bound tightly with a single DNA molecule chain. The DNA is a large long (up to 1 meter long) amino acid chain. It consists of a ‘pair’ of spiral strands, connected ...
AT CG - Middletown Public Schools
... DNA is made up of nucleotides that each contain a sugar, a phosphate, and a base. The four possible bases are adenine, cytosine, thymine, and guanine. Remember that adenine and thymine are complementary and form pairs, and cytosine and guanine are complementary and form pairs. 1. Below is half of a ...
... DNA is made up of nucleotides that each contain a sugar, a phosphate, and a base. The four possible bases are adenine, cytosine, thymine, and guanine. Remember that adenine and thymine are complementary and form pairs, and cytosine and guanine are complementary and form pairs. 1. Below is half of a ...
Chapter 7 Biology
... • Scientists whom are famed to have discovered the double helix structure of DNA ...
... • Scientists whom are famed to have discovered the double helix structure of DNA ...
DNA
... All living things have DNA •We recycle the DNA in foods we eat. It is broken down into its basic parts and reused, like legos. •DNA is easy to extract from non-cooked foods ...
... All living things have DNA •We recycle the DNA in foods we eat. It is broken down into its basic parts and reused, like legos. •DNA is easy to extract from non-cooked foods ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.