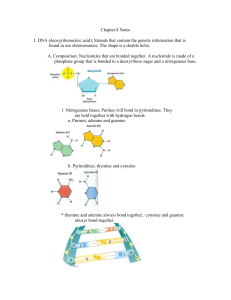
Nucleic acid review sheet
... What is the material in each cell that contains a set of instructions that controls all genetic traits? ...
... What is the material in each cell that contains a set of instructions that controls all genetic traits? ...
DNA
... • DNA is found in the mitochondria. • mDNA is only found in the egg. Sperm has no mitochondria so mDNA is passed to offspring from the mother. • One sequence of DNA is a genome or gene. • Unwind all our DNA, it will stretch from the moon and back 6000X. ...
... • DNA is found in the mitochondria. • mDNA is only found in the egg. Sperm has no mitochondria so mDNA is passed to offspring from the mother. • One sequence of DNA is a genome or gene. • Unwind all our DNA, it will stretch from the moon and back 6000X. ...
1. RNA is a different nucleic acid and differs from DNA on 3 things
... A transfer RNA molecule has two ends. One end has a specific binding site for a particular amino acid. The other end has a particular sequence of three nucleotides, the anticodon that can base pair with a codon. The appropriate molecule of t-RNA attaches to and carries the activated amino acid to th ...
... A transfer RNA molecule has two ends. One end has a specific binding site for a particular amino acid. The other end has a particular sequence of three nucleotides, the anticodon that can base pair with a codon. The appropriate molecule of t-RNA attaches to and carries the activated amino acid to th ...
DNA/RNA Worksheet TACGGCACCGTTAGGATT
... During replication, what would be the complementary bases to the following nucleotide sequence: A-A-G-G-T-C-T-C-A-C __________________________________ ...
... During replication, what would be the complementary bases to the following nucleotide sequence: A-A-G-G-T-C-T-C-A-C __________________________________ ...
Quiz 3-DNA.doc
... 7. How many amino acids are there? a. 20 b. 30 c. 40 d. 10 8. The disease that stops someone’s hemoglobin from getting to part of their body is called: a. Sickle-cell anemia b. Platelet dialysis c. Hemoglobina pseudomona d. Alzheimers 9. Only ___% of genes produce protein a. 1 b. 10 c. 20 d. 30 e. 4 ...
... 7. How many amino acids are there? a. 20 b. 30 c. 40 d. 10 8. The disease that stops someone’s hemoglobin from getting to part of their body is called: a. Sickle-cell anemia b. Platelet dialysis c. Hemoglobina pseudomona d. Alzheimers 9. Only ___% of genes produce protein a. 1 b. 10 c. 20 d. 30 e. 4 ...
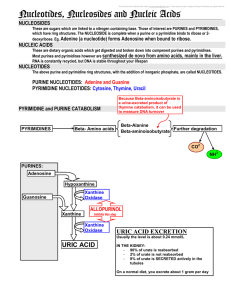
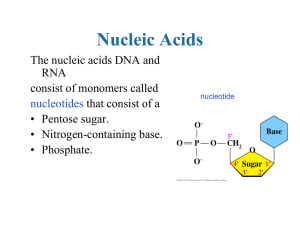
3 Nucleosides nucleotides and nucleic acids
... These are sugars which are linked to a nitrogen containing base. Those of interest are PURINES and PYRIMIDINES, which have ring structures. The NUCLEOSIDE is complete when a purine or a pyrimidine binds to ribose or 2deoxyribose. Eg. Adenine (a nucleotide) forms Adenosine when bound to ribose. ...
... These are sugars which are linked to a nitrogen containing base. Those of interest are PURINES and PYRIMIDINES, which have ring structures. The NUCLEOSIDE is complete when a purine or a pyrimidine binds to ribose or 2deoxyribose. Eg. Adenine (a nucleotide) forms Adenosine when bound to ribose. ...
Proteins and Nucleic Acids Proteins (pp.46-48) Monomer
... Proteins (pp.46-48) Monomer-basic structure Types of proteins and their functions Number of amino acids o what makes them different from one another o what's responsible for giving them their chemical properties Polymers o Bond responsible for linking amino acids together o Levels of Protein ...
... Proteins (pp.46-48) Monomer-basic structure Types of proteins and their functions Number of amino acids o what makes them different from one another o what's responsible for giving them their chemical properties Polymers o Bond responsible for linking amino acids together o Levels of Protein ...
106 DNA- Proteins
... Nucleic Acids (DNA & RNA) • Nucleic acids carry genetic information. • DNA (deoxyribonucleic acids) have molecular weights around 6 - 16 106 amu and are found inside the nucleus of the cell. • RNA (ribonucleic acids) have molecular weights around 20,000 to 40,000 amu and are found in the cytoplas ...
... Nucleic Acids (DNA & RNA) • Nucleic acids carry genetic information. • DNA (deoxyribonucleic acids) have molecular weights around 6 - 16 106 amu and are found inside the nucleus of the cell. • RNA (ribonucleic acids) have molecular weights around 20,000 to 40,000 amu and are found in the cytoplas ...
Slide 1
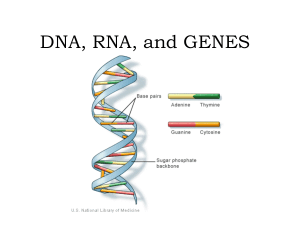
... Adenine Base Pairs with Thymine Uracil Base Pairs with Adenine Guanine Base Pairs with Cytosine Cytosine Base Pairs with Guanine ...
... Adenine Base Pairs with Thymine Uracil Base Pairs with Adenine Guanine Base Pairs with Cytosine Cytosine Base Pairs with Guanine ...
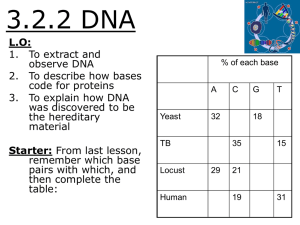
3.2.2 DNA - misslongscience / FrontPage
... 3.2.2 DNA L.O: 1. To extract and observe DNA 2. To describe how bases code for proteins 3. To explain how DNA was discovered to be the hereditary material Starter: From last lesson, remember which base pairs with which, and then complete the table: ...
... 3.2.2 DNA L.O: 1. To extract and observe DNA 2. To describe how bases code for proteins 3. To explain how DNA was discovered to be the hereditary material Starter: From last lesson, remember which base pairs with which, and then complete the table: ...
DNA, RNA, and GENES
... • Mutations are permanent changes in the DNA sequence of a cell’s gene or chromosome. • Mutations can be caused by outside factors like X-rays, sunlight, and chemicals. • A change in gene or chromosome can change the traits of an organism. ...
... • Mutations are permanent changes in the DNA sequence of a cell’s gene or chromosome. • Mutations can be caused by outside factors like X-rays, sunlight, and chemicals. • A change in gene or chromosome can change the traits of an organism. ...
January 7, 2014 Notes Transcription: process of copying DNA into
... January 7, 2014 Notes Transcription: process of copying DNA into an RNA template. (Occurs in nucleus) ...
... January 7, 2014 Notes Transcription: process of copying DNA into an RNA template. (Occurs in nucleus) ...
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis: Power Point presentation
... are linked by 3’-5’ ester bonds between deoxyribose and phosphate. ...
... are linked by 3’-5’ ester bonds between deoxyribose and phosphate. ...
Answers to the Study Guide for C12 Molecular Genetics Labeled
... the heredity factor that is passed on from generation to generation. If both were in the cells then both would contribute to the heredity information. 2. Replication is when DNA makes a copy of itself using base pairing rules. 3. Two double stranded DNA each having a parental strand and a new compli ...
... the heredity factor that is passed on from generation to generation. If both were in the cells then both would contribute to the heredity information. 2. Replication is when DNA makes a copy of itself using base pairing rules. 3. Two double stranded DNA each having a parental strand and a new compli ...
Mutations Can Change the Meaning of Genes
... How Mutations Affect Genes Mutation: any change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA Types of Mutations: Base substitutions: replacement of one nucleotide w/ another. May or may not affect protein Base deletions & Base insertions: May be more harmful b/c all subsequent codons will be altered ...
... How Mutations Affect Genes Mutation: any change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA Types of Mutations: Base substitutions: replacement of one nucleotide w/ another. May or may not affect protein Base deletions & Base insertions: May be more harmful b/c all subsequent codons will be altered ...
DNA Review Cards
... potential least effect on the protein. Describe the process of transcription. What is a mutagen? What is the primary enzyme in transcription. Give examples of mutagens. What type of cell must a mutation occur in to be passed on to offspring? ...
... potential least effect on the protein. Describe the process of transcription. What is a mutagen? What is the primary enzyme in transcription. Give examples of mutagens. What type of cell must a mutation occur in to be passed on to offspring? ...
Chapter 11 Notes
... 2. Another enzyme, DNA polymerase attaches free nucleotides to their complementary base pair by hydrogen bonding. 3. Because this is directional, the pairing of bases must occur in a 5’ to 3’ direction. ...
... 2. Another enzyme, DNA polymerase attaches free nucleotides to their complementary base pair by hydrogen bonding. 3. Because this is directional, the pairing of bases must occur in a 5’ to 3’ direction. ...
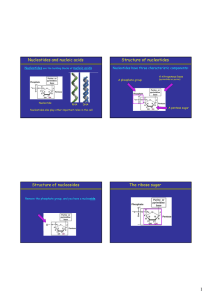
Nucleotides and nucleic acids Structure of nucleotides Structure of
... (bases in nucleic acids) plays an important role in function. • Nucleic acid structure depends on the sequence of bases and on the type of ribose sugar (ribose, or 2'-deoxyribose). • Hydrogen bonding interactions are especially important in nucleic acids. ...
... (bases in nucleic acids) plays an important role in function. • Nucleic acid structure depends on the sequence of bases and on the type of ribose sugar (ribose, or 2'-deoxyribose). • Hydrogen bonding interactions are especially important in nucleic acids. ...
Cloze passage 4
... CLOZE PASSAGE No 4 Transcription and Translation Complete the following sentences using appropriate words or short phrases a) The process where DNA makes an exact copy of itself is called …………………….. b) A string of amino acids is called a poly …………………. c) The site for protein synthesis in a cell d) 2 ...
... CLOZE PASSAGE No 4 Transcription and Translation Complete the following sentences using appropriate words or short phrases a) The process where DNA makes an exact copy of itself is called …………………….. b) A string of amino acids is called a poly …………………. c) The site for protein synthesis in a cell d) 2 ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.