DNA Replication - cloudfront.net
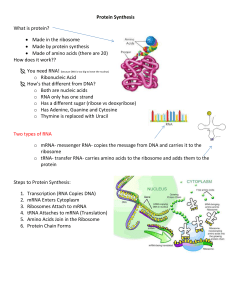
... 16. What brings a copy of information from the DNA to the ribosome? 17. What binds to the mRNA on 1 end and brings an amino acid on the other? 18. What makes up part of the ribosome and hold the mRNA during translation? 19. Which RNA makes the proteins? 20.What is the process that makes mRNA from DN ...
... 16. What brings a copy of information from the DNA to the ribosome? 17. What binds to the mRNA on 1 end and brings an amino acid on the other? 18. What makes up part of the ribosome and hold the mRNA during translation? 19. Which RNA makes the proteins? 20.What is the process that makes mRNA from DN ...
DNA - Doktorscience
... • DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic Acid and is found in structures called chromosomes in the nucleus of cells. • Chromosomes are made of both proteins and nucleic acids, and when a cell is not dividing they are stored as a spaghetti like tangle called chromatin. • DNA directs everything a cell does ...
... • DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic Acid and is found in structures called chromosomes in the nucleus of cells. • Chromosomes are made of both proteins and nucleic acids, and when a cell is not dividing they are stored as a spaghetti like tangle called chromatin. • DNA directs everything a cell does ...
DNA/RNA
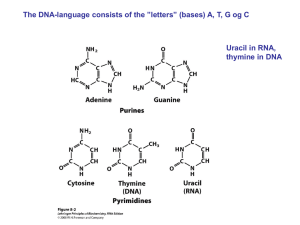
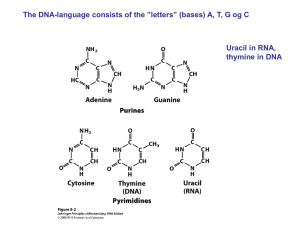
... and growth of an organism 9 Double stranded helix made up of nucleotides – four bases; Adenine, Thymine, Guanine and Cytosine 9 For encoding genetic information, the central feature of DNA structure is the A-T and G-C base pairing. http://student.ccbcmd.edu/~gkaiser/biotutorials/dna/fg4.html ...
... and growth of an organism 9 Double stranded helix made up of nucleotides – four bases; Adenine, Thymine, Guanine and Cytosine 9 For encoding genetic information, the central feature of DNA structure is the A-T and G-C base pairing. http://student.ccbcmd.edu/~gkaiser/biotutorials/dna/fg4.html ...
Review Game
... 100 What are the three parts of a nucleotide? Draw a picture to show. Deoxyribose sugar, phosphate, nitrogenous base 200 Who are the two scientists that discovered the shape of DNA? Watson and Crick 300 What makes up a nucleosome? DNA and histones 400 What is the type of bond that forms between the ...
... 100 What are the three parts of a nucleotide? Draw a picture to show. Deoxyribose sugar, phosphate, nitrogenous base 200 Who are the two scientists that discovered the shape of DNA? Watson and Crick 300 What makes up a nucleosome? DNA and histones 400 What is the type of bond that forms between the ...
DNA RNA-Protein Synthesis Homework
... Nucleic acids are the same in RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) as in DNA with one exception, Thymine is too big to be held by a one sided molecule so it is replaced by Uracil. So A-U and C-G are the pairs in RNA Single sided ladder structure that has sugar and phosphates and nucleotides. ...
... Nucleic acids are the same in RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) as in DNA with one exception, Thymine is too big to be held by a one sided molecule so it is replaced by Uracil. So A-U and C-G are the pairs in RNA Single sided ladder structure that has sugar and phosphates and nucleotides. ...
Randy Carroll
... 1. The main functions of DNA are is to store and transmit genetic information that tells cells which protein to make and when to make them. 3. The base pairing rules describe the pairing behavior of the bases. These rules state that cytosine bonds with guanine and adenine bonds ith thymine. 4. Enzym ...
... 1. The main functions of DNA are is to store and transmit genetic information that tells cells which protein to make and when to make them. 3. The base pairing rules describe the pairing behavior of the bases. These rules state that cytosine bonds with guanine and adenine bonds ith thymine. 4. Enzym ...
(DNA) and ribose (RNA)
... almost pure cellulose. What would happen if no organism could utilize cellulose (like humans)? ...
... almost pure cellulose. What would happen if no organism could utilize cellulose (like humans)? ...
which together form the gene "stories" NOTE
... humans have 46, dogs78, mice40, some bacteriaonly one DNA gives the cells specific instructions to create protiens for the organism they belong to ...
... humans have 46, dogs78, mice40, some bacteriaonly one DNA gives the cells specific instructions to create protiens for the organism they belong to ...
Code DNA!
... This is the process of copying DNA to RNA. The process of nuclear division in cells that produces daughter cells that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent cell. ...
... This is the process of copying DNA to RNA. The process of nuclear division in cells that produces daughter cells that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent cell. ...
DNA dna_essays
... called nucleotides • Nucleotides are made from 3 types of molecules: – Deoxyribose sugar – Phosphate group – Nucleic acid base (Nitrogen Base) ...
... called nucleotides • Nucleotides are made from 3 types of molecules: – Deoxyribose sugar – Phosphate group – Nucleic acid base (Nitrogen Base) ...
Biology Molecular Genetic Review
... 15. Why do only a specific amino acid attach to each transfer RNA? ...
... 15. Why do only a specific amino acid attach to each transfer RNA? ...
Organic Compounds - West Branch Schools
... Four groups of Organic Cmpds. Found in Living things 1. Carbohydrates - made up of C, H, O 1:2:1 Main source of energy for living things Structural in plants and some animals ...
... Four groups of Organic Cmpds. Found in Living things 1. Carbohydrates - made up of C, H, O 1:2:1 Main source of energy for living things Structural in plants and some animals ...
Document
... • A Gene is the fundamental physical and functional unit of heredity. A gene is an ordered sequence of nucleotides located in a particular position on a particular chromosome that encodes a specific functional product (i.e., a protein or RNA molecule). • A Genome is all the genetic material (DNA) in ...
... • A Gene is the fundamental physical and functional unit of heredity. A gene is an ordered sequence of nucleotides located in a particular position on a particular chromosome that encodes a specific functional product (i.e., a protein or RNA molecule). • A Genome is all the genetic material (DNA) in ...
Genomics wordsearch
... nucleotides in a DNA/RNA molecule which codes for an amino acid Cytosine – A nucleotide component of DNA/RNA ...
... nucleotides in a DNA/RNA molecule which codes for an amino acid Cytosine – A nucleotide component of DNA/RNA ...
Topic 7 The Discovery of DNA & Its Roles
... groups of three and in the correct reading frame The code is nearly universal ...
... groups of three and in the correct reading frame The code is nearly universal ...
Reproduction
... Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and bonucIeic acid (ANA) are two of the cell’s most Important molecules. These nucleic acids have a complex three-dimensional structure that enab les them to direct protein synthesis in the cell. • Study the structure of the DNA and RNA molecules shown below. Fill in the ...
... Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and bonucIeic acid (ANA) are two of the cell’s most Important molecules. These nucleic acids have a complex three-dimensional structure that enab les them to direct protein synthesis in the cell. • Study the structure of the DNA and RNA molecules shown below. Fill in the ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.