AND DNA Genes are located on chromosomes in the nucleus of
... known as nucleotides. And each nucleotide has a sugar, a phosphate, and a base inside. The four bases are adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine. Adenine binds to thymine, while guanine and cytosine bind. Groups of three code for aminos. Long strings of amino acids make proteins which send messages ...
... known as nucleotides. And each nucleotide has a sugar, a phosphate, and a base inside. The four bases are adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine. Adenine binds to thymine, while guanine and cytosine bind. Groups of three code for aminos. Long strings of amino acids make proteins which send messages ...
TIP Translation - dna
... Name: _____________________ Date: ____________ Class:_________ DNA Translation Quiz Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. What materials make up each nucleotide in a DNA molecule? a. amino acid, base, and protein c. mRNA, tRNA, and a r ...
... Name: _____________________ Date: ____________ Class:_________ DNA Translation Quiz Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. What materials make up each nucleotide in a DNA molecule? a. amino acid, base, and protein c. mRNA, tRNA, and a r ...
BUILDING THE LIFE MOLECULES: DNA AND RNA The
... The dissemination area of the Centro de Biotecnologia Molecular Estrutural (CBME) have been developing a program of new tools to help teaching and learning of structural molecular biology area at all levels, from elementary to graduate schools. In this way, we have developed a kit denoted Building t ...
... The dissemination area of the Centro de Biotecnologia Molecular Estrutural (CBME) have been developing a program of new tools to help teaching and learning of structural molecular biology area at all levels, from elementary to graduate schools. In this way, we have developed a kit denoted Building t ...
Nucleic Acids
... • Adjacent nucleotides are joined by covalent bonds that form between the –OH group on the 3´ carbon of one nucleotide and the phosphate on the 5´ carbon on the next • These links create a backbone of sugar-phosphate units with nitrogenous bases as appendages ...
... • Adjacent nucleotides are joined by covalent bonds that form between the –OH group on the 3´ carbon of one nucleotide and the phosphate on the 5´ carbon on the next • These links create a backbone of sugar-phosphate units with nitrogenous bases as appendages ...
notes_14C_nucacids
... - Weak noncovalent force caused by overlapping of p-orbitals; also called pi stacking. In DNA, aromatic stacking between the nucleotides contributes to its stability. The pyrimidine and purine bases, which are parallel to each other in DNA, participate in aromatic stacking due to the overlap of thei ...
... - Weak noncovalent force caused by overlapping of p-orbitals; also called pi stacking. In DNA, aromatic stacking between the nucleotides contributes to its stability. The pyrimidine and purine bases, which are parallel to each other in DNA, participate in aromatic stacking due to the overlap of thei ...
Protein Synth Notes GO New
... Example Problem 1. Write out the complementary DNA bases for the DNA strand: DNA #1: A A C G T G C A T T G A C G G DNA #2: __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ B. RNA molecule: 1. sugar: 2. nitrogen bases & pairings: 3. # of strands: 4. location: starts in Types of RNA ...
... Example Problem 1. Write out the complementary DNA bases for the DNA strand: DNA #1: A A C G T G C A T T G A C G G DNA #2: __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ B. RNA molecule: 1. sugar: 2. nitrogen bases & pairings: 3. # of strands: 4. location: starts in Types of RNA ...
Lecture 10: Nucleic acids (DNA & RNA)
... A nucleotide is formed in the cell when a base attaches to the 1' carbon of the sugar and a phosphate attaches to the 5' carbon of the same sugar . ...
... A nucleotide is formed in the cell when a base attaches to the 1' carbon of the sugar and a phosphate attaches to the 5' carbon of the same sugar . ...
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid)
... Above is an example of a nucleotide. In DNA, the sugar is deoxyribose and the organic base is either: A T ...
... Above is an example of a nucleotide. In DNA, the sugar is deoxyribose and the organic base is either: A T ...
WINK DNA Structure and Replication
... and chromosomes in coding the instructions for characteristic traits transferred from parent to offspring. * Develop and use models to explain how genetic information (DNA) is copied for transmission to subsequent generations of cells (mitosis). ...
... and chromosomes in coding the instructions for characteristic traits transferred from parent to offspring. * Develop and use models to explain how genetic information (DNA) is copied for transmission to subsequent generations of cells (mitosis). ...
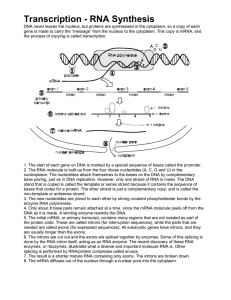
Transcription
... non-template or antisense strand. 3. The new nucleotides are joined to each other by strong covalent phosphodiester bonds by the enzyme RNA polymerase. 4. Only about 8 base pairs remain attached at a time, since the mRNA molecule peels off from the DNA as it is made. A winding enzyme rewinds the DNA ...
... non-template or antisense strand. 3. The new nucleotides are joined to each other by strong covalent phosphodiester bonds by the enzyme RNA polymerase. 4. Only about 8 base pairs remain attached at a time, since the mRNA molecule peels off from the DNA as it is made. A winding enzyme rewinds the DNA ...
S-strain (virulent)
... •Discovered by Watson and Crick •Consist of long strands of nucleotides •Deoxyribose •Phosphate group •Nitrogenous bases ...
... •Discovered by Watson and Crick •Consist of long strands of nucleotides •Deoxyribose •Phosphate group •Nitrogenous bases ...
DNA and RNA are nucleic acids that carry out cellular
... structure to ribose, but it has an H instead of an OH at the 2′ position. Bases can be divided into two categories: purines and pyrimidines. Purines have a double ring structure, and pyrimidines have a single ring. ...
... structure to ribose, but it has an H instead of an OH at the 2′ position. Bases can be divided into two categories: purines and pyrimidines. Purines have a double ring structure, and pyrimidines have a single ring. ...
DNA and RNA are nucleic acids that carry out cellular
... DNA) and ribose (found in RNA). Deoxyribose is similar in structure to ribose, but it has an H instead of an OH at the 2′ position. Bases can be divided into two categories: purines and pyrimidines. Purines have a double ring structure, and pyrimidines have a single ring. ...
... DNA) and ribose (found in RNA). Deoxyribose is similar in structure to ribose, but it has an H instead of an OH at the 2′ position. Bases can be divided into two categories: purines and pyrimidines. Purines have a double ring structure, and pyrimidines have a single ring. ...
Bonding is more than attraction
... - Adenosine triphosphate is a single nucleotide with two extra energy-storing phosphate groups. • Why is it important to cells? • ATP is the energy currency of the cell. ...
... - Adenosine triphosphate is a single nucleotide with two extra energy-storing phosphate groups. • Why is it important to cells? • ATP is the energy currency of the cell. ...
RNA
... RNA stands for ____________________________________ RNA takes the DNA’s instructions out of the __________________ and into the _______________________ of the cell where there is room for ____________________________________(protein synthesis) ...
... RNA stands for ____________________________________ RNA takes the DNA’s instructions out of the __________________ and into the _______________________ of the cell where there is room for ____________________________________(protein synthesis) ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.