Document
... 5. ___A protein is a polymer consisting of a specific sequence of: a. amino acids b. RNA nucleotides c. fatty acids d. DNA nucleotides. 6. ___During translation, one end of a tRNA molecule pairs with a complementary: a. nucleotide sequence in DNA b. tRNA molecule c. mRNA codon d. protein molecule. ...
... 5. ___A protein is a polymer consisting of a specific sequence of: a. amino acids b. RNA nucleotides c. fatty acids d. DNA nucleotides. 6. ___During translation, one end of a tRNA molecule pairs with a complementary: a. nucleotide sequence in DNA b. tRNA molecule c. mRNA codon d. protein molecule. ...
DNA RNA-Protein Synthesis Homework
... Nucleic acids are the same in RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) as in DNA with one exception, Thymine is too big to be held by a one sided molecule so it is replaced by Uracil. So A-U and C-G are the pairs in RNA Single sided ladder structure that has sugar and phosphates and nucleotides. ...
... Nucleic acids are the same in RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) as in DNA with one exception, Thymine is too big to be held by a one sided molecule so it is replaced by Uracil. So A-U and C-G are the pairs in RNA Single sided ladder structure that has sugar and phosphates and nucleotides. ...
Document
... Nucleotides (Gout, Lesh-Nyhan) De Novo Pathway Activated ribose (PRPP) + amino acids + ATP + CO2 +………. Nucleotides ...
... Nucleotides (Gout, Lesh-Nyhan) De Novo Pathway Activated ribose (PRPP) + amino acids + ATP + CO2 +………. Nucleotides ...
2-3 DNA to Proteins - Lighthouse Christian Academy
... chromosome so that a copy of the needed gene can be made. This is copy is called RNA (ribonucleic acid). RNA is similar to DNA except it is only one strand. o RNA to Ribosome – The RNA then leaves the nucleus and attaches to a ribosome which “reads” the code on the ...
... chromosome so that a copy of the needed gene can be made. This is copy is called RNA (ribonucleic acid). RNA is similar to DNA except it is only one strand. o RNA to Ribosome – The RNA then leaves the nucleus and attaches to a ribosome which “reads” the code on the ...
deoxyribonucleic acid contained in the chromosomes humans have
... humans have 46, dogs78, mice40, some bacteriaonly one ...
... humans have 46, dogs78, mice40, some bacteriaonly one ...
Section 4.3 – DNA
... Code contained in hereditary material Stored in cells that have a nucleus 1952 – Rosalind Franklin discovered that DNA is 2 chains in a spiral -‐ 1953 – Watson and Crick made a DNA model o ...
... Code contained in hereditary material Stored in cells that have a nucleus 1952 – Rosalind Franklin discovered that DNA is 2 chains in a spiral -‐ 1953 – Watson and Crick made a DNA model o ...
Unit 3 * Molecular Genetics
... Nucleic acids are named as such because they were originally found in the nucleus of the cell and contained phosphate groups (related to phosphoric acid). ...
... Nucleic acids are named as such because they were originally found in the nucleus of the cell and contained phosphate groups (related to phosphoric acid). ...
Human Genetic Variation - Mediapolis Community School
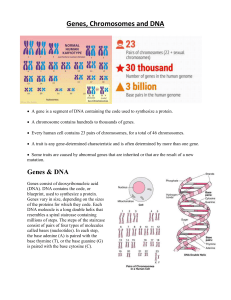
... • Genes are pieces of DNA, and most genes contain information for making a specific protein. • Genes exist in 2 forms at each location on a chromosome. These are called alleles. • Alleles can be dominant or recessive. ...
... • Genes are pieces of DNA, and most genes contain information for making a specific protein. • Genes exist in 2 forms at each location on a chromosome. These are called alleles. • Alleles can be dominant or recessive. ...
ANSWER KEY Nucleic Acid and DNA Replication Outline Notes
... During MITOSIS- chromosomes (DNA) are copied (replicated) ...
... During MITOSIS- chromosomes (DNA) are copied (replicated) ...
the nucleic acids - Y11-Biology-SG
... Nucleic acids were molecules first discovered in the nucleus of cells. These molecules are essential to life, are composed of 4 repeating units which, unlike proteins, are always the same: the nucleotides. There are 2 types of nucleic acids: the DNA and the RNA. ...
... Nucleic acids were molecules first discovered in the nucleus of cells. These molecules are essential to life, are composed of 4 repeating units which, unlike proteins, are always the same: the nucleotides. There are 2 types of nucleic acids: the DNA and the RNA. ...
Slide 1
... molecule is half old DNA and half new (one strand is from the original molecule and one strand is newly synthesized using the old strand as a template). ...
... molecule is half old DNA and half new (one strand is from the original molecule and one strand is newly synthesized using the old strand as a template). ...
Biology Summary Sheet
... Chromosomes are located in the nucleus of a cell. Genes are located on chromosomes and are made of DNA. DNA is a molecule that consists of two strands connected together by bases. DNA is described as a double-stranded helix. There are 4 bases named; adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine ...
... Chromosomes are located in the nucleus of a cell. Genes are located on chromosomes and are made of DNA. DNA is a molecule that consists of two strands connected together by bases. DNA is described as a double-stranded helix. There are 4 bases named; adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine ...
Genetics Lab - Identification of a Nucleic Acid
... must determine whether the nucleic acid is DNA or RNA, whether it is single-stranded or double-stranded. Based on this information, you should be able to identify the Virulent Virus. The following equipment and reagents will be available for week one, and might be helpful when designing your experim ...
... must determine whether the nucleic acid is DNA or RNA, whether it is single-stranded or double-stranded. Based on this information, you should be able to identify the Virulent Virus. The following equipment and reagents will be available for week one, and might be helpful when designing your experim ...
Macromolecule Flapbook
... 1. Fold a sheet of paper “hot dog style.” (Landscape). 2. Divide one side of the sheet of paper into four equal sections. 3. Label each section as follows: Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids 4. Then cut each segment (top side only to form flaps!) ...
... 1. Fold a sheet of paper “hot dog style.” (Landscape). 2. Divide one side of the sheet of paper into four equal sections. 3. Label each section as follows: Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids 4. Then cut each segment (top side only to form flaps!) ...
Slide 1
... to an mRNA sequence of interest • One of Two main effects can occur: – Translation arrest (no protein) – Recruits RNAase that degrades mRNA ...
... to an mRNA sequence of interest • One of Two main effects can occur: – Translation arrest (no protein) – Recruits RNAase that degrades mRNA ...
Transparency master
... complements the codons on the mRNA Codon - a group of 3 nucleotides in mRNA that specifies an amino acid Transcription – process by which mRNA molecules are copied from the DNA Translation – when codons in mRNA are decoded into a sequence of amino acids DNA – deoxyribonucleic acid, double-stranded h ...
... complements the codons on the mRNA Codon - a group of 3 nucleotides in mRNA that specifies an amino acid Transcription – process by which mRNA molecules are copied from the DNA Translation – when codons in mRNA are decoded into a sequence of amino acids DNA – deoxyribonucleic acid, double-stranded h ...
DNA - EPHS Knowles Biology
... 20. Where does mRNA take the triplicate code after it leaves the nucleus? 21. Name two things tRNA carries. 22. Where does translation occur in the cell? 23. When codons are matched with anticodons amino acids begin to link together to form? 24. What is protein synthesis? 25. What is the name of the ...
... 20. Where does mRNA take the triplicate code after it leaves the nucleus? 21. Name two things tRNA carries. 22. Where does translation occur in the cell? 23. When codons are matched with anticodons amino acids begin to link together to form? 24. What is protein synthesis? 25. What is the name of the ...
ERT 101 Biochemistry
... copies of its genome to its descendants. The key to DNA replication is the complementary structure of the two strands: Adenine and guanine in one strand bond with thymine and cytosine, respectively, in the other. DNA replication is a simple concept - a cell separates the two original strands and use ...
... copies of its genome to its descendants. The key to DNA replication is the complementary structure of the two strands: Adenine and guanine in one strand bond with thymine and cytosine, respectively, in the other. DNA replication is a simple concept - a cell separates the two original strands and use ...
Genes Chromosomes and DNA
... A trait is any gene-determined characteristic and is often determined by more than one gene. Some traits are caused by abnormal genes that are inherited or that are the result of a new mutation. ...
... A trait is any gene-determined characteristic and is often determined by more than one gene. Some traits are caused by abnormal genes that are inherited or that are the result of a new mutation. ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.