DNA notes File
... A nucleotide is when one phosphate group, one nitrogen base and one _______________ are ...
... A nucleotide is when one phosphate group, one nitrogen base and one _______________ are ...
Lecture 6
... f. DNA replication traps random error in time, for natural selection to work on Origin of LCA a. Problem of improbability before DNA, random mutation traps history b. Two models, not mutually exclusive i. RNA world can from 3-D structures and be catalysts, replicate and carry information ii. Probl ...
... f. DNA replication traps random error in time, for natural selection to work on Origin of LCA a. Problem of improbability before DNA, random mutation traps history b. Two models, not mutually exclusive i. RNA world can from 3-D structures and be catalysts, replicate and carry information ii. Probl ...
Identify which nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) contains each of the
... A mRNA has the sequence of codons 5′ CCC|AGA|GCC 3′ . If a base substitution in the DNA changes the mRNA codon of AGA to GGA, how is the amino acid sequence affected in the resulting protein? Can you predict whether this might have an effect on the protein function? ...
... A mRNA has the sequence of codons 5′ CCC|AGA|GCC 3′ . If a base substitution in the DNA changes the mRNA codon of AGA to GGA, how is the amino acid sequence affected in the resulting protein? Can you predict whether this might have an effect on the protein function? ...
Biology Chapter 12 Review 5-6
... 7. What units make up the backbone of DNA? 8. Explain how the information Watson and Crick acquired from Rosalind Franklin and Chargaff was used to determine the structure of DNA. 9. Explain complementary base pairing and the bases involved. 10. What hold base pairs together and how many? 11. Explai ...
... 7. What units make up the backbone of DNA? 8. Explain how the information Watson and Crick acquired from Rosalind Franklin and Chargaff was used to determine the structure of DNA. 9. Explain complementary base pairing and the bases involved. 10. What hold base pairs together and how many? 11. Explai ...
Transcription is the process by which RNA polymerase copies a
... amino acids that make up all proteins. Large proteins such as hemoglobin contain as many as 574 amino acids. Vocabulary DNA – Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid, doubled stranded genetic material Purine – A double ring Nitrogenous base Pyrimidine – A single ring nitrogenous base Prokaryote – Bacteria, singled ...
... amino acids that make up all proteins. Large proteins such as hemoglobin contain as many as 574 amino acids. Vocabulary DNA – Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid, doubled stranded genetic material Purine – A double ring Nitrogenous base Pyrimidine – A single ring nitrogenous base Prokaryote – Bacteria, singled ...
Structure and History of DNA 1-8
... Maclyn McCarty reported that they had found the “transforming principle” DNA! ...
... Maclyn McCarty reported that they had found the “transforming principle” DNA! ...
CS 262—Lecture 1 Notes • 4-‐5 HWs, 3 late days • (Optional
... o A binds with T and C binds with G o As such, DNA is double stranded • DNA must be read from 5’ to 3’ end • RNA usually single-‐stranded o Uracil replaces Thymine in RNA • Gene transcription: ...
... o A binds with T and C binds with G o As such, DNA is double stranded • DNA must be read from 5’ to 3’ end • RNA usually single-‐stranded o Uracil replaces Thymine in RNA • Gene transcription: ...
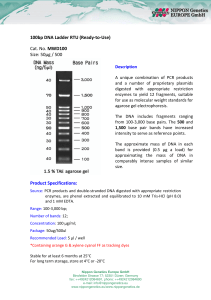
100bp DNA Ladder RTU (Ready-to-Use) Cat. No. MWD100 Size
... A unique combination of PCR products and a number of proprietary plasmids digested with appropriate restriction enzymes to yield 12 fragments, suitable for use as molecular weight standards for agarose gel electrophoresis. The DNA includes fragments ranging from 100-3,000 base pairs. The 500 and 1,5 ...
... A unique combination of PCR products and a number of proprietary plasmids digested with appropriate restriction enzymes to yield 12 fragments, suitable for use as molecular weight standards for agarose gel electrophoresis. The DNA includes fragments ranging from 100-3,000 base pairs. The 500 and 1,5 ...
What is a protein? - Hicksville Public Schools
... • This is called transcription • Brings code to ribosome *** remember, when it copies the code from DNA, A will pair up with U there will not by any T in RNA. ...
... • This is called transcription • Brings code to ribosome *** remember, when it copies the code from DNA, A will pair up with U there will not by any T in RNA. ...
CH 5: Carbs, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids – Study Chart I
... Directions: Use your textbook, class notes, and/or internet resources to complete the charts below. In the “box” to the right of each molecule, write a brief description explaining what the molecule is, or does, or is used for, in living things. ...
... Directions: Use your textbook, class notes, and/or internet resources to complete the charts below. In the “box” to the right of each molecule, write a brief description explaining what the molecule is, or does, or is used for, in living things. ...
Name Ch 12 Study Guide
... 21) What is protein synthesis? 22) Where does transcription take place? _______________________________ 23) Where does translation take place? _______________________________ 24) What is a codon? 25) What is an anti-codon? 26) There are 64 possible codons and 20 amino acids. What does this mean? ...
... 21) What is protein synthesis? 22) Where does transcription take place? _______________________________ 23) Where does translation take place? _______________________________ 24) What is a codon? 25) What is an anti-codon? 26) There are 64 possible codons and 20 amino acids. What does this mean? ...
Name: Date: Per: ______ Study Guide for AP Biology CHEMISTRY
... 2. 3.3 pg.43 What 2 major functions do nucleic acids perform in organisms? 3. 3.1. illustrate an amino acid with all 4 component parts, in what forms can the Carboxyl & Amino groups be found? Why to they have these 2 forms? ...
... 2. 3.3 pg.43 What 2 major functions do nucleic acids perform in organisms? 3. 3.1. illustrate an amino acid with all 4 component parts, in what forms can the Carboxyl & Amino groups be found? Why to they have these 2 forms? ...
2D Barcode Quiz
... Thymine, Guanine, Adenine and Cytosine are the four bases or ‘nucleotides’ that make up DNA Adenine and Guanine are Pyrimidines (6-point ring), Cytosine and Thymine are Purines (fused 5- and 6-point rings) DNA has a triple helix structure Adenine pairs with Thymine through 2 Hydrogen bonds, Cytosine ...
... Thymine, Guanine, Adenine and Cytosine are the four bases or ‘nucleotides’ that make up DNA Adenine and Guanine are Pyrimidines (6-point ring), Cytosine and Thymine are Purines (fused 5- and 6-point rings) DNA has a triple helix structure Adenine pairs with Thymine through 2 Hydrogen bonds, Cytosine ...
Assignment 2 with Key
... When two strands of DNA anneal to form a double helix, their absorbance at 260 nm decreases relative to the sum of A 260 of the individual strands. This hypochromicity is used to determine the extent of duplex formation. ...
... When two strands of DNA anneal to form a double helix, their absorbance at 260 nm decreases relative to the sum of A 260 of the individual strands. This hypochromicity is used to determine the extent of duplex formation. ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.