mastering protein synthesis
... MASTERING PROTEIN SYNTHESIS From this DNA, you have all the information you need to build protein. 5’ ATGGTTACAGTCTATTAGATGCTATTTCAACACCAATAA 3’ 3’ TACCAATGTCAGATAATCTACGATAAAGTTGTGGTTATT 5’ ...
... MASTERING PROTEIN SYNTHESIS From this DNA, you have all the information you need to build protein. 5’ ATGGTTACAGTCTATTAGATGCTATTTCAACACCAATAA 3’ 3’ TACCAATGTCAGATAATCTACGATAAAGTTGTGGTTATT 5’ ...
Ch - Fairview High School
... Function in cells – Fat – made from glycerol and fatty acids Example: Triglyceride from glycerol and 3 fatty acids: Saturated fatty acid – contains ____ C-C double bonds; contains as many bonds to _______ atoms as possible. Saturated fats pack together very tightly; at room temperature they are typi ...
... Function in cells – Fat – made from glycerol and fatty acids Example: Triglyceride from glycerol and 3 fatty acids: Saturated fatty acid – contains ____ C-C double bonds; contains as many bonds to _______ atoms as possible. Saturated fats pack together very tightly; at room temperature they are typi ...
No Slide Title
... • In the replication of a double-stranded or duplex DNA molecule, both original (parental) DNA strands are copied • When copying is finished, the two new duplexes, each consisting of one of the original strands plus its copy, separate from each other (semiconservative replication) ...
... • In the replication of a double-stranded or duplex DNA molecule, both original (parental) DNA strands are copied • When copying is finished, the two new duplexes, each consisting of one of the original strands plus its copy, separate from each other (semiconservative replication) ...
dna review - NVHSIntroBioPiper1
... There are three main differences between DNA and RNA: 1. RNA has the sugar Ribose / DNA has the sugar Deoxyribose. 2. RNA is single stranded / DNA is double stranded. 3. In RNA, adenine pairs with uracil / in DNA, adenine pairs with thymine. ...
... There are three main differences between DNA and RNA: 1. RNA has the sugar Ribose / DNA has the sugar Deoxyribose. 2. RNA is single stranded / DNA is double stranded. 3. In RNA, adenine pairs with uracil / in DNA, adenine pairs with thymine. ...
From boron analogues of amino acids to boronated DNA
... boron analogues of the a-amino acids. These have ranged from simple glycine analogues such as H3NBH2COOH and Me2NHBH2COOH to alanine analogues. A diverse variety of analogues, including precursors and derivatives (such as peptides) have expressed potent pharmacological activity, including anticancer ...
... boron analogues of the a-amino acids. These have ranged from simple glycine analogues such as H3NBH2COOH and Me2NHBH2COOH to alanine analogues. A diverse variety of analogues, including precursors and derivatives (such as peptides) have expressed potent pharmacological activity, including anticancer ...
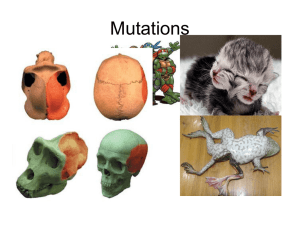
mutations - Pasadena High School
... Frame Shift: The fat caa tet hew eer at. (Frame shift mutations affect all subsequent amino acids!) ...
... Frame Shift: The fat caa tet hew eer at. (Frame shift mutations affect all subsequent amino acids!) ...
Carbon Compounds
... Nucleic Acids • Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary (genetic) information. • There are 2 kinds of nucleic acids: – Ribonucleic acid (RNA), which contains the sugar ribose – Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), which contains the sugar deoxyribose ...
... Nucleic Acids • Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary (genetic) information. • There are 2 kinds of nucleic acids: – Ribonucleic acid (RNA), which contains the sugar ribose – Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), which contains the sugar deoxyribose ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... Permanent, sudden change in nucleotides sequence will change the sequence of amino acids of the polypeptide chain to be synthesized, therefore altering the genotype of a cell/organism. An example of gene mutation is sickle cell anaemia. ...
... Permanent, sudden change in nucleotides sequence will change the sequence of amino acids of the polypeptide chain to be synthesized, therefore altering the genotype of a cell/organism. An example of gene mutation is sickle cell anaemia. ...
Chapter 2 Notes - Anatomy
... Atom—smallest unit of all matter 2 Regions of the atom: 1.) Nucleus—dense center of the atom 2.) Electron Cloud—the region outside the nucleus *arranged in levels around the nucleus 1st level—can hold up to 2 electrons 2nd level—can hold up to 8 electrons 3rd level—can hold up to 18 electrons 4th le ...
... Atom—smallest unit of all matter 2 Regions of the atom: 1.) Nucleus—dense center of the atom 2.) Electron Cloud—the region outside the nucleus *arranged in levels around the nucleus 1st level—can hold up to 2 electrons 2nd level—can hold up to 8 electrons 3rd level—can hold up to 18 electrons 4th le ...
Nucliec acids and dna review
... 79. Sketch and label a tRNA molecule & tell its function. 80. Define translation & tell how it starts. 81. Where are amino acids found in a cell & how are they transported? 82. What is an anticodon & where is it found on tRNA? 83. What codon on mRNA would bind with these anticodons a. AAA b. GGA c. ...
... 79. Sketch and label a tRNA molecule & tell its function. 80. Define translation & tell how it starts. 81. Where are amino acids found in a cell & how are they transported? 82. What is an anticodon & where is it found on tRNA? 83. What codon on mRNA would bind with these anticodons a. AAA b. GGA c. ...
Transcirption and Translation Practice
... c) Notice from the table of the genetic code (included at the end of this lab) that 61 codons represent the 20 different amino acids. Why do you think it is advantageous, from a genetic perspective, to have this redundancy (i.e. the same amino acid is represented by more than one codon)? ...
... c) Notice from the table of the genetic code (included at the end of this lab) that 61 codons represent the 20 different amino acids. Why do you think it is advantageous, from a genetic perspective, to have this redundancy (i.e. the same amino acid is represented by more than one codon)? ...
Carbohydrates are
... Proteins are important to the structures of cells and organisms and participate in everything they do. the most important role for proteins is as enzymes. ...
... Proteins are important to the structures of cells and organisms and participate in everything they do. the most important role for proteins is as enzymes. ...
Biomolecules PPT
... Examples – meats, nuts and beans, fish •Makes muscle, feathers, hair and nails and enzymes •An enzyme is a molecule that speeds up or slows down a chemical reaction so that it can occur at body temperature. ...
... Examples – meats, nuts and beans, fish •Makes muscle, feathers, hair and nails and enzymes •An enzyme is a molecule that speeds up or slows down a chemical reaction so that it can occur at body temperature. ...
CH 13
... RNA has the information to make proteins •We say mRNA codes for proteins •Where was this information before any mRNA was made? _____________________ •HOW does RNA code for proteins? •The triplet code: ...
... RNA has the information to make proteins •We say mRNA codes for proteins •Where was this information before any mRNA was made? _____________________ •HOW does RNA code for proteins? •The triplet code: ...
What are the three steps in PCR?
... It is often used in DNA fingerprinting It requires gel electrophoresis which separates DNA by size ...
... It is often used in DNA fingerprinting It requires gel electrophoresis which separates DNA by size ...
DNA Unit Study Guide
... 1. What are proteins and why are they important in cells? 2. What are amino acids? 3. What determines the differences between proteins of a cow and a human? 4. Protein Synthesis in a cell begins with a process call Transcription: the making of a messenger RNA molecule. What does the word Transcripti ...
... 1. What are proteins and why are they important in cells? 2. What are amino acids? 3. What determines the differences between proteins of a cow and a human? 4. Protein Synthesis in a cell begins with a process call Transcription: the making of a messenger RNA molecule. What does the word Transcripti ...
Replication, Transcription, Translation
... 1. Know the parts of a DNA nucleotide 2. Know the meaning o, and understand the process for the following words: replication, transcription, translation. 3. Know the respective sugars and nitrogenous bases that DNA and RNA contain. 4. Be able to name each of the 3 types of RNA and be able to explain ...
... 1. Know the parts of a DNA nucleotide 2. Know the meaning o, and understand the process for the following words: replication, transcription, translation. 3. Know the respective sugars and nitrogenous bases that DNA and RNA contain. 4. Be able to name each of the 3 types of RNA and be able to explain ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.