13.3 RNA and Gene Expression
... This is known as gene expression. Proteins determine the structure and function of organisms (traits). ...
... This is known as gene expression. Proteins determine the structure and function of organisms (traits). ...
4.1 Le Noyau
... • A joins with T • G joins with C • But the order and number of these bases can vary greatly within the DNA molecule ...
... • A joins with T • G joins with C • But the order and number of these bases can vary greatly within the DNA molecule ...
notes for mondays lab
... 2. Proteinase K: an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of cellular proteins by splitting them into smaller peptides and amino acids 3. Buffer AL: a cell lysis solution that breaks open cell and nuclear membranes 4. Ethanol: used to precipitate DNA from the extracted material 5. Buffer AW1 and AW2: ...
... 2. Proteinase K: an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of cellular proteins by splitting them into smaller peptides and amino acids 3. Buffer AL: a cell lysis solution that breaks open cell and nuclear membranes 4. Ethanol: used to precipitate DNA from the extracted material 5. Buffer AW1 and AW2: ...
Name Class ______ Date ______ The Genetic Code 1. Genetic
... Name _____________________________ Class __________ Date __________ 9. A researcher identifies the nucleotide sequence AAC in a long strand of RNA inside a nucleus. In the genetic code, AAC codes for the amino acid asparagine. When the RNA becomes involved in protein synthesis, will asparagines nec ...
... Name _____________________________ Class __________ Date __________ 9. A researcher identifies the nucleotide sequence AAC in a long strand of RNA inside a nucleus. In the genetic code, AAC codes for the amino acid asparagine. When the RNA becomes involved in protein synthesis, will asparagines nec ...
Anaerobic Respiration - Deans Community High School
... membrane and enters the ____________. Each triplet of bases on mRNA is called a __________. tRNA A second type of RNA is found in the cell’s cytoplasm. This is called ____________ _____ (______). Each molecule of tRNA has an exposed triplet of bases, known as an anticodon. This anticodon corresponds ...
... membrane and enters the ____________. Each triplet of bases on mRNA is called a __________. tRNA A second type of RNA is found in the cell’s cytoplasm. This is called ____________ _____ (______). Each molecule of tRNA has an exposed triplet of bases, known as an anticodon. This anticodon corresponds ...
2.2 PPT_Proteins and Nucleic Acids
... Brown Paper Bag Test: A test for LIPIDS/FATS. If test is positive, it will leave a greasy residue on the brown paper, telling you there IS a lipid! Biuret’s Reagent: A test for PROTEINS. If test is positive, it turn pink or purple, telling you that there IS a ...
... Brown Paper Bag Test: A test for LIPIDS/FATS. If test is positive, it will leave a greasy residue on the brown paper, telling you there IS a lipid! Biuret’s Reagent: A test for PROTEINS. If test is positive, it turn pink or purple, telling you that there IS a ...
Study Guide: The Cell
... 2. What are the three types of RNA are and their functions? 3. Differentiate between transcription and translation? ...
... 2. What are the three types of RNA are and their functions? 3. Differentiate between transcription and translation? ...
DNA notes
... • The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the base pairs A=T (2 bonds) and G=C (3 bonds) • The base pairs, like the steps on a spiral staircase, extend in to the center of the molecule • The "frame" of the double helix comes from the phosphatedeoxyribose linkages that connect nuc ...
... • The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the base pairs A=T (2 bonds) and G=C (3 bonds) • The base pairs, like the steps on a spiral staircase, extend in to the center of the molecule • The "frame" of the double helix comes from the phosphatedeoxyribose linkages that connect nuc ...
DNA replication - Sonoma Valley High School
... the molecule and it uncoils. • New N bases come in and bond to each side. • Polymerase joins them into a new molecule. • It also “proofreads” the new strands for ...
... the molecule and it uncoils. • New N bases come in and bond to each side. • Polymerase joins them into a new molecule. • It also “proofreads” the new strands for ...
Macromolecules (Biomolecules)
... 3) What is the name given to small molecules that make up larger molecules? 4) Listed below are the names of the four major classes of macromolecules as well as their monomers. Match up the monomer(s) with their parent compound: lipids, amino acids, fatty acids, carbohydrates, glycerol, monosacchari ...
... 3) What is the name given to small molecules that make up larger molecules? 4) Listed below are the names of the four major classes of macromolecules as well as their monomers. Match up the monomer(s) with their parent compound: lipids, amino acids, fatty acids, carbohydrates, glycerol, monosacchari ...
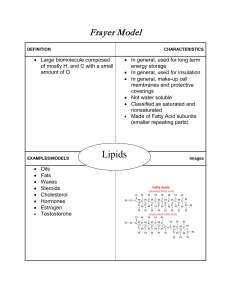
Frayer Model
... • Composed of C, H, N, O and sometimes S • Help organisms form structural components • Carry out all cellular reactions • Function based on 3-dimensional shape • Made of amino acid subunits (smaller repeating parts) • Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions ...
... • Composed of C, H, N, O and sometimes S • Help organisms form structural components • Carry out all cellular reactions • Function based on 3-dimensional shape • Made of amino acid subunits (smaller repeating parts) • Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions ...
BioSc 231 Exam 3 2005
... that would be produced by the RNA polymerase binding to this promoter (up to the end of the molecule). (4 points) ...
... that would be produced by the RNA polymerase binding to this promoter (up to the end of the molecule). (4 points) ...
Macromolecules practice worksheet key
... them different chemical properties that range from acidic to basic and hydrophilic and hydrophobic. ...
... them different chemical properties that range from acidic to basic and hydrophilic and hydrophobic. ...
Chapter 15: Protein Synthesis
... • Enzymes unwind the double helix and separate the two strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases only in the region where the gene to be transcribed is located • RNA polymerase synthesises messenger RNA (mRNA) using one of the strands of DNA as RNA polymerase a template ...
... • Enzymes unwind the double helix and separate the two strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases only in the region where the gene to be transcribed is located • RNA polymerase synthesises messenger RNA (mRNA) using one of the strands of DNA as RNA polymerase a template ...
Biosem1Finalreview - Uplift Summit International
... Hershey Chase experiment Contributions of various scientists in the field of DNA research – Avery, Chargaff, Wilkins and Franklin, Watson and Crick Structure of DNA Base pairing rules DNA replication Central dogma Three types of RNA Transcription Translation Genetic code, codons; Interpreting the ge ...
... Hershey Chase experiment Contributions of various scientists in the field of DNA research – Avery, Chargaff, Wilkins and Franklin, Watson and Crick Structure of DNA Base pairing rules DNA replication Central dogma Three types of RNA Transcription Translation Genetic code, codons; Interpreting the ge ...
3rd Quarter Assessment Review - Belle Vernon Area School District
... • 3. DNA Polymerase (2 of 2 enzymes) finish the process ...
... • 3. DNA Polymerase (2 of 2 enzymes) finish the process ...
Macromolecule: Carbohydrates Polarity: Polar Functions: Store
... DNA – contains genetic information of the organism (double helix) RNA – assists in converting the instructions from DNA into the a.a. sequence of proteins (single stranded) ...
... DNA – contains genetic information of the organism (double helix) RNA – assists in converting the instructions from DNA into the a.a. sequence of proteins (single stranded) ...
DNA structure
... • Composed of proteins and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) • Actually make polypeptides • 2 subunits, large and small – Small locks mRNA ...
... • Composed of proteins and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) • Actually make polypeptides • 2 subunits, large and small – Small locks mRNA ...
Glossary of Key Terms in Chapter Two
... complementary strands (17.2) the opposite strands of the double helix are hydrogen bonded to one another such that adenine and thymine or guanine and cytosine are always paired. degenerate code (17.5) a term used to describe the fact that different triplet codons may be used to specify a single amin ...
... complementary strands (17.2) the opposite strands of the double helix are hydrogen bonded to one another such that adenine and thymine or guanine and cytosine are always paired. degenerate code (17.5) a term used to describe the fact that different triplet codons may be used to specify a single amin ...
Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... Details Of The Structure • DNA is formed from two nucleotide polymers each with covalent bonds between the sugar and phosphate groups (backbone structure) and variable nucleotide bases capable of Hydrogen bonding Conserved region ...
... Details Of The Structure • DNA is formed from two nucleotide polymers each with covalent bonds between the sugar and phosphate groups (backbone structure) and variable nucleotide bases capable of Hydrogen bonding Conserved region ...
Energy Transfer in Living Things (Chapter 6)
... • A gene is a unit of DNA that codes for a polypeptide (protein chain). • Genes can have several parts: –Promoter: controls where and when the gene is expressed –Open Reading Frame: coding sequence of the gene –Terminator Sequence: ends transcription –Enhancer: areas other than promoter than can ‘up ...
... • A gene is a unit of DNA that codes for a polypeptide (protein chain). • Genes can have several parts: –Promoter: controls where and when the gene is expressed –Open Reading Frame: coding sequence of the gene –Terminator Sequence: ends transcription –Enhancer: areas other than promoter than can ‘up ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.