Structure and Function of DNA
... DNA stores all of the genetic information for the cell. If it located in the nucleus but can also be found in the mitochondria and the chloroplast. Serves as the blueprint for making proteins. ...
... DNA stores all of the genetic information for the cell. If it located in the nucleus but can also be found in the mitochondria and the chloroplast. Serves as the blueprint for making proteins. ...
Document
... backbone at 180o • Actually a distorted ladder with poles closer to each other, on one side • Major/minor groove recognition ...
... backbone at 180o • Actually a distorted ladder with poles closer to each other, on one side • Major/minor groove recognition ...
DNA - Laboratory of Theory of Biopolymers
... C. Branden, J. Tooze: „Introduction to protein structure” ...
... C. Branden, J. Tooze: „Introduction to protein structure” ...
The Genetic Code and Transcription Chapter 12 Honors Genetics
... synthesis and 3 stop codons for ending protein synthesis for a specific protein. • A given amino acid can have more than one codon sequence. ...
... synthesis and 3 stop codons for ending protein synthesis for a specific protein. • A given amino acid can have more than one codon sequence. ...
Chemistry 100 Quiz 6-
... Now that we have an amino acid chain, we can begin to shape an actual protein. Discuss how a simple amino acid chain is folded into various structures. Include information like bonding, shapes, levels of 6 pts. organization, etc. Draw pictures if you'd like! The amino acid chain represents the prote ...
... Now that we have an amino acid chain, we can begin to shape an actual protein. Discuss how a simple amino acid chain is folded into various structures. Include information like bonding, shapes, levels of 6 pts. organization, etc. Draw pictures if you'd like! The amino acid chain represents the prote ...
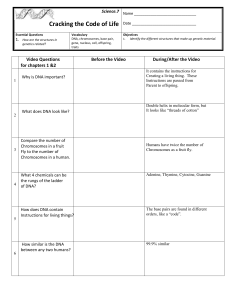
Science.7 Cracking the Code of Life Name Date Essential Questions
... Date _______________________________ Objectives 1. Identify the different structures that make up genetic material. ...
... Date _______________________________ Objectives 1. Identify the different structures that make up genetic material. ...
dna_notes - KScience
... a template needs to be variable because proteins are variable experimental work has identified the nucleus (containing DNA) as being the container of a cell’s information experimental work has identified nucleic acids as being able to transform bacterial cells (Avery) DNA is capable of being ...
... a template needs to be variable because proteins are variable experimental work has identified the nucleus (containing DNA) as being the container of a cell’s information experimental work has identified nucleic acids as being able to transform bacterial cells (Avery) DNA is capable of being ...
DNA Replication
... Genome = All of the genetic material (DNA) in a cell. Prokaryotic cell has only one genome located in the ...
... Genome = All of the genetic material (DNA) in a cell. Prokaryotic cell has only one genome located in the ...
Genetic Changes = Mutations
... 5. Similarities: both involve DNA Both might result in either positive or negative Differences: Body cell DNA mutations affect the individual Sex cell DNA mutations affect the next generation 6. cancer … uncontrolled cell division 7. Point mutation: a change in a single N-base pair in DNA a. End res ...
... 5. Similarities: both involve DNA Both might result in either positive or negative Differences: Body cell DNA mutations affect the individual Sex cell DNA mutations affect the next generation 6. cancer … uncontrolled cell division 7. Point mutation: a change in a single N-base pair in DNA a. End res ...
Handout on the Central Dogma
... A Codon is a triplet of base pairs. Each codon corresponds to one of twenty Amino acids -- it’s the amino acids that are the building-blocks of proteins, which do the work of the cell. A gene is a sequence of codons. Each gene corresponds to a particular protein that is used by the cell to do its wo ...
... A Codon is a triplet of base pairs. Each codon corresponds to one of twenty Amino acids -- it’s the amino acids that are the building-blocks of proteins, which do the work of the cell. A gene is a sequence of codons. Each gene corresponds to a particular protein that is used by the cell to do its wo ...
Ms Gentry`s Nucleic acids powerpoint File
... base pairs RNA nucleotides form a complementary strand called mRNA (messenger) a copy of the original DNA (TRANSCRIPTION) The mRNA peels away and leaves the nucleus through a nuclear pore and attaches to a ribosome tRNA (transfer) brings amino acids to the ribosome in the correct order accordi ...
... base pairs RNA nucleotides form a complementary strand called mRNA (messenger) a copy of the original DNA (TRANSCRIPTION) The mRNA peels away and leaves the nucleus through a nuclear pore and attaches to a ribosome tRNA (transfer) brings amino acids to the ribosome in the correct order accordi ...
DNA, RNA, & Protein Synthesis
... from the mRNA codon • tRNA molecules bring the amino acids in the correct order according to the codon – Every 3 bases codes for a particular amino acid – Look up the codon on page 303 of textbook to find amino acid • Amino acid sequence determines the type of protein ...
... from the mRNA codon • tRNA molecules bring the amino acids in the correct order according to the codon – Every 3 bases codes for a particular amino acid – Look up the codon on page 303 of textbook to find amino acid • Amino acid sequence determines the type of protein ...
Appendix Genomic
... A purine base that is found paired with thymine (T) in DNA and with uracil (U) in RNA. Adenine is one of the bases that makes up the nucleotide, which are the subunits present in DNA chains. AMINO ACIDS Fundamental protein elements that are encoded by a codon and linked together through peptide bond ...
... A purine base that is found paired with thymine (T) in DNA and with uracil (U) in RNA. Adenine is one of the bases that makes up the nucleotide, which are the subunits present in DNA chains. AMINO ACIDS Fundamental protein elements that are encoded by a codon and linked together through peptide bond ...
Unit 1 - Human Cells
... The two strands run anti-parallel to each other The strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the bases ...
... The two strands run anti-parallel to each other The strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the bases ...
Athena, Jen and Natalie`s Powerpt
... Transcription When a cell needs to make specific polypeptides Transcription factors tell a special enzyme where to bind Upstream from a gene, template strand of DNA, This enzyme is called RNA polymerase It binds to a site packed with adenine and thymine It’s not transcribed but unwinding is very ea ...
... Transcription When a cell needs to make specific polypeptides Transcription factors tell a special enzyme where to bind Upstream from a gene, template strand of DNA, This enzyme is called RNA polymerase It binds to a site packed with adenine and thymine It’s not transcribed but unwinding is very ea ...
Protein Synthesis Review Guide
... then translated into a protein, is a VERY regulated process! The body has control measures in place so that you don’t just make the protein willy-nilly. You only make it when your body requires it. The process of GENE REGULATION or GENE EXPRESSION can be controlled at many different points and by ma ...
... then translated into a protein, is a VERY regulated process! The body has control measures in place so that you don’t just make the protein willy-nilly. You only make it when your body requires it. The process of GENE REGULATION or GENE EXPRESSION can be controlled at many different points and by ma ...
Common Assessment Review
... protein. Occurs after transcription in the cytoplasm. Involves the ribosomes Steps: mRNA leaves the nucleus and attaches to the ribosomes, where it acts as a pattern to line up amino acids - Each triplet codon codes for an amino acid - The ribosome reads each triplet codon (on the mRNA) - In DNA: A ...
... protein. Occurs after transcription in the cytoplasm. Involves the ribosomes Steps: mRNA leaves the nucleus and attaches to the ribosomes, where it acts as a pattern to line up amino acids - Each triplet codon codes for an amino acid - The ribosome reads each triplet codon (on the mRNA) - In DNA: A ...
Mini lab 11.1 and 11.2
... Completes the assignment or experiment satisfactorily, but the explanations have minor flaws Begins the assignment and explanation satisfactorily; but omits significant parts or fails to complete. Assignment and its explanations are not accurate. Group did not demonstrate understanding or authentic ...
... Completes the assignment or experiment satisfactorily, but the explanations have minor flaws Begins the assignment and explanation satisfactorily; but omits significant parts or fails to complete. Assignment and its explanations are not accurate. Group did not demonstrate understanding or authentic ...
Class4 1-6 Win16 Enzymes and Nucleic Acids Notes
... Building DNA: Making a Copy “It has not escaped our attention that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material.” -Watson and Crick, 1953 ...
... Building DNA: Making a Copy “It has not escaped our attention that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material.” -Watson and Crick, 1953 ...
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
... • DNA is too big and too sensitive to leave the nucleus. However, proteins are made in the ribosomes, so the information in DNA must be transferred. • It will be transferred to a molecule of RNA • RNA is also used because it allows the genetic information to move from the nucleus (safe) to the cytop ...
... • DNA is too big and too sensitive to leave the nucleus. However, proteins are made in the ribosomes, so the information in DNA must be transferred. • It will be transferred to a molecule of RNA • RNA is also used because it allows the genetic information to move from the nucleus (safe) to the cytop ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.