Learning Targets - Unit 9 DNA, RNA, Proteins, Mutation
... distinguish between a codon and an anticodon ...
... distinguish between a codon and an anticodon ...
Guided Notes DNA Replication, Transcription, and Translation
... 1. A section of the DNA molecule unwinds and becomes a ___________________ladder. 2. The 2 nucleotide chains are separated by __________________enzymes, which break the hydrogen bonds between the bases. 3. DNA polymerases bind to the 2 sides of DNA moving along in opposite directions, attaching free ...
... 1. A section of the DNA molecule unwinds and becomes a ___________________ladder. 2. The 2 nucleotide chains are separated by __________________enzymes, which break the hydrogen bonds between the bases. 3. DNA polymerases bind to the 2 sides of DNA moving along in opposite directions, attaching free ...
Exam 1 Review Bio 212: 1. Describe the difference between
... 17. DNA is described as less reactive than RNA or protein. The reason can be attributed to which one of the below? a. DNA double helix introduces more stability b. Lack of the –OH group in the 2’ sugar of DNA c. The hydropho ...
... 17. DNA is described as less reactive than RNA or protein. The reason can be attributed to which one of the below? a. DNA double helix introduces more stability b. Lack of the –OH group in the 2’ sugar of DNA c. The hydropho ...
Document
... c.) in the promoter? Ask yourself—What acts at the promoter?! RNA Polymerase…Okay, there are some critical regions in the promoter (namely –10 and –35) that serve as binding sites for RNA Polymerase. If those were mutated, could that possibly result inproduction of a non-functional protein? YES! Mut ...
... c.) in the promoter? Ask yourself—What acts at the promoter?! RNA Polymerase…Okay, there are some critical regions in the promoter (namely –10 and –35) that serve as binding sites for RNA Polymerase. If those were mutated, could that possibly result inproduction of a non-functional protein? YES! Mut ...
Nucleic Acid Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid (DNA)Ribose Nucleic Acid
... A nitrogenous base (purine & pyrimidine rings) A phosphate Nucleosides= Base + Sugar They glycosylamines consisting of a nucleobase bound to a ribose or deoxyribose sugar via a beta-glycosidic linkage. ...
... A nitrogenous base (purine & pyrimidine rings) A phosphate Nucleosides= Base + Sugar They glycosylamines consisting of a nucleobase bound to a ribose or deoxyribose sugar via a beta-glycosidic linkage. ...
Biological Molecules Team – Game – Tournament Questions
... 28.Name the lipid that has a backbone of four fused carbon rings. 29.Lipids with two fatty acid chains and a polar head are called …? 30.Fatty acids are saturated if they have/ have no double C=C bonds? 31.Name the lipid found primarily in cell and organelle membranes? 32.What is the monomer of prot ...
... 28.Name the lipid that has a backbone of four fused carbon rings. 29.Lipids with two fatty acid chains and a polar head are called …? 30.Fatty acids are saturated if they have/ have no double C=C bonds? 31.Name the lipid found primarily in cell and organelle membranes? 32.What is the monomer of prot ...
Week 3
... each other) making up a 4 letter alphabet which encodes all the genetic information in all known forms of life. In RNA, Thymine doesn’t exist but is replaced by Uracil which is very similar in structure and also complements Adenine.*we discussed that copying DNA and making and RNA molecule from a DN ...
... each other) making up a 4 letter alphabet which encodes all the genetic information in all known forms of life. In RNA, Thymine doesn’t exist but is replaced by Uracil which is very similar in structure and also complements Adenine.*we discussed that copying DNA and making and RNA molecule from a DN ...
Chapter 6: Biochemistry
... Copy the 4 molecules into your notes (lipid, carbohydrate, protein, nucleic acid) ...
... Copy the 4 molecules into your notes (lipid, carbohydrate, protein, nucleic acid) ...
the element makes na RNA copy of itself which is reversed
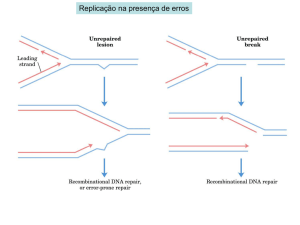
... • Breakage and joining also directed by enzymes. • Homologous recombination occurs during synapsis in meiosis I, general recombination in bacteria, and viral genetic exchange. • Molecular mechanism proposed by Holliday and Whitehouse (1964). • Depends on complementary base pairing. ...
... • Breakage and joining also directed by enzymes. • Homologous recombination occurs during synapsis in meiosis I, general recombination in bacteria, and viral genetic exchange. • Molecular mechanism proposed by Holliday and Whitehouse (1964). • Depends on complementary base pairing. ...
Biol 256 SI UNIT 1B_Biochem_Organic Molecules Macromolecules
... _____________ are biological catalyst that works by ______________ the activation energy of a chemical reaction. Proteins serve as effective buffers by combining with H+ or OH-. Nucleic Acids Nucleic Acids are a type of polymer/macromolecule composed of the basic units called ____________. Each of t ...
... _____________ are biological catalyst that works by ______________ the activation energy of a chemical reaction. Proteins serve as effective buffers by combining with H+ or OH-. Nucleic Acids Nucleic Acids are a type of polymer/macromolecule composed of the basic units called ____________. Each of t ...
END OF SEMESTER EXAM PREPARATION AND REVISION
... − G≡C is a strong bond – hydrogen bonding − Two complementary strands in DNA – double helix − Direction is from 5’ –> 3’ ends ...
... − G≡C is a strong bond – hydrogen bonding − Two complementary strands in DNA – double helix − Direction is from 5’ –> 3’ ends ...
DNA Study guide
... 5. Know the role the various enzymes play in DNA replication. 6. How are mutations corrected? RNA and Transcription (section 8.4) 1. Know the three types of RNA and their functions. 2. Be able to explain the steps of transcription. 3. Know the role the various enzymes play in RNA transcription. 4. K ...
... 5. Know the role the various enzymes play in DNA replication. 6. How are mutations corrected? RNA and Transcription (section 8.4) 1. Know the three types of RNA and their functions. 2. Be able to explain the steps of transcription. 3. Know the role the various enzymes play in RNA transcription. 4. K ...
Biochemistry Review Game
... • You will need to be the first group to hold up the correct white board in order to get points! ...
... • You will need to be the first group to hold up the correct white board in order to get points! ...
Introduction Document
... atom and the N atom) and ψ (between the Cα atom and the other C atom) for the different amino acids would give exact structure. Very difficult problem. The three dimensional form of a protein is related to its function. A folded protein has varied nooks and bulges to bind to other molecules to build ...
... atom and the N atom) and ψ (between the Cα atom and the other C atom) for the different amino acids would give exact structure. Very difficult problem. The three dimensional form of a protein is related to its function. A folded protein has varied nooks and bulges to bind to other molecules to build ...
Nucleic acids
... genetically transmitted characteristics of a bacterium was DNA. Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction These are the chemical link between generations dating back to the beginning of life on earth. It is a complex macromolecule that stores information ...
... genetically transmitted characteristics of a bacterium was DNA. Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction These are the chemical link between generations dating back to the beginning of life on earth. It is a complex macromolecule that stores information ...
DNA Study Guide
... - Translation is the process that converts mRNA into a protein. - Translation uses the codons on the mRNA to code for amino acids that create proteins. ...
... - Translation is the process that converts mRNA into a protein. - Translation uses the codons on the mRNA to code for amino acids that create proteins. ...
Central Dogma.pptx
... Uses original (parent strand) as a template to create to new daughter strands (semi-conservative replication). ...
... Uses original (parent strand) as a template to create to new daughter strands (semi-conservative replication). ...
Vocabulary List
... 4. Nucleotide – monomer of DNA or RNA composed of phosphoric acid, sugar (deoxyribose for DNA and ribose for RNA) and a nitrogen base (A,T,C,G for DNA and A,U,C,G for RNA). 5. Nitrogenous Bases – the parts of DNA and RNA that pair (A,T,C,G for DNA and A,U,C,G for RNA). 6. DNA Replication – the proce ...
... 4. Nucleotide – monomer of DNA or RNA composed of phosphoric acid, sugar (deoxyribose for DNA and ribose for RNA) and a nitrogen base (A,T,C,G for DNA and A,U,C,G for RNA). 5. Nitrogenous Bases – the parts of DNA and RNA that pair (A,T,C,G for DNA and A,U,C,G for RNA). 6. DNA Replication – the proce ...
DNA Strand 1 - Duncanville ISD
... 1. How many amino acids were made from this strand of DNA? _______ 2. How many proteins were made from this strand of DNA? ________ Codon Charts: knowing how to All of the amino the amino acids ...
... 1. How many amino acids were made from this strand of DNA? _______ 2. How many proteins were made from this strand of DNA? ________ Codon Charts: knowing how to All of the amino the amino acids ...
Additional Lab Exercise: Amino Acid Sequence in
... Background Information Enzymes are proteins. In order to carry on their very specific functions, the sequence of the amino acids in their structure must be precise. The DNA in the chromosomes of cells, through its own order of bases, is the determining factor in the amino acid sequence. Ribosomes, m ...
... Background Information Enzymes are proteins. In order to carry on their very specific functions, the sequence of the amino acids in their structure must be precise. The DNA in the chromosomes of cells, through its own order of bases, is the determining factor in the amino acid sequence. Ribosomes, m ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.