How are protein made in our cells?
... Recall, a RNA strand was created in the nucleus. This code must send the message to the ribosome mRNA. mRNA is released into the cytoplasm. mRNA attaches to a ribosome. rRNA Codons will move through the ribosome by tRNA. Codons on mRNA will attach to anticodon on tRNA molecule. After this occurs, th ...
... Recall, a RNA strand was created in the nucleus. This code must send the message to the ribosome mRNA. mRNA is released into the cytoplasm. mRNA attaches to a ribosome. rRNA Codons will move through the ribosome by tRNA. Codons on mRNA will attach to anticodon on tRNA molecule. After this occurs, th ...
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter #2
... (NOTE: the 8 essential amino acids are in red. These cannot be synthesized by the human body and must be obtained from food. Arginine and histidine are essential only for children.) ...
... (NOTE: the 8 essential amino acids are in red. These cannot be synthesized by the human body and must be obtained from food. Arginine and histidine are essential only for children.) ...
File
... Since polymerase III cannot begin the synthesis of a polynucleotide, Primase must first add a primer, made of RNA nucleotides, to the origin of replication ...
... Since polymerase III cannot begin the synthesis of a polynucleotide, Primase must first add a primer, made of RNA nucleotides, to the origin of replication ...
Intest Aid IB - SpeechNutrients.eu
... What are the functions of nucleotides? Besides being the building blocks for DNA and RNA, nucleotides are involved at a cellular level*. Nucleotides are essential for: a) transfer of energy b) production of protein c) mediation of hormone signals *Nucleotides consist of a nitrogen-containing base, a ...
... What are the functions of nucleotides? Besides being the building blocks for DNA and RNA, nucleotides are involved at a cellular level*. Nucleotides are essential for: a) transfer of energy b) production of protein c) mediation of hormone signals *Nucleotides consist of a nitrogen-containing base, a ...
Name DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis Test Review Study your
... the promoter and starts adding complementary nucleotides. In RNA A pairs with U, T pairs with A and G and C pair with each other. The RNA polymerase adds new nucleotides until it reaches the end of the gene where it stops. ...
... the promoter and starts adding complementary nucleotides. In RNA A pairs with U, T pairs with A and G and C pair with each other. The RNA polymerase adds new nucleotides until it reaches the end of the gene where it stops. ...
Document
... Amino acid – a chain of these make up a protein Replication – the copying of a DNA molecule mRNA – a chemical used to read the DNA in the nucleus which takes the message to the ribosomes where proteins are made Mutation – an abnormality or deformation of an organism due to pollutants in the ...
... Amino acid – a chain of these make up a protein Replication – the copying of a DNA molecule mRNA – a chemical used to read the DNA in the nucleus which takes the message to the ribosomes where proteins are made Mutation – an abnormality or deformation of an organism due to pollutants in the ...
DNA Replication, Transcription and Translation assessment
... 2.7.1 Explain the process of DNA replication in eukaryotes, including the role of enzymes (helicase, DNA polymerase, RNA primase and DNA ligase), Okazaki fragments and deoxynucleoside triphosphates. 2.7.2 Explain the significance of complementary base pairing in the conservation of the base sequence ...
... 2.7.1 Explain the process of DNA replication in eukaryotes, including the role of enzymes (helicase, DNA polymerase, RNA primase and DNA ligase), Okazaki fragments and deoxynucleoside triphosphates. 2.7.2 Explain the significance of complementary base pairing in the conservation of the base sequence ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... 3. What are the three parts of an RNA nucleotide? Nitrogen base, 5-Carbon Sugar, and Phosphate Group 4. What are the three differences between RNA and DNA? The Sugars, (Ribose vs. Deoxyribose,) the nitrogen bases, (U vs. T), and the structure (single stranded vs. double helix.) 5. What are the three ...
... 3. What are the three parts of an RNA nucleotide? Nitrogen base, 5-Carbon Sugar, and Phosphate Group 4. What are the three differences between RNA and DNA? The Sugars, (Ribose vs. Deoxyribose,) the nitrogen bases, (U vs. T), and the structure (single stranded vs. double helix.) 5. What are the three ...
Biochemistry Review Worksheet - CHS Science Department Mrs
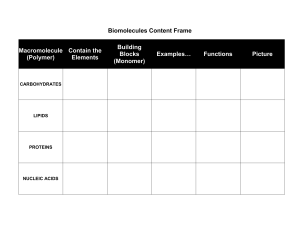
... ______________ is a unique element with the remarkable ability to form strong, stable chemical bonds with many different types of atoms. Macromolecules are molecules made from repeating subunits called __________________ The four major macromolecules in living cells are carbohydrates, lipids, protei ...
... ______________ is a unique element with the remarkable ability to form strong, stable chemical bonds with many different types of atoms. Macromolecules are molecules made from repeating subunits called __________________ The four major macromolecules in living cells are carbohydrates, lipids, protei ...
Worksheet: Mutations Practice
... There are three ways that DNA can be altered when a mutation (change in DNA sequence) occurs. 1. Substitution – one base-pairs is replaced by another: Example: G to C or A to G C G T C 2. Insertion – one or more base pairs is added to a sequence: Example: CGATGG –– CGAATGG GCTACC GCTTACC 3. Deletion ...
... There are three ways that DNA can be altered when a mutation (change in DNA sequence) occurs. 1. Substitution – one base-pairs is replaced by another: Example: G to C or A to G C G T C 2. Insertion – one or more base pairs is added to a sequence: Example: CGATGG –– CGAATGG GCTACC GCTTACC 3. Deletion ...
the chemical constituents of cells constituents include
... • non-essential amino acids are those amino acids that can be synthesized by the body • essential amino acids are those amino acids that cannot be synthesized by the body and must obtain from other sources • plants can synthesize all amino acids ...
... • non-essential amino acids are those amino acids that can be synthesized by the body • essential amino acids are those amino acids that cannot be synthesized by the body and must obtain from other sources • plants can synthesize all amino acids ...
DNA to RNA practice
... Since DNA is too large of a molecule to fit outside the nucleus, a messenger is needed to get to the ribosome. DNA is converted into a single stranded RNA molecule, called mRNA. This process is called transcription. Draw your codon lines to separate the triplets. Using the base pairing rules for DNA ...
... Since DNA is too large of a molecule to fit outside the nucleus, a messenger is needed to get to the ribosome. DNA is converted into a single stranded RNA molecule, called mRNA. This process is called transcription. Draw your codon lines to separate the triplets. Using the base pairing rules for DNA ...
Reading Guide
... 3. What are other functions of nucleotides other than building blocks of DNA and RNA? 4. Draw the DNA strand dAdTdC. Label the 5’ and 3’ ends. Label the phosphodiester bond. 5. Draw the AT base pair and indicate hydrogen bonding. Do the same for the GC base pair. 6. Describe “typical” DNA (B-DNA for ...
... 3. What are other functions of nucleotides other than building blocks of DNA and RNA? 4. Draw the DNA strand dAdTdC. Label the 5’ and 3’ ends. Label the phosphodiester bond. 5. Draw the AT base pair and indicate hydrogen bonding. Do the same for the GC base pair. 6. Describe “typical” DNA (B-DNA for ...
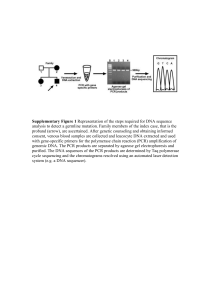
Figure 2 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence
... Supplementary Figure 1 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence analysis to detect a germline mutation. Family members of the index case, that is the proband (arrow), are ascertained. After genetic counseling and obtaining informed consent, venous blood samples are collected and leucocy ...
... Supplementary Figure 1 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence analysis to detect a germline mutation. Family members of the index case, that is the proband (arrow), are ascertained. After genetic counseling and obtaining informed consent, venous blood samples are collected and leucocy ...
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
... Mutations are any change in the genetic code: 1. DNA may not replicate properly and the incorrect base attached 2. There may be a mistake in transcription 3. There may be a mistake in translation ...
... Mutations are any change in the genetic code: 1. DNA may not replicate properly and the incorrect base attached 2. There may be a mistake in transcription 3. There may be a mistake in translation ...
Unit 7 - Cobb Learning
... mRNA contains the messages from the DNA and are sent to ____________________ for them to read the instructions for making proteins ...
... mRNA contains the messages from the DNA and are sent to ____________________ for them to read the instructions for making proteins ...
The Master Molecule
... The DNA of genes is made of four nucleotide bases: two purines, adenine (A) and guanine (G); and two pyrimidines, thymine (T) and cytosine (C). The genetic code is based on these four letters, AGCT, that encode the amino acids making up the body‘s peptides and proteins. The genetic code is the same ...
... The DNA of genes is made of four nucleotide bases: two purines, adenine (A) and guanine (G); and two pyrimidines, thymine (T) and cytosine (C). The genetic code is based on these four letters, AGCT, that encode the amino acids making up the body‘s peptides and proteins. The genetic code is the same ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.