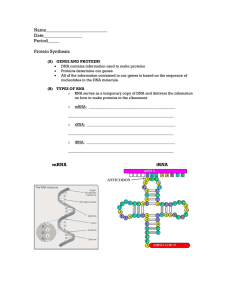
Nucleic Acid structure - part 1
... Hershey-Chase 1952 More evidence that DNA carries genetic info ...
... Hershey-Chase 1952 More evidence that DNA carries genetic info ...
Name___________________________ Date_________________ Period_____
... RNA Polymerase knows where to bind on the DNA due to spots on the DNA called promoters, which act as start point signals for transcription. ...
... RNA Polymerase knows where to bind on the DNA due to spots on the DNA called promoters, which act as start point signals for transcription. ...
Macromolecules of Life Macromolecules of Life
... enzymatic activity As enzyme, y ,p proteins bring substrates to appropriate configurations for chemical reactions to proceed. Proteins synthesized by various multicellular organisms group into major functional f l categories. ...
... enzymatic activity As enzyme, y ,p proteins bring substrates to appropriate configurations for chemical reactions to proceed. Proteins synthesized by various multicellular organisms group into major functional f l categories. ...
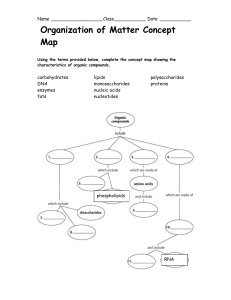
Polymers vs. monomers wkst. and concept map
... ________________________________________ 20. Your best friend tells you that they are deathly allergic to certain amino acids in food. Your mom has prepared dinner already, so you need to tell her not to serve what macromolecule to them? ...
... ________________________________________ 20. Your best friend tells you that they are deathly allergic to certain amino acids in food. Your mom has prepared dinner already, so you need to tell her not to serve what macromolecule to them? ...
BY2208 SF Genetics Central Dogma McConnell_1.1
... Genes must contain information! Genes must replicate! ...
... Genes must contain information! Genes must replicate! ...
BIOL 241 Nucleic Acids and Gene Expression I. Genes (Overview) A
... 3. bases project from backbone (forming side chains) 4. H-bonds can form between bases (on other chains) a. double stranded b. double helix E. Law of complementary base-pairing 1. adenine to thymine 2. guanine to cytosine 3. sequence of bases in one chain determines the sequence of bases in the othe ...
... 3. bases project from backbone (forming side chains) 4. H-bonds can form between bases (on other chains) a. double stranded b. double helix E. Law of complementary base-pairing 1. adenine to thymine 2. guanine to cytosine 3. sequence of bases in one chain determines the sequence of bases in the othe ...
Molecular Biology Unit Review Guide
... 12. Label the diagrams below with the following terms (briefly explain the function/definition of each): RNA primase, transcription factor proteins, promoter, coding region, sense strand, antisense strand, mRNA, 5’ end (of each), 3’ end (of each), nucleoside triphosphate, complimentary base pairing, ...
... 12. Label the diagrams below with the following terms (briefly explain the function/definition of each): RNA primase, transcription factor proteins, promoter, coding region, sense strand, antisense strand, mRNA, 5’ end (of each), 3’ end (of each), nucleoside triphosphate, complimentary base pairing, ...
Semester Exam Review
... Relationship of monomers to polymers. Give examples Difference between RNA and DNA What is the difference between active and passive transport? Give examples ...
... Relationship of monomers to polymers. Give examples Difference between RNA and DNA What is the difference between active and passive transport? Give examples ...
Cellular Division
... DNA is made up of subunits which scientists called nucleotides. Each nucleotide is made up of a sugar, a phosphate and a base. There are 4 different bases in a DNA molecule: adenine (a purine) cytosine (a pyrimidine) guanine (a purine) thymine (a pyrimidine) The number of purine bases equals ...
... DNA is made up of subunits which scientists called nucleotides. Each nucleotide is made up of a sugar, a phosphate and a base. There are 4 different bases in a DNA molecule: adenine (a purine) cytosine (a pyrimidine) guanine (a purine) thymine (a pyrimidine) The number of purine bases equals ...
PIG - enzymes
... • Increased concentration of H+ ions means lower pH • Hydrogen ions are positive so are attracted to negatively charged molecules • Hydrogen bonds hold tertiary structure in place • Hydrogen ions react with hydrogen bonds which alters the tertiary structure ...
... • Increased concentration of H+ ions means lower pH • Hydrogen ions are positive so are attracted to negatively charged molecules • Hydrogen bonds hold tertiary structure in place • Hydrogen ions react with hydrogen bonds which alters the tertiary structure ...
Macromolecules Review ws Name the 6 main elements that make
... 16. Chains of amino acids make polypeptides which can join together to make a protein. 17. Phosholipids makes up cell membranes. 18. Fats are made of an alcohol called glycerol and three fatty acids chains. This is known as a triglyceride 19. If there are all SINGLE bonds between carbons in the fat ...
... 16. Chains of amino acids make polypeptides which can join together to make a protein. 17. Phosholipids makes up cell membranes. 18. Fats are made of an alcohol called glycerol and three fatty acids chains. This is known as a triglyceride 19. If there are all SINGLE bonds between carbons in the fat ...
DO NOW
... Why does the leading strand form continuously while the lagging strand is formed in fragments? ...
... Why does the leading strand form continuously while the lagging strand is formed in fragments? ...
Presentación de PowerPoint
... further histone holding these together; Do not allow histone wrapped around DNA. Most of the DNA of a human cell is contained in the nucleus. Distinguish between unique and highly repetitive sequences in nuclear DNA. ...
... further histone holding these together; Do not allow histone wrapped around DNA. Most of the DNA of a human cell is contained in the nucleus. Distinguish between unique and highly repetitive sequences in nuclear DNA. ...
understanding dna molecule of heredity - Cal State LA
... The nucleotide is held together by a backbone made of sugars and phosphate group The backbone carries four types of molecules called bases It is the sequence of these four bases that encodes information The main job of the DNA is to encode the sequence of amino acids residues ...
... The nucleotide is held together by a backbone made of sugars and phosphate group The backbone carries four types of molecules called bases It is the sequence of these four bases that encodes information The main job of the DNA is to encode the sequence of amino acids residues ...
week2
... Most of our DNA helps with Expression (we think) Genes are only a small part of the entire Genome. ...
... Most of our DNA helps with Expression (we think) Genes are only a small part of the entire Genome. ...
Biochemistry Learning Targets and Essential Vocabulary name describe
... name and describe the functions of the four groups of organic compounds found in living things. (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, & Nucleic Acids) describe how polymers are built from monomers (dehydration synthesis) and ...
... name and describe the functions of the four groups of organic compounds found in living things. (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, & Nucleic Acids) describe how polymers are built from monomers (dehydration synthesis) and ...
Guided Notes-Genetic Code
... What is the three base code known as? How many codons are there? How many code for amino acids? There are 61 codons that code for amino acids but only 20 amino acids. Explain Give an example of above What are the other three codons for? Is there a start codon? Is the genetic code universal? What is ...
... What is the three base code known as? How many codons are there? How many code for amino acids? There are 61 codons that code for amino acids but only 20 amino acids. Explain Give an example of above What are the other three codons for? Is there a start codon? Is the genetic code universal? What is ...
Macromolecules
... molecule is also formed from the OH groups. This reaction is catalyzed by a polymerase enzyme. This same type of condensation reaction can occur to form many kinds of polymers, from proteins to carbohydrates, nucleic acids to triglycerides. ...
... molecule is also formed from the OH groups. This reaction is catalyzed by a polymerase enzyme. This same type of condensation reaction can occur to form many kinds of polymers, from proteins to carbohydrates, nucleic acids to triglycerides. ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.