Genetics Review Game
... a tall pea plant from a genetic cross between two heterozygous tall pea plants? Three out of four (75%) ...
... a tall pea plant from a genetic cross between two heterozygous tall pea plants? Three out of four (75%) ...
Chapter 1
... Replication of DNA is undertaken by a complex of enzymes that separate the parental strands and synthesize the daughter strands. The replication fork is the point at which the parental strands are separated. The enzymes that synthesize DNA are called DNA polymerases. o The enzymes that synthesize RN ...
... Replication of DNA is undertaken by a complex of enzymes that separate the parental strands and synthesize the daughter strands. The replication fork is the point at which the parental strands are separated. The enzymes that synthesize DNA are called DNA polymerases. o The enzymes that synthesize RN ...
Notes Unit 4 Part 7
... 3. Each codon has a complementary ______________ which is found on tRNA. For every codon read, tRNA attaches the anticodon. anticodon = complementary base sequence to the __________ codon 4. Attached to the other end of the ___________ is an _____________ acid. When tRNA binds to mRNA, amino acids ...
... 3. Each codon has a complementary ______________ which is found on tRNA. For every codon read, tRNA attaches the anticodon. anticodon = complementary base sequence to the __________ codon 4. Attached to the other end of the ___________ is an _____________ acid. When tRNA binds to mRNA, amino acids ...
Genetic Material PP - stephanieccampbell.com
... Is it nucleic acids that contain the genetic code or is it proteins? a) Proteins contain 20 amino acids that can be organized in countless ways to determine traits b) Nucleic acids only contained 4 different nucleotides ...
... Is it nucleic acids that contain the genetic code or is it proteins? a) Proteins contain 20 amino acids that can be organized in countless ways to determine traits b) Nucleic acids only contained 4 different nucleotides ...
Bacterial Nucleic Acids
... • One major difference between DNA and RNA is the sugar, with the 2deoxyribose in DNA being replaced by the alternative pentose sugar ribose in RNA. ...
... • One major difference between DNA and RNA is the sugar, with the 2deoxyribose in DNA being replaced by the alternative pentose sugar ribose in RNA. ...
RNA - Ms Kim`s Biology Class
... _____ 9. made x-ray defraction pictures that helped determine the shape of DNA _____ 10. Determined the double helix structure of DNA _____ 11. won a Noble Prize for work using x-ray crystallography to help determine DNA’s structure _____ 12. used r and s strains of bacteria to determine that DNA is ...
... _____ 9. made x-ray defraction pictures that helped determine the shape of DNA _____ 10. Determined the double helix structure of DNA _____ 11. won a Noble Prize for work using x-ray crystallography to help determine DNA’s structure _____ 12. used r and s strains of bacteria to determine that DNA is ...
Macromolecules Worksheet
... polypeptide or protein_ 8. What is a long chain of amino acids called? covalent_ 9. What type of bond involves the sharing of electrons? deoxyribose_ 10. What sugar does DNA contain? base or alkaline_ 11. When the pH is greater than 7, it is called this. ribose_ 12. What sugar does RNA contain? elec ...
... polypeptide or protein_ 8. What is a long chain of amino acids called? covalent_ 9. What type of bond involves the sharing of electrons? deoxyribose_ 10. What sugar does DNA contain? base or alkaline_ 11. When the pH is greater than 7, it is called this. ribose_ 12. What sugar does RNA contain? elec ...
Slide 1
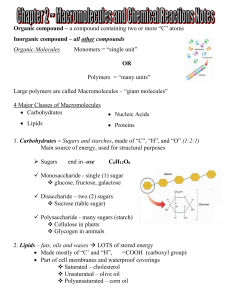
... Biochemistry is the area of chemistry that focuses on the study of compounds and processes occurring in living systems. Important classes of biological compounds that we will be responsible for: Carbohydrates: molecules composed of C, H and O in a 1 to 2 to 1 ratio (carbohydrates play a role in prov ...
... Biochemistry is the area of chemistry that focuses on the study of compounds and processes occurring in living systems. Important classes of biological compounds that we will be responsible for: Carbohydrates: molecules composed of C, H and O in a 1 to 2 to 1 ratio (carbohydrates play a role in prov ...
Study Guide 8 - Bacterial Genetics Chptr 8
... i. Insertional inactivation of the gene in which the transposon lands ii. A transposon can insert elsewhere in the same DNA molecule, or into an entirely different DNA molecule iii. Some transposons simply “jump or hop”; others replicate then jump ...
... i. Insertional inactivation of the gene in which the transposon lands ii. A transposon can insert elsewhere in the same DNA molecule, or into an entirely different DNA molecule iii. Some transposons simply “jump or hop”; others replicate then jump ...
Slide 1 - New Century Academy
... -6 billion base pairs -Genome will fill 1,200 AP bio books -Replicated in just a few hours -Errors occur in 1/10 billion base pairs -Most of Replication is known about prokaryotic cells – Eukaryotic is similar to ...
... -6 billion base pairs -Genome will fill 1,200 AP bio books -Replicated in just a few hours -Errors occur in 1/10 billion base pairs -Most of Replication is known about prokaryotic cells – Eukaryotic is similar to ...
CH 3 RG 2014 Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life
... and the other end of the chain 3´. Finally, label one nucleotide. 14. Notice that there are 5 nitrogen bases. Which four are found in DNA? ...
... and the other end of the chain 3´. Finally, label one nucleotide. 14. Notice that there are 5 nitrogen bases. Which four are found in DNA? ...
Molecular Biology and DNA
... Once in the cytoplasm, TRANSLATION from RNA to protein can begin • mRNA attaches to a ribosome site in the cytoplasm where a rRNA (ribosomal RNA) is located • Free-floating in the cytoplasm are nucleotide bases to pair up on the mRNA. These are called tRNA for transfer RNA. They transfer the bases ...
... Once in the cytoplasm, TRANSLATION from RNA to protein can begin • mRNA attaches to a ribosome site in the cytoplasm where a rRNA (ribosomal RNA) is located • Free-floating in the cytoplasm are nucleotide bases to pair up on the mRNA. These are called tRNA for transfer RNA. They transfer the bases ...
Science 103: Outline 17
... (v) A tRNA (plus amino acid) with the anticodon corresponding to the third codon binds and the first tRNA (empty) leaves. (v) The ribosomes move down the mRNA until they reach a stop codon. The ribosomes detach from the mRNA and the protein is released. 4. Fate of Proteins Where in the cell would tr ...
... (v) A tRNA (plus amino acid) with the anticodon corresponding to the third codon binds and the first tRNA (empty) leaves. (v) The ribosomes move down the mRNA until they reach a stop codon. The ribosomes detach from the mRNA and the protein is released. 4. Fate of Proteins Where in the cell would tr ...
Translation - Net Start Class
... transcribed from DNA in the nucleus and released in the cytoplasm ...
... transcribed from DNA in the nucleus and released in the cytoplasm ...
Biotechnology Key Terms and Concepts
... labeled nucleic acid molecule used to tag a specific DNA sequence III. Examples of biotechnology A. Cloning-a technique used to achieve a population of genetically identical cells produced from a single cell. Cloning is how scientists make a genetic duplicate of an organism. Cloning has the potentia ...
... labeled nucleic acid molecule used to tag a specific DNA sequence III. Examples of biotechnology A. Cloning-a technique used to achieve a population of genetically identical cells produced from a single cell. Cloning is how scientists make a genetic duplicate of an organism. Cloning has the potentia ...
Modern Genetics
... way known as base pairing. Adenine (A) and Thymine (T) bond together. Guanine (G) and Cytosine (C) bond together. No other combinations are possible. ...
... way known as base pairing. Adenine (A) and Thymine (T) bond together. Guanine (G) and Cytosine (C) bond together. No other combinations are possible. ...
Lecture 3 (BY 14)
... Sterols and Derivatives • No fatty acids • Rigid backbone of four fused-together carbon rings • __________- most common type in animals ...
... Sterols and Derivatives • No fatty acids • Rigid backbone of four fused-together carbon rings • __________- most common type in animals ...
Central Dogma - Arkansas State University
... The Process of Transcription-2 • RNA synthesis continues (Elongation), only one DNA strand (template) is transcribed. • RNA nucleotides, complementary to bases on DNA strand, are connected to make mRNA ...
... The Process of Transcription-2 • RNA synthesis continues (Elongation), only one DNA strand (template) is transcribed. • RNA nucleotides, complementary to bases on DNA strand, are connected to make mRNA ...
What does DNA do?
... ___ 3) Follow the base pair rule to fill in the missing base pairs for each strand. ___ 4) Compare your strands. Are they similar? What have you done? Where did this process take place in the cell? Why is this process important? They are identical copies of each other (mirror images). This process t ...
... ___ 3) Follow the base pair rule to fill in the missing base pairs for each strand. ___ 4) Compare your strands. Are they similar? What have you done? Where did this process take place in the cell? Why is this process important? They are identical copies of each other (mirror images). This process t ...
Biochemistry File - Northwest ISD Moodle
... 4. Proteins – polymers of amino acids joined by peptide bonds Used to build cells, transport molecules, and control the rate of reactions Made of “C”, “H”, “O”, and “N” 20 different amino acids ...
... 4. Proteins – polymers of amino acids joined by peptide bonds Used to build cells, transport molecules, and control the rate of reactions Made of “C”, “H”, “O”, and “N” 20 different amino acids ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.