0c5168dab2ecd61778b5bb175973dab5 UNPDF
... monomers together in a certain sequence/order they have ______________________ a. The process of “putting monomers together” is called b. What is lost during the process ? c. What kind of bond is formed generally? Specifically between amino acids of a protein? d. What must be added to break the bond ...
... monomers together in a certain sequence/order they have ______________________ a. The process of “putting monomers together” is called b. What is lost during the process ? c. What kind of bond is formed generally? Specifically between amino acids of a protein? d. What must be added to break the bond ...
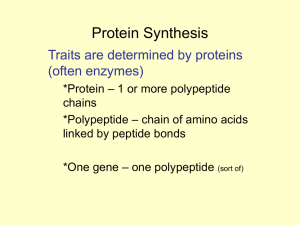
Protein Synthesis
... Traits are determined by proteins (often enzymes) *Protein – 1 or more polypeptide chains *Polypeptide – chain of amino acids linked by peptide bonds ...
... Traits are determined by proteins (often enzymes) *Protein – 1 or more polypeptide chains *Polypeptide – chain of amino acids linked by peptide bonds ...
History of Genetics
... • 1910: Thomas Hunt Morgan: proved that genes are located on the chromosome • 1941: Beadle and Tatum - show how genes direct the synthesis of enzymes that control metabolic processes “1 gene = 1 enzyme” • 1952: Hershey and Chase - conducted experiments which helped to confirm that DNA was the geneti ...
... • 1910: Thomas Hunt Morgan: proved that genes are located on the chromosome • 1941: Beadle and Tatum - show how genes direct the synthesis of enzymes that control metabolic processes “1 gene = 1 enzyme” • 1952: Hershey and Chase - conducted experiments which helped to confirm that DNA was the geneti ...
Genetics Study Guide
... 1. What is a plant that has two dominant genes or two recessive genes called? 2. The “rungs” of the DNA ladder are made up of __________. 3. What is heredity? 4. How are sex cells different from other human cells? 5. What is the name of the process for the way cells divide in asexual reproduction? 6 ...
... 1. What is a plant that has two dominant genes or two recessive genes called? 2. The “rungs” of the DNA ladder are made up of __________. 3. What is heredity? 4. How are sex cells different from other human cells? 5. What is the name of the process for the way cells divide in asexual reproduction? 6 ...
pdf
... most cases, a gene encodes a polypeptide. In most organisms the pathway for gene expression is the transcription of DNA into RNA, which is then translated into protein. Chapter 2 covers the structures of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and methods for analyzing them biochemically. Methods for isolating ...
... most cases, a gene encodes a polypeptide. In most organisms the pathway for gene expression is the transcription of DNA into RNA, which is then translated into protein. Chapter 2 covers the structures of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and methods for analyzing them biochemically. Methods for isolating ...
Chapter 8: DNA and RNA - Tenafly Public Schools
... Part of DNA sequence is transcribed (copied) into RNA RNA polymerase carries out transcription by binding directly to DNA and matching nucleotides one at a time AACTGT on DNA UUGACA on RNA ...
... Part of DNA sequence is transcribed (copied) into RNA RNA polymerase carries out transcription by binding directly to DNA and matching nucleotides one at a time AACTGT on DNA UUGACA on RNA ...
Biology - secondary
... molecule than aerobic cellular respiration 107-110 • Building big muscles is an example of catabolic metabolism 119 • 109-Cellular formation is the breakdown of food without O2 • The RNA molecule that contains the code for a polypeptide chain of amino acids is called transfer RNA ...
... molecule than aerobic cellular respiration 107-110 • Building big muscles is an example of catabolic metabolism 119 • 109-Cellular formation is the breakdown of food without O2 • The RNA molecule that contains the code for a polypeptide chain of amino acids is called transfer RNA ...
DNA Extraction Glucose and salt are : added to increase the osmotic
... EDTA protects the DNA from degradative enzymes (called DNAses); EDTA binds divalent cations that are necessary for DNAse activity. NaOH and SDS (a detergent) : The alkaline mixtures ruptures the cells, and the SDS detergent breaks apart the lipid membrane and solubilizes cellular proteins. NaOH also ...
... EDTA protects the DNA from degradative enzymes (called DNAses); EDTA binds divalent cations that are necessary for DNAse activity. NaOH and SDS (a detergent) : The alkaline mixtures ruptures the cells, and the SDS detergent breaks apart the lipid membrane and solubilizes cellular proteins. NaOH also ...
Molecular_Evolution
... • We now know that most of the DNA does not code for amino acid sequences • Non-coding segments guide translation and are called introns • Coding segments are called exons ...
... • We now know that most of the DNA does not code for amino acid sequences • Non-coding segments guide translation and are called introns • Coding segments are called exons ...
Big Picture wkst
... _____ 6. DNA is contained in a different way in prokaryotic cells than it is in eukaryotic cells because a. eukaryotes are single-celled organisms. b. only eukaryotic cells have a cell membrane. c. DNA is found only in eukaryotic cells. d. prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus. _____ 7. Carbon-based mole ...
... _____ 6. DNA is contained in a different way in prokaryotic cells than it is in eukaryotic cells because a. eukaryotes are single-celled organisms. b. only eukaryotic cells have a cell membrane. c. DNA is found only in eukaryotic cells. d. prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus. _____ 7. Carbon-based mole ...
CHM 105 - Test 3 Review
... 14. The sit on the enzyme where reaction occurs is known as the ___________ site. 15. These substances bind to the enzyme and interfere with the reaction. _______________ 16. Two main categories of nucleic acids. (full names) ________________________________________ _________________________________ ...
... 14. The sit on the enzyme where reaction occurs is known as the ___________ site. 15. These substances bind to the enzyme and interfere with the reaction. _______________ 16. Two main categories of nucleic acids. (full names) ________________________________________ _________________________________ ...
5 Chapter 12 DNA RNA
... cellular structures that contain genetic information that is passed from one generation to the next – Composed of Chromatin • Which is made up of DNA and a protein ...
... cellular structures that contain genetic information that is passed from one generation to the next – Composed of Chromatin • Which is made up of DNA and a protein ...
DNA Glossary - FutureLearn
... the male gender- determining Y chromosome is a different size and shape to the X chromosome. ...
... the male gender- determining Y chromosome is a different size and shape to the X chromosome. ...
File - Dixie Middle School Science
... • Virus -made of DNA and protein • The experiments • a virus with either radioactive DNA or radioactive protein were used to infect bacteria • Either the radioactive proteins or radioactive DNA would be transferred to the bacteria • Identifying which one is transferred would identify the genetic mat ...
... • Virus -made of DNA and protein • The experiments • a virus with either radioactive DNA or radioactive protein were used to infect bacteria • Either the radioactive proteins or radioactive DNA would be transferred to the bacteria • Identifying which one is transferred would identify the genetic mat ...
Chapter 12 Powerpoint
... molecule’s electrons diffract X-Rays at particular angles and the resulting pattern, like the one above, can be used to solve the structure of a crystal. ...
... molecule’s electrons diffract X-Rays at particular angles and the resulting pattern, like the one above, can be used to solve the structure of a crystal. ...
THE CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE
... 2.precursors are ribonucleoside triphosphates 3.Single stranded (some viruses double) extra OH means molecule too bulky to form stable double helix base pairing in places - double helix and hairpins ...
... 2.precursors are ribonucleoside triphosphates 3.Single stranded (some viruses double) extra OH means molecule too bulky to form stable double helix base pairing in places - double helix and hairpins ...
Protein Synthesis PowerPoint
... – turning DNA’s code into messenger RNA TRANSLATION – turning mRNA into an amino acid chain = PROTEIN ...
... – turning DNA’s code into messenger RNA TRANSLATION – turning mRNA into an amino acid chain = PROTEIN ...
biology name
... 14. Codons are found on _________ while anticodons are found on _________. In each case, the code is really a sequence of ____ bases (use a number) that code for a particular _____________________. 15. What would the transfer RNA and corresponding amino acids be according to the mRNA below? mRNA ...
... 14. Codons are found on _________ while anticodons are found on _________. In each case, the code is really a sequence of ____ bases (use a number) that code for a particular _____________________. 15. What would the transfer RNA and corresponding amino acids be according to the mRNA below? mRNA ...
Previously in Bio308
... How does RNA polymerase work and what does it make? How does it know where to start and stop? How does a ribosome work and what does it make? How does it know where to start and stop? If the DNA in every cell in your body is the ...
... How does RNA polymerase work and what does it make? How does it know where to start and stop? How does a ribosome work and what does it make? How does it know where to start and stop? If the DNA in every cell in your body is the ...
Genetics Review Game
... a tall pea plant from a genetic cross between two heterozygous tall pea plants? Three out of four (75%) ...
... a tall pea plant from a genetic cross between two heterozygous tall pea plants? Three out of four (75%) ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.