Chemical Compounds Overview
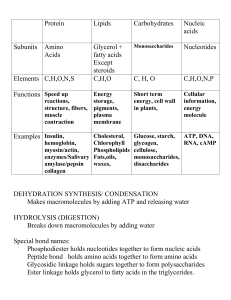
... d. Dehydration synthesis- Reaction in which water in removed to form a bond, creating a polymer. e. Hydrolysis- Reverse of dehydration synthesis. Polymers are broken down into monomers by adding water. 2. Lipids a. Store energy. Form some membranes. b. Monomer- Glycerol + 3 fatty acids c. Polymer- f ...
... d. Dehydration synthesis- Reaction in which water in removed to form a bond, creating a polymer. e. Hydrolysis- Reverse of dehydration synthesis. Polymers are broken down into monomers by adding water. 2. Lipids a. Store energy. Form some membranes. b. Monomer- Glycerol + 3 fatty acids c. Polymer- f ...
Slide 1
... maintenance of life. In metabolism some substances are broken down to yield energy for vital processes while other substances, necessary for life, are synthesized. B. Polymers – a large molecule that is made up of many small molecules linked (covalent bonds) together. 1. Dehydration synthesis – when ...
... maintenance of life. In metabolism some substances are broken down to yield energy for vital processes while other substances, necessary for life, are synthesized. B. Polymers – a large molecule that is made up of many small molecules linked (covalent bonds) together. 1. Dehydration synthesis – when ...
Modern Biology: Chapter 3
... – (CH2O)n general formula n = 3–8 monosaccharides – Hundreds of glucose monomers make glycogen (animals) or starch & cellulose (plants) ...
... – (CH2O)n general formula n = 3–8 monosaccharides – Hundreds of glucose monomers make glycogen (animals) or starch & cellulose (plants) ...
Modern Biology: Chapter 3
... – (CH2O)n general formula n = 3–8 monosaccharides – Hundreds of glucose monomers make glycogen (animals) or starch & cellulose (plants) ...
... – (CH2O)n general formula n = 3–8 monosaccharides – Hundreds of glucose monomers make glycogen (animals) or starch & cellulose (plants) ...
Macromolecules - Teacher Pages
... A molecule made up of many smaller molecules. Formed by a reaction called dehydration synthesis – which means water must be removed to bond them together. The building block of a polymer. Varies depending on the type of molecule being built ...
... A molecule made up of many smaller molecules. Formed by a reaction called dehydration synthesis – which means water must be removed to bond them together. The building block of a polymer. Varies depending on the type of molecule being built ...
Enzymes/Macromolecules/Bonding
... differing only in the side chain Properties of side chains account for structural and functional differences ...
... differing only in the side chain Properties of side chains account for structural and functional differences ...
Student worksheet for Proteins
... Student—please print this worksheet and complete it as you interact with the tutorial. The completed worksheet should be turned in to your assigned teacher. Tutorial: Proteins Protein Definition: (PRO-teen) A molecule made up of amino acids that are needed for the body to function properly. 1. Prote ...
... Student—please print this worksheet and complete it as you interact with the tutorial. The completed worksheet should be turned in to your assigned teacher. Tutorial: Proteins Protein Definition: (PRO-teen) A molecule made up of amino acids that are needed for the body to function properly. 1. Prote ...
02-3 Carbon Compounds
... • Sucrose (glucose+fructose) • Lactose (glucose+galactose) • Maltose (glucose+glucose) ...
... • Sucrose (glucose+fructose) • Lactose (glucose+galactose) • Maltose (glucose+glucose) ...
Biochemistry Test Review KEY
... 12. What is the name of the structure above and what is its function? Nucleic acid 13. What is a common element found in all organic compounds? Carbon 14. What effect does pH levels have on a certain enzyme? Slows or speeds up rate of reaction, as well as the modifies the enzyme’s shape 15. Describ ...
... 12. What is the name of the structure above and what is its function? Nucleic acid 13. What is a common element found in all organic compounds? Carbon 14. What effect does pH levels have on a certain enzyme? Slows or speeds up rate of reaction, as well as the modifies the enzyme’s shape 15. Describ ...
Macromolecules - Van Buren Public Schools
... Term note: Synthesis = to make or form • Dehydration Synthesis – Water is removed – Bonds form between two monomers – One molecule donates –OH and the other molecules donate the –H Put it together = H2O ...
... Term note: Synthesis = to make or form • Dehydration Synthesis – Water is removed – Bonds form between two monomers – One molecule donates –OH and the other molecules donate the –H Put it together = H2O ...
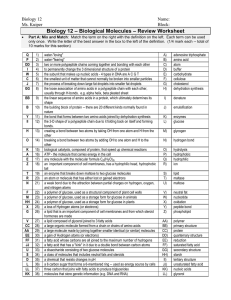
Biology 12 - Biologically Important Molecules – Review Worksheet
... a fatty acid that has a "kink" in it due to a double bond between carbon atoms a disaccharide consisting of two glucose molecules a class of molecules that includes neutral fats and steroids a chemical that resists changes in pH a 6 carbon sugar that forms a 6-membered ring -- used as energy source ...
... a fatty acid that has a "kink" in it due to a double bond between carbon atoms a disaccharide consisting of two glucose molecules a class of molecules that includes neutral fats and steroids a chemical that resists changes in pH a 6 carbon sugar that forms a 6-membered ring -- used as energy source ...
Chapter 3: Molecules of Life The molecules of life contain a high
... ______________________________: two or more polypeptide chains that are closely associated or covalently bonded together Enzymes often attach sugars to proteins (____________________) or lipids to proteins (____________________) Heat, some salts, shifts in pH, or detergents can denature (unravel) a ...
... ______________________________: two or more polypeptide chains that are closely associated or covalently bonded together Enzymes often attach sugars to proteins (____________________) or lipids to proteins (____________________) Heat, some salts, shifts in pH, or detergents can denature (unravel) a ...
Quiz 2
... - Non-Polar hydrophobic – Alanine, Isoluecine, Leucine, Methionine, Phenylalanine, Tryppotophan, Valine - Primary(single a.a.) - Secondary (covalent bonds create alpha helix or beta pleated sheets) - Tertiary – three dimensional shape – hydrogen bonds, covalent bonds, hydrophobic side chains, van de ...
... - Non-Polar hydrophobic – Alanine, Isoluecine, Leucine, Methionine, Phenylalanine, Tryppotophan, Valine - Primary(single a.a.) - Secondary (covalent bonds create alpha helix or beta pleated sheets) - Tertiary – three dimensional shape – hydrogen bonds, covalent bonds, hydrophobic side chains, van de ...
called “organic molecules”
... •“Saturated fat” – all three fatty acid chains contain the maximum possible number of hydrogen atoms : animal fats,butter,lard •“Unsaturated fat” – less than the maximum number of hydrogen atoms in one or more of it’s fatty acid chains : corn oil, olive oil ...
... •“Saturated fat” – all three fatty acid chains contain the maximum possible number of hydrogen atoms : animal fats,butter,lard •“Unsaturated fat” – less than the maximum number of hydrogen atoms in one or more of it’s fatty acid chains : corn oil, olive oil ...
BIOLOGY Unit 1 Notes: Characteristics of Life & Biomolecules
... – Existing cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
... – Existing cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
Organic molecules
... • Monomers of Lipids are fatty acids: -saturated fats = butter (main cause of high blood pressure) -trans fats = margarine, beef, pork (raise cholesterol levels) -unsaturated fats = nuts, olive oil -polyunsaturated fats = fish, cooking oils (may help lower cholesterol) Which type is best for you? w ...
... • Monomers of Lipids are fatty acids: -saturated fats = butter (main cause of high blood pressure) -trans fats = margarine, beef, pork (raise cholesterol levels) -unsaturated fats = nuts, olive oil -polyunsaturated fats = fish, cooking oils (may help lower cholesterol) Which type is best for you? w ...
Biochemistry
... Biomolecules •Biomolecules are molecules that are made and used by living things. •A polymer is a large molecule that is made up of smaller molecules called monomers. ...
... Biomolecules •Biomolecules are molecules that are made and used by living things. •A polymer is a large molecule that is made up of smaller molecules called monomers. ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.