Organic Compounds
... the structure. These are clusters of atoms that behave in a particular manner regardless of how the rest of the molecule looks. ...
... the structure. These are clusters of atoms that behave in a particular manner regardless of how the rest of the molecule looks. ...
Biological (organic) Molecules
... Transport molecules between cells Relay messages – hormones Speed up reactions – enzymes ...
... Transport molecules between cells Relay messages – hormones Speed up reactions – enzymes ...
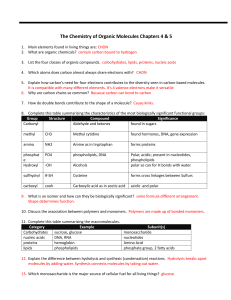
Unit 1 Page 1 Unit Vocabulary Terms Carbohydrate
... that allows for the utilization of glucose by cells. ● Hemoglobin - An iron-containing protein in red blood cells that binds to oxygen and carries it throughout the bloodstream. ● Lipids - Family of compounds, including fats, phospholipids, and steroids, that are insoluble in water. ● Phospholipids ...
... that allows for the utilization of glucose by cells. ● Hemoglobin - An iron-containing protein in red blood cells that binds to oxygen and carries it throughout the bloodstream. ● Lipids - Family of compounds, including fats, phospholipids, and steroids, that are insoluble in water. ● Phospholipids ...
Midterm Review Project Ch 5
... Macromolecule= polymer made from monomers dehydration reaction: water molecule lost, bond forms hydrolysis: water added, bond broken ...
... Macromolecule= polymer made from monomers dehydration reaction: water molecule lost, bond forms hydrolysis: water added, bond broken ...
Hardening of the arteries
... tertiary and quaternary (The most complex). A protein in blood cells that has this quaternary structure. C 300 ...
... tertiary and quaternary (The most complex). A protein in blood cells that has this quaternary structure. C 300 ...
Chapter 6, Section 3
... Organic: contains carbon ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
... Organic: contains carbon ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
Chem of life
... Carbon (C), nitrogen (N), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O) and sometimes (S) Parts of the cell membrane Parts of organelles Muscles have lots of protein ...
... Carbon (C), nitrogen (N), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O) and sometimes (S) Parts of the cell membrane Parts of organelles Muscles have lots of protein ...
Original
... In a single cellulose molecule, thousands of glucose monomers are linked in long straight chains. These tend to form H bonds with each other. ...
... In a single cellulose molecule, thousands of glucose monomers are linked in long straight chains. These tend to form H bonds with each other. ...
Chapter 4 - Organic Chemistry, Biochemistry
... Monosaccharides may be bonded together to form long chains called polysaccharides. ...
... Monosaccharides may be bonded together to form long chains called polysaccharides. ...
Biological Molecules - Princeton High School
... Saturated: Each carbon atom is single-bonded to 4 other atoms; straight chain; molecules are close together; solid ...
... Saturated: Each carbon atom is single-bonded to 4 other atoms; straight chain; molecules are close together; solid ...
Biochemistry Jeopardy C.P. Bio.
... is formed by chemically bonding two of these monosaccharides. ...
... is formed by chemically bonding two of these monosaccharides. ...
2.1 Molecules and metabolism
... • Anabolism is the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler molecules including the formation of macromolecules from monomers by condensation reactions. • Catabolism is the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules including the hydrolysis of macromolecules into monomers. Applications ...
... • Anabolism is the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler molecules including the formation of macromolecules from monomers by condensation reactions. • Catabolism is the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules including the hydrolysis of macromolecules into monomers. Applications ...
UNIT 4 NOTES
... B. Four types of carbon-based molecules are found in living things 1. Carbohydrates – starches and sugars a. monosaccharide – simple sugars (fructose and glucose) b. disaccharide – two sugars bonded together c. polysaccharide – polymers of monosaccharide (starch and cellulose) 2. Lipids – nonpolar m ...
... B. Four types of carbon-based molecules are found in living things 1. Carbohydrates – starches and sugars a. monosaccharide – simple sugars (fructose and glucose) b. disaccharide – two sugars bonded together c. polysaccharide – polymers of monosaccharide (starch and cellulose) 2. Lipids – nonpolar m ...
04-05 Biochem review sheet answers ws
... 5. Explain how carbon’s need for four electrons contributes to the diversity seen in carbon-based molecules. It is compatible with many different elements. It’s 4 valence electrons make it versatile 6. Why are carbon chains so common? Because carbon can bond to carbon 7. How do double bonds contribu ...
... 5. Explain how carbon’s need for four electrons contributes to the diversity seen in carbon-based molecules. It is compatible with many different elements. It’s 4 valence electrons make it versatile 6. Why are carbon chains so common? Because carbon can bond to carbon 7. How do double bonds contribu ...
... 1. What are macromolecules? Four main classes of large biological molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids) made up of many smaller molecules and atoms. 2. What are monomers? small chemical unit that can join together with other small units to form larger units called polymer 3. Wha ...
Biological Macromolecules
... Biological Macromolecules Monomers = single unit Polymer = many units bound together ...
... Biological Macromolecules Monomers = single unit Polymer = many units bound together ...
Modern Biology: Chapter 3
... – (CH2O)n general formula n = 3–8 monosaccharides – Hundreds of glucose monomers make glycogen (animals) or starch & cellulose (plants) ...
... – (CH2O)n general formula n = 3–8 monosaccharides – Hundreds of glucose monomers make glycogen (animals) or starch & cellulose (plants) ...
Biology Unit 2 Organic Notes The Chemistry of Carbon Organic
... Lipids are generally not soluble in water. The common categories of lipids are: ...
... Lipids are generally not soluble in water. The common categories of lipids are: ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.