* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biochemistry
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
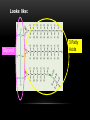
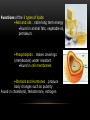
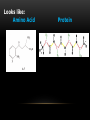
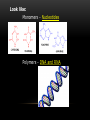
BIOCHEMISTRY Vocabulary: Structure – what something looks like Function – a job Mono- prefix meaning “one” Poly – prefix meaning “many” -ose and – saccharide are suffixes meaning “sugar” What is a molecule? A molecule is a very small piece of something. It is made up of different kinds of atoms. Example – a Water molecule (H2O) is made of 2 atoms of hydrogen and 1 atom of oxygen. A water molecule looks like this: The atoms in molecules are held together by forces called bonds. Biomolecules •Biomolecules are molecules that are made and used by living things. •A polymer is a large molecule that is made up of smaller molecules called monomers. •Most biomolecules are polymers. •Biomolecules are organic. This means they contain a chain of carbon atoms. All Biomolecules contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen There are 4 kinds of biomolecules: Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids. 1. Carbohydrates Made of: CHO (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen) Monomer: monosaccharides such as glucose and sucrose Looks like: Polymer: polysaccharides such as starch and glycogen Looks like: Functions: •Make cell walls strong. •Provide quick energy for animals (sugar makes you hyper) Found in: •Fruits (fructose is fruit sugar) •Breads and pasta (in the form of starches) •Plant cells (lignin and cellulose make plant cells strong, chitin makes the walls of mushrooms strong) 2. Lipids Made of: CHO (Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen) Lipids are NOT polymers. They are made of glycerol and fatty acids. Looks like: Glycerol 3 Fatty Acids Functions of the 3 types of lipids: •Fats and oils – store long term energy Found in animal fats, vegetable oil, petroleum. •Phospholipids – makes coverings (membranes) water resistant Found in cell membranes •Steroids and Hormones – produce body changes such as puberty Found in cholesterol, testosterone, estrogen 3. Proteins Made of: CHON - Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, and Nitrogen Monomer - Amino Acid •20 different types •Different side chains (R-groups) •Ex–tryptophan Polymer – peptides •Once the polypeptide is made it twists and folds into a protein. •Shape dictates what a protein does. •Held together by hydrogen bonds called peptide bonds. Looks like: Amino Acid Protein Functions: Control chemical reaction rates. Proteins that control reactions are called enzymes •Bone and muscle movement -Collagen •Transport substances – hemoglobin •Fight disease – antibodies 4. Nucleic Acids Made of: CHONP - Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Phosphorous Look like: Monomers - Nucleotides Polymers - DNA and RNA Function: Transmits genetic information from parents to offspring