* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download UNIT 2 Targets - Biochemistry
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
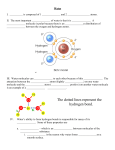
Name:______________________________________________________________ Period:_______ Date:_____________________________ BIOLOGY TARGETS Unit 2 – Biochemistry Remember… I can connect two or more targets together into one cohesive idea or explanation. I can recall lab/activity concepts, skills, and results from this unit as specific examples of the targets. I can use the BioThemes to connect the content and labs/activities in a detailed and reflective manner. TARGET 2.1 I can describe the basic structure of atoms including the charge and location of its 3 subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. 2.2 I can explain why atoms form bonds. 2.3 I can distinguish between polar covalent, nonpolar covalent and ionic bonds. 2.4 I can explain why water is a polar molecule, and can draw a diagram of a water molecule that shows its uneven distribution of charge. 2.5 I can explain that hydrogen bonding is an intermolecular force between water molecules, and can draw a diagram of how water molecules hydrogen bond. 2.6 I can distinguish between adhesion and cohesion. 2.7 I can describe the important properties of water that result from hydrogen bonding: capillary action, high specific heat capacity, high heat of vaporization, high surface tension, ability to be a universal solvent, and its ability to expand when it freezes. 2.8 I can explain what acids and bases are, and how the pH scale allows us to measure whether something is an acid or a base. 2.9 I can explain how each of the following maintains homeostasis in the human body: excretory system, digestive system, antacids, circulatory system, and buffers. 2.10 I can identify the six most common elements in organic molecules (C,H,N,O,P,S). 2.11 I can explain how carbon can join to other carbon atoms in chains and rings to form large and complex molecules. 2.12 I can describe the general structure of the 4 major categories of biomolecules that compose living organisms (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids). 2.13 I can identify the building blocks of the four major categories of biomolecules. 2.14 I can explain the primary functions of the four major categories of biomolecules. 2.15 I can identify the chemical indicators that test for the presence of glucose, starch, protein, and lipids, as well as describe what a “positive result” looks like for each test. 2.16 I can explain how dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis relate to the formation and break down of organic molecules (monomer vs. polymer). 2.17 I can describe the general formula for a chemical reaction, identifying any reactants and products. 2.18 I can explain that enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions. 2.19 2.20 I can describe the specifics of enzyme structure and function: identify the substrate(s), binding at the active site, identify the product(s) formed, and how the enzyme can be re-used after the products are formed. I can explain that the activity of enzymes is affected by changes in temperature and pH of the surroundings (denatured), as well as by the concentration of the enzyme.