File - Mrs. Badger`s Honors Biology Class
... a. carry a message that, when translated, forms proteins. b. form a portion of ribosomes, a cell’s protein factories. c. string together complementary RNA and DNA strands. d. bring amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. _____ 3. What is the term for a three-nucleotide sequence that codes f ...
... a. carry a message that, when translated, forms proteins. b. form a portion of ribosomes, a cell’s protein factories. c. string together complementary RNA and DNA strands. d. bring amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. _____ 3. What is the term for a three-nucleotide sequence that codes f ...
Power Point 2 - G. Holmes Braddock
... When carbohydrates are consumed the body breaks them down into glucose. Then the glucose moves into your bloodstream and goes to your organs and tissues, where it is used to fuel cellular activity. Simple carbohydrates occur when there is more glucose in the body than your cells need, it is converte ...
... When carbohydrates are consumed the body breaks them down into glucose. Then the glucose moves into your bloodstream and goes to your organs and tissues, where it is used to fuel cellular activity. Simple carbohydrates occur when there is more glucose in the body than your cells need, it is converte ...
1 - Wsfcs
... What type of molecule is this? __________________ This process is called a ___________________ ______________________. (on board) If you were to break this large molecule apart into the two original glucose molecules, the process would be ______________________ (on board). What would you have to add ...
... What type of molecule is this? __________________ This process is called a ___________________ ______________________. (on board) If you were to break this large molecule apart into the two original glucose molecules, the process would be ______________________ (on board). What would you have to add ...
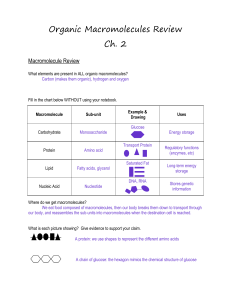
Compounds of Life Chart
... o Maltose, lactose (found in milk) and sucrose (table sugar) Polysaccharides – made of two or more monosaccharides o Starch (how plants store glucose) o Cellulose (dietary fiber in animals, component of cell walls in plants) o Glycogen (how animals store glucose) ...
... o Maltose, lactose (found in milk) and sucrose (table sugar) Polysaccharides – made of two or more monosaccharides o Starch (how plants store glucose) o Cellulose (dietary fiber in animals, component of cell walls in plants) o Glycogen (how animals store glucose) ...
Proteins and Nucleic Acids Proteins (pp.46-48) Monomer
... Proteins (pp.46-48) Monomer-basic structure Types of proteins and their functions Number of amino acids o what makes them different from one another o what's responsible for giving them their chemical properties Polymers o Bond responsible for linking amino acids together o Levels of Protein ...
... Proteins (pp.46-48) Monomer-basic structure Types of proteins and their functions Number of amino acids o what makes them different from one another o what's responsible for giving them their chemical properties Polymers o Bond responsible for linking amino acids together o Levels of Protein ...
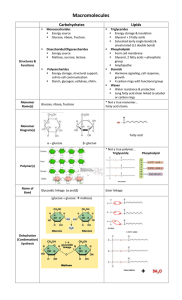
Remember: Condensation makes bonds: Hydrolysis breaks bonds.
... IB Biology 3.2 Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins ...
... IB Biology 3.2 Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins ...
MacromoleculeReview
... 23. A peptide bond is always formed between the ______________________ group of one _________________________ and the ______________________ group of the next. 24. Using a structural formula diagram, show how a peptide bond is formed between two amino acids. ...
... 23. A peptide bond is always formed between the ______________________ group of one _________________________ and the ______________________ group of the next. 24. Using a structural formula diagram, show how a peptide bond is formed between two amino acids. ...
Biological_Molecules worksheet - answers
... 4. List 3 functions of fats in the human body: a. They make up cell membranes b. Long term energy source – they release as twice as much energy as carbohydrates/protein. ...
... 4. List 3 functions of fats in the human body: a. They make up cell membranes b. Long term energy source – they release as twice as much energy as carbohydrates/protein. ...
Biochemistry_2011
... element chemically bonded together - Can only be chemically separated into elements ...
... element chemically bonded together - Can only be chemically separated into elements ...
Instructor: Brendan Leezer
... Example = sucrose (table sugar) formed by combining glucose and fructose Polysaccharides = The largest carbohydrate molecules. They are polymers composed of many monosaccharide subunits. Examples = starch, glycogen, and cellulose Starch consists of highly branched chains of glucose units. o It is ...
... Example = sucrose (table sugar) formed by combining glucose and fructose Polysaccharides = The largest carbohydrate molecules. They are polymers composed of many monosaccharide subunits. Examples = starch, glycogen, and cellulose Starch consists of highly branched chains of glucose units. o It is ...
Macromolecules Review ws Name the 6 main elements that make
... Large molecules containing many atoms ...
... Large molecules containing many atoms ...
chapter 5 large biological molecules
... Hydrolysis – adding H20 to break apart polymers Carbohydrates include sugars and their polymers: Monosaccharides – single sugars, variations of CH20 with 3-7 C’s. Glucose has 6, called hexose. Trioses and pentoses common. Have –OH attached to all C’s except one which has a C=O (carbonyl). Terminal ...
... Hydrolysis – adding H20 to break apart polymers Carbohydrates include sugars and their polymers: Monosaccharides – single sugars, variations of CH20 with 3-7 C’s. Glucose has 6, called hexose. Trioses and pentoses common. Have –OH attached to all C’s except one which has a C=O (carbonyl). Terminal ...
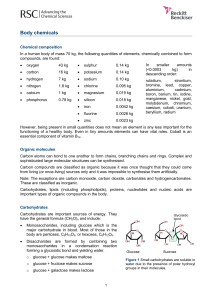
Body chemicals
... functioning of a healthy body. Even in tiny amounts elements can have vital roles. Cobalt is an essential component of vitamin B12. Organic molecules Carbon atoms can bond to one another to form chains, branching chains and rings. Complex and ...
... functioning of a healthy body. Even in tiny amounts elements can have vital roles. Cobalt is an essential component of vitamin B12. Organic molecules Carbon atoms can bond to one another to form chains, branching chains and rings. Complex and ...
UNIT 2: BIOCHEMISTRY/ENZYMES
... How do we get these macromolecules? • When we eat, large organic food molecules such as proteins and starches must initially be broken down to enter cells • Proteins amino acids • Starches simple sugars • These nutrients can now enter the cell and be used as building blocks of compounds needed ...
... How do we get these macromolecules? • When we eat, large organic food molecules such as proteins and starches must initially be broken down to enter cells • Proteins amino acids • Starches simple sugars • These nutrients can now enter the cell and be used as building blocks of compounds needed ...
Chapter 6, Section 3
... 1. Carbon forms bonds easily because it has 4 valence electrons. 2. Carbon atoms can bond to other carbon atoms, forming chains that are almost unlimited in length. 3. All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), and phosphorous (P). ...
... 1. Carbon forms bonds easily because it has 4 valence electrons. 2. Carbon atoms can bond to other carbon atoms, forming chains that are almost unlimited in length. 3. All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), and phosphorous (P). ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.