Biological Macromolecules
... organic, meaning they all contain hydrocarbons…Carbon atoms (with attached Hydrogens!) Other elements may include Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Sulfur ...
... organic, meaning they all contain hydrocarbons…Carbon atoms (with attached Hydrogens!) Other elements may include Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Sulfur ...
View Ch. 3 PowerPoint here.
... – Formation of large molecules by the removal of water – Monomers are joined to form polymers, endergonic ...
... – Formation of large molecules by the removal of water – Monomers are joined to form polymers, endergonic ...
Carbon Compounds
... molecules made of similar repeating units. 1. Polymer = macromolecule 2. Monomer = smaller units that fit together to form polymers (macromolecules) ...
... molecules made of similar repeating units. 1. Polymer = macromolecule 2. Monomer = smaller units that fit together to form polymers (macromolecules) ...
Macromolecules Notes File
... ____________________ - molecules used to store energy in organisms as well as structural materials. Made of C,H,O,. Less oxygen than in carbohydrates. Twice the amount of energy storage. Soluble in nonpolar solvents. ...
... ____________________ - molecules used to store energy in organisms as well as structural materials. Made of C,H,O,. Less oxygen than in carbohydrates. Twice the amount of energy storage. Soluble in nonpolar solvents. ...
Chemistry Test Study Guide
... 21. _____________________ are the monomers for nucleic acids. 22. _____________ and ______________ are the two types of nucleic acids. 23. Name the function of nucleic acids. _________________________________________ 24. Describe/Draw the structure of DNA. ( What does it look like?) ________________ ...
... 21. _____________________ are the monomers for nucleic acids. 22. _____________ and ______________ are the two types of nucleic acids. 23. Name the function of nucleic acids. _________________________________________ 24. Describe/Draw the structure of DNA. ( What does it look like?) ________________ ...
Molecole per la vita
... Triglycerides are lipids that are obtained by means of the esterification reaction between glycerol and fatty acids and form the fatty tissues of animals and plants. Triglycerides may be saturated or unsaturated depending on whether the hydrocarbon chains of the fatty acids contain double bonds or n ...
... Triglycerides are lipids that are obtained by means of the esterification reaction between glycerol and fatty acids and form the fatty tissues of animals and plants. Triglycerides may be saturated or unsaturated depending on whether the hydrocarbon chains of the fatty acids contain double bonds or n ...
Chapter 3 Test Review
... The large molecules can be broken down into smaller that are exactly alike. ...
... The large molecules can be broken down into smaller that are exactly alike. ...
Organic Molecule
... 2 Types of Fatty Acids Saturated: If each carbon atom in a lipid’s fatty acid has single covalent bonds. - Results in straight chains(Solid at room ...
... 2 Types of Fatty Acids Saturated: If each carbon atom in a lipid’s fatty acid has single covalent bonds. - Results in straight chains(Solid at room ...
1 - Bulldogbiology.com
... a. Used as the main source of energy by all living things b. Simple sugars such as glucose and fructose are called monosaccharides and end with the suffix -ose c. Also used by plants and some animals for structural purposes Lipids- large and varied group of molecules made up of carbon and hydrogen t ...
... a. Used as the main source of energy by all living things b. Simple sugars such as glucose and fructose are called monosaccharides and end with the suffix -ose c. Also used by plants and some animals for structural purposes Lipids- large and varied group of molecules made up of carbon and hydrogen t ...
2.3 Study Guide - Issaquah Connect
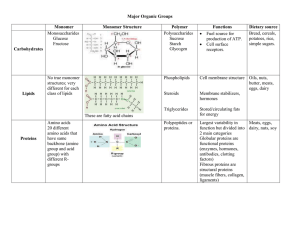
... MAIN IDEA: Four main types of carbon-based molecules are found in living things. Complete the table with functions and examples of each type of carbon-based molecule. ...
... MAIN IDEA: Four main types of carbon-based molecules are found in living things. Complete the table with functions and examples of each type of carbon-based molecule. ...
Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen
... Each small organic molecule can be a unit of a large organic molecule called a macromolecule. There are four classes of macromolecules (polysaccharides or carbohydrates, triglycerides or lipids, polypeptides or proteins, and nucleic acids such as DNA & RNA). Carbohydrates and lipids are made of only ...
... Each small organic molecule can be a unit of a large organic molecule called a macromolecule. There are four classes of macromolecules (polysaccharides or carbohydrates, triglycerides or lipids, polypeptides or proteins, and nucleic acids such as DNA & RNA). Carbohydrates and lipids are made of only ...
Key: Biomolecule Study Guide 1) In animals, excess carbohydrates
... Key: Biomolecule Study Guide ...
... Key: Biomolecule Study Guide ...
Energetics - The Practical Educator
... • Same chemical formula but different structure= isomers ...
... • Same chemical formula but different structure= isomers ...
Biology 1 – Chem4kids
... between different amino acids). Name and describe the 2 smaller groups of atoms combined in the common group. (Refer to both the paragraph and the diagram) ...
... between different amino acids). Name and describe the 2 smaller groups of atoms combined in the common group. (Refer to both the paragraph and the diagram) ...
Macromolecules For Identification
... amounts nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur. • They are called "macromolecules" because they are very large, containing long chains of carbon and hydrogen atoms and often consists of repeating smaller molecules bonded together in a repeating pattern (polymers). ...
... amounts nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur. • They are called "macromolecules" because they are very large, containing long chains of carbon and hydrogen atoms and often consists of repeating smaller molecules bonded together in a repeating pattern (polymers). ...
Chapter 3
... • 2 monosaccharides linked together by dehydration synthesis • Used for sugar transport or energy storage • Examples: sucrose, lactose, maltose ...
... • 2 monosaccharides linked together by dehydration synthesis • Used for sugar transport or energy storage • Examples: sucrose, lactose, maltose ...
Biochemistry
... Proteins are the most complex macromolecules in the cell. They are composed of linear polymers called polypeptides, which contain amino acids connected by peptide bonds. ...
... Proteins are the most complex macromolecules in the cell. They are composed of linear polymers called polypeptides, which contain amino acids connected by peptide bonds. ...
Macromolecules of Life
... transports oxygen through the blood Hormone proteins. Ex, insulin which regulates the amount of sugar in the blood Help control movement. Ex. proteins in muscles which control contraction Enzymes are catalysts that speed up chemical reactions Ex. digestive enzymes which break down food in the digest ...
... transports oxygen through the blood Hormone proteins. Ex, insulin which regulates the amount of sugar in the blood Help control movement. Ex. proteins in muscles which control contraction Enzymes are catalysts that speed up chemical reactions Ex. digestive enzymes which break down food in the digest ...
Major Organic Groups - Lemon Bay High School
... Meats, eggs, function but divided into dairy, nuts, soy 2 main categories Globular proteins are functional proteins (enzymes, hormones, antibodies, clotting factors) Fibrous proteins are structural proteins (muscle fibers, collagen, ligaments) ...
... Meats, eggs, function but divided into dairy, nuts, soy 2 main categories Globular proteins are functional proteins (enzymes, hormones, antibodies, clotting factors) Fibrous proteins are structural proteins (muscle fibers, collagen, ligaments) ...
biochemistry - SchoolNotes.com
... of ENERGY! • Plants use carbohydrates for structure (CELLULOSE) – include sugars and complex carbohydrates (starches) – contain the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio ...
... of ENERGY! • Plants use carbohydrates for structure (CELLULOSE) – include sugars and complex carbohydrates (starches) – contain the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio ...
The Chemical Building Blocks of Life
... • Unsaturated- has double bonds ex veggie oil • Polyunsaturated- has more than one double bond ...
... • Unsaturated- has double bonds ex veggie oil • Polyunsaturated- has more than one double bond ...
Organic Macromolecules
... Read Chapter 3 in your book and fill out this graphic organizer. You will use this when you do your Macromolecule Flapbook. Organic Molecule Simple Carbohydrate ...
... Read Chapter 3 in your book and fill out this graphic organizer. You will use this when you do your Macromolecule Flapbook. Organic Molecule Simple Carbohydrate ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.