Remediation/Corrections Packet
... The four main classes of organic compounds (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) that are essential to the proper functioning of all living things are known as polymers or macromolecules. All of these compounds are built primarily of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen but in different ratio ...
... The four main classes of organic compounds (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) that are essential to the proper functioning of all living things are known as polymers or macromolecules. All of these compounds are built primarily of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen but in different ratio ...
Chemical Bulilding Block
... • Fructose is a structural isomer of glucose • Galactose is a stereoisomer of glucose • Enzymes that act on different sugars can distinguish structural and stereoisomers of this basic six-carbon skeleton ...
... • Fructose is a structural isomer of glucose • Galactose is a stereoisomer of glucose • Enzymes that act on different sugars can distinguish structural and stereoisomers of this basic six-carbon skeleton ...
Macro-molecule study guide / worksheet
... 3. There are two basic kinds of nucleic acids. Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) which contains the sugar ribose and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) which contains the sugar deoxyribose. 4. DNA - 2 strands of nucleotides; RNA - 1 strand of nucleotides Enzymes - with few exceptions, they are proteins Catalyst - sub ...
... 3. There are two basic kinds of nucleic acids. Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) which contains the sugar ribose and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) which contains the sugar deoxyribose. 4. DNA - 2 strands of nucleotides; RNA - 1 strand of nucleotides Enzymes - with few exceptions, they are proteins Catalyst - sub ...
Name: Period: _____ Vocabulary Unit 2 Biomolecule Molecules
... A biomolecule containing hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio and is used as a primary energy source ...
... A biomolecule containing hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio and is used as a primary energy source ...
Section 2.3 and 2.4 Guided Notes
... _________________________________________________ when an unfavorable change in the temperature or pH cause a protein to unravel and lose its shape (this cannot be reversed) • Example: scrambled eggs are denatured protein ...
... _________________________________________________ when an unfavorable change in the temperature or pH cause a protein to unravel and lose its shape (this cannot be reversed) • Example: scrambled eggs are denatured protein ...
What are macromolecules?
... MACROMOLECULES Macro = large Molecule = smallest unit of most compounds Macromolecules in the cell are all carbon- ...
... MACROMOLECULES Macro = large Molecule = smallest unit of most compounds Macromolecules in the cell are all carbon- ...
Bio-Chemistry
... Bio-Chemistry Quiz 1. What are the 3 different types of Carbohydrates? 2. Give me an example of where you can find lipids? ...
... Bio-Chemistry Quiz 1. What are the 3 different types of Carbohydrates? 2. Give me an example of where you can find lipids? ...
Biochemistry
... • All chemical reactions in living things are catalyzed by enzymes. • Enzymes are special proteins that help lower the activation energy of a chemical reaction » Enzymes combine with the substrate at the enzyme’s active site and help the chemical action proceed. » Enzymes may bring molecules togethe ...
... • All chemical reactions in living things are catalyzed by enzymes. • Enzymes are special proteins that help lower the activation energy of a chemical reaction » Enzymes combine with the substrate at the enzyme’s active site and help the chemical action proceed. » Enzymes may bring molecules togethe ...
BIO C211 - BITS Pilani
... In addition to Part One (General Handout for all courses appended to the time table) this part gives further specific details regarding the course. Course No. ...
... In addition to Part One (General Handout for all courses appended to the time table) this part gives further specific details regarding the course. Course No. ...
Bio-Macromolecules Worksheet.doc
... Carbohydrates are sugars, starches, and glycogen which are used for short and long term energy storage in cells and structural molecules in cell walls and exoskeletons. Carbohydrates are made of only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (CHO). They are found in bread, potatoes, pasta, and fruits. Carbohydra ...
... Carbohydrates are sugars, starches, and glycogen which are used for short and long term energy storage in cells and structural molecules in cell walls and exoskeletons. Carbohydrates are made of only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (CHO). They are found in bread, potatoes, pasta, and fruits. Carbohydra ...
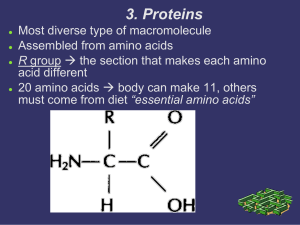
3. Proteins
... Key components of reactions that give energy, and make, or break down compounds Only needed in small amounts ...
... Key components of reactions that give energy, and make, or break down compounds Only needed in small amounts ...
Organic chemistry
... Biochemistry is the study of the chemical interactions of living things. Biochemists study the structures and physical properties of biological molecules. ...
... Biochemistry is the study of the chemical interactions of living things. Biochemists study the structures and physical properties of biological molecules. ...
Organic chemistry ppt
... Why is Carbon important to life? • Carbon is light weight and small • Carbon atoms have 4 valence electrons. – Can bond with other elements and itself to form unlimited (in length) chains that can even fold to form rings ...
... Why is Carbon important to life? • Carbon is light weight and small • Carbon atoms have 4 valence electrons. – Can bond with other elements and itself to form unlimited (in length) chains that can even fold to form rings ...
Chemistry/Biochemistry Review
... 17. Many monomers joined together 18. Many sugars linked together 19. Monomer for carbohydrates 20. Monomer for lipids 21. Monomer for nucleic acids 22. Monomer for proteins 23. Single units/building blocks of polymers 24. Type of lipid that is solid at room temperature 25. Supply main/primary sourc ...
... 17. Many monomers joined together 18. Many sugars linked together 19. Monomer for carbohydrates 20. Monomer for lipids 21. Monomer for nucleic acids 22. Monomer for proteins 23. Single units/building blocks of polymers 24. Type of lipid that is solid at room temperature 25. Supply main/primary sourc ...
Macromolecules
... Monosaccharides typically have five or six carbon atoms. Monosaccharides can, such as the ribose and deoxyribose of RNA and DNA, can serve very important functions in cells. Ex. Glucose- blood sugar Fructose- sugar in fruit ...
... Monosaccharides typically have five or six carbon atoms. Monosaccharides can, such as the ribose and deoxyribose of RNA and DNA, can serve very important functions in cells. Ex. Glucose- blood sugar Fructose- sugar in fruit ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.