Macromolecules and the Molecules of Life
... • Made of CHNOP • Large molecules formed by joining polymers • Monomers • The basic units that bond together to form molecules essential to life • Bond via condensation reaction • Monomer + monomer = polymer + water • Polymers • Several monomers joined together • Separate via Hydrolysis • Breakdown ...
... • Made of CHNOP • Large molecules formed by joining polymers • Monomers • The basic units that bond together to form molecules essential to life • Bond via condensation reaction • Monomer + monomer = polymer + water • Polymers • Several monomers joined together • Separate via Hydrolysis • Breakdown ...
Biochemistry Self-Test
... 3. In a condensation reaction, two molecules combine and a molecule of _________ is produced. 4. A substance that tends not to react with water, "Water hating" , is ________________________ 5. Breaking of _______________ bonds is the first thing that happens when water is heated, which means that it ...
... 3. In a condensation reaction, two molecules combine and a molecule of _________ is produced. 4. A substance that tends not to react with water, "Water hating" , is ________________________ 5. Breaking of _______________ bonds is the first thing that happens when water is heated, which means that it ...
Mid Term Review 2008
... Amino acids, Ribosomes, Enzymes, words ending in “in” (trypsin, pepsin) ...
... Amino acids, Ribosomes, Enzymes, words ending in “in” (trypsin, pepsin) ...
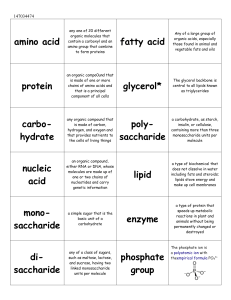
The Four Organic Compounds Notes
... Provide structure for cells, bones, muscles, tissues, organs, hormones, most everything in the body! Special Function: Carries out cell metabolism (via enzymes) ...
... Provide structure for cells, bones, muscles, tissues, organs, hormones, most everything in the body! Special Function: Carries out cell metabolism (via enzymes) ...
Biology I SB1bc Enzymes and Macromolecules Test Study Guide
... 7. Draw a picture of (A) a substrate, (B) an ES complex, and (C) the products. ...
... 7. Draw a picture of (A) a substrate, (B) an ES complex, and (C) the products. ...
Biology I SB1bc Enzymes and Macromolecules Test Study Guide
... 7. Draw a picture of (A) a substrate, (B) an ES complex, and (C) the products. ...
... 7. Draw a picture of (A) a substrate, (B) an ES complex, and (C) the products. ...
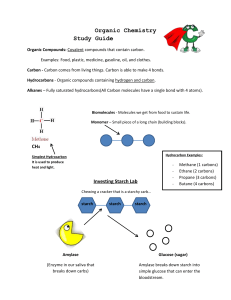
Organic Chemistry Study Guide Organic Compounds: Covalent
... Examples: Food, plastic, medicine, gasoline, oil, and clothes. Carbon - Carbon comes from living things. Carbon is able to make 4 bonds. Hydrocarbons - Organic compounds containing hydrogen and carbon. Alkanes – Fully saturated hydrocarbons(All Carbon molecules have a single bond with 4 atoms). ...
... Examples: Food, plastic, medicine, gasoline, oil, and clothes. Carbon - Carbon comes from living things. Carbon is able to make 4 bonds. Hydrocarbons - Organic compounds containing hydrogen and carbon. Alkanes – Fully saturated hydrocarbons(All Carbon molecules have a single bond with 4 atoms). ...
Organic Chemistry and Macromolecules
... ex: fats and oils • Proteins—organic molecule that is structural and speeds up chemical reactions; ex: enzymes and hemaglobin ...
... ex: fats and oils • Proteins—organic molecule that is structural and speeds up chemical reactions; ex: enzymes and hemaglobin ...
Macromolecules For Identification
... smaller amounts nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur. • They are called "macromolecules" because they are very large, containing long chains of carbon and hydrogen atoms and often consists of repeating smaller molecules bonded together in a repeating pattern (polymers). ...
... smaller amounts nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur. • They are called "macromolecules" because they are very large, containing long chains of carbon and hydrogen atoms and often consists of repeating smaller molecules bonded together in a repeating pattern (polymers). ...
File
... a) serve as energy reserves in many organisms b) include cartilage and chitin c) include fats that are broken down into one fatty acid molecule and three glycerol molecules d) are composed of monosaccharides e) none of the above __ 14. What type of LIPIDS are found in ALL biological MEMBRANES? a) tr ...
... a) serve as energy reserves in many organisms b) include cartilage and chitin c) include fats that are broken down into one fatty acid molecule and three glycerol molecules d) are composed of monosaccharides e) none of the above __ 14. What type of LIPIDS are found in ALL biological MEMBRANES? a) tr ...
The Chemical Building Blocks of Life
... • Biological molecules consist predominantly of carbon atoms bonded to other carbon atoms or to atoms of oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, or hydrogen. (p. 36) • Hydrocarbons are molecules consisting only of carbon and hydrogen; thus, they store considerable energy. (p. 36) • Functional groups have definite ...
... • Biological molecules consist predominantly of carbon atoms bonded to other carbon atoms or to atoms of oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, or hydrogen. (p. 36) • Hydrocarbons are molecules consisting only of carbon and hydrogen; thus, they store considerable energy. (p. 36) • Functional groups have definite ...
Organic Macromolecules
... Describe how polymers are formed and broken down in organics Compare the chemical structure of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids and how they are related to living things. ...
... Describe how polymers are formed and broken down in organics Compare the chemical structure of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids and how they are related to living things. ...
Biochemistry Learning Targets and Essential Vocabulary name describe
... name and describe the functions of the four groups of organic compounds found in living things. (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, & Nucleic Acids) describe how polymers are built from monomers (dehydration synthesis) and ...
... name and describe the functions of the four groups of organic compounds found in living things. (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, & Nucleic Acids) describe how polymers are built from monomers (dehydration synthesis) and ...
File
... explores the ____________processes within and related to ________organisms. It is a laboratory based science that brings together biology and chemistry. By using chemical knowledge and techniques, biochemists can understand and solve ______________ problems ...
... explores the ____________processes within and related to ________organisms. It is a laboratory based science that brings together biology and chemistry. By using chemical knowledge and techniques, biochemists can understand and solve ______________ problems ...
Concepts in Biochemistry 3/e
... 1. Biological information flow from DNA RNA Protein. Write about the whole process from replication to translation to protein in 100-200 words. 2. Discuss the uses of biochemistry in environmental science, gene engineering & cloning and clinical chemistry. ...
... 1. Biological information flow from DNA RNA Protein. Write about the whole process from replication to translation to protein in 100-200 words. 2. Discuss the uses of biochemistry in environmental science, gene engineering & cloning and clinical chemistry. ...
The Chemistry of Molecular Biology
... attaches to nitrogen of purine or pyrimidine • Acidic nature due to phosphate group • Nucleotides are linked by phosphodiester bonds ...
... attaches to nitrogen of purine or pyrimidine • Acidic nature due to phosphate group • Nucleotides are linked by phosphodiester bonds ...
Organic Molecules - NVHSIntroBioPiper1
... four bonds It can even bond with itself This allows carbon to form long chains to form bigger compounds ...
... four bonds It can even bond with itself This allows carbon to form long chains to form bigger compounds ...
Introduction to 9th Grade Biology
... Lipids • Our body needs them for insulation, cushioning, and energy storage. • Three important groups – Fats & Oils – Phospholipids (cell membrane) – Steroids (cholesterol) ...
... Lipids • Our body needs them for insulation, cushioning, and energy storage. • Three important groups – Fats & Oils – Phospholipids (cell membrane) – Steroids (cholesterol) ...
macromolecule notes
... 1. ________________: a common storage form of glucose in plants (breads, pasta, potatoes) 2. ________________: a polysaccharide contained in the cell walls of ________________; gives strength and rigidity to plant cells. 3. ________________: a common storage form of glucose in animals (stored in the ...
... 1. ________________: a common storage form of glucose in plants (breads, pasta, potatoes) 2. ________________: a polysaccharide contained in the cell walls of ________________; gives strength and rigidity to plant cells. 3. ________________: a common storage form of glucose in animals (stored in the ...
organic molecules
... 1. Amine (NH2) on one end, carboxyl (COOH) on the other end, and H and R groups a. portion that differs: R-group 2. More than 20 different amino acids in nature 3. Sequence of amino acids determines the protein C. 2 amino acids joined by a peptide bond forms a dipeptide. A long chain is called a pol ...
... 1. Amine (NH2) on one end, carboxyl (COOH) on the other end, and H and R groups a. portion that differs: R-group 2. More than 20 different amino acids in nature 3. Sequence of amino acids determines the protein C. 2 amino acids joined by a peptide bond forms a dipeptide. A long chain is called a pol ...
Lesson
... * Stages involved with formation of proteins * Primary, secondary, tertiary & quaternary structures ...
... * Stages involved with formation of proteins * Primary, secondary, tertiary & quaternary structures ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.