Molecules of Life Additional Notes
... 10. Plants convert excess sugars into starches for long-term storage. Cellulose is a polysaccharide contained in the cell walls of plants. Cellulose gives strength and rigidity to plant cells and makes up about 50 percent of wood. ...
... 10. Plants convert excess sugars into starches for long-term storage. Cellulose is a polysaccharide contained in the cell walls of plants. Cellulose gives strength and rigidity to plant cells and makes up about 50 percent of wood. ...
The Molecules of Life
... It is used by plant cells to store energy Potatoes and grains Glycogen is used by animal cells to store energy It is hydrolyzed to release glucose when we need energy Cellulose is the most abundant organic compound on Earth It makes up the walls of plant cells It cannot be chemically broken by any e ...
... It is used by plant cells to store energy Potatoes and grains Glycogen is used by animal cells to store energy It is hydrolyzed to release glucose when we need energy Cellulose is the most abundant organic compound on Earth It makes up the walls of plant cells It cannot be chemically broken by any e ...
Atom - TeacherWeb
... and polymer for each category with examples. Know general functions of examples in each category. What are the four levels of organization of a protein? What are the three parts of an amino acid or nucleic acid? Definition only for Dehydration synthesis and Hydrolysis Read molecular formulas with co ...
... and polymer for each category with examples. Know general functions of examples in each category. What are the four levels of organization of a protein? What are the three parts of an amino acid or nucleic acid? Definition only for Dehydration synthesis and Hydrolysis Read molecular formulas with co ...
energy, chemical reactions and organic compounds list the four
... are amphiphilic, the fatty acid tail is hydrophobic and the phosphate head is hydrophilic. Eicosanoids – are derived from a fatty acid called arachidonic acid. They primarily function as hormone‐like chemical signals between cells. Prostaglandin is a cell which is produced in all tissues and play ...
... are amphiphilic, the fatty acid tail is hydrophobic and the phosphate head is hydrophilic. Eicosanoids – are derived from a fatty acid called arachidonic acid. They primarily function as hormone‐like chemical signals between cells. Prostaglandin is a cell which is produced in all tissues and play ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... II. State whether the following are true or false, if false, give reason ...
... II. State whether the following are true or false, if false, give reason ...
Biomolecules Unit Review File
... 12. Draw a single nucleotide. Draw a chain of nucleic acid. How many strands does DNA have? How many strands does RNA have? 13. What provides more energy lipids or carbohydrates? What type of energy are each of them? 14. What is glycogen? Where can you find it? What organisms utilize glycogen? 15. W ...
... 12. Draw a single nucleotide. Draw a chain of nucleic acid. How many strands does DNA have? How many strands does RNA have? 13. What provides more energy lipids or carbohydrates? What type of energy are each of them? 14. What is glycogen? Where can you find it? What organisms utilize glycogen? 15. W ...
Ch.3 Review Using Vocabulary a) A monomer is a simpler, smaller
... 6. A carbon atom has four electrons in its outermost energy level therefore it readily forms four covalent bonds with the atoms of other elements and it may also bond with itself which results in an enormous variety of organic compounds. 7. Functional groups influence the characteristics of the mole ...
... 6. A carbon atom has four electrons in its outermost energy level therefore it readily forms four covalent bonds with the atoms of other elements and it may also bond with itself which results in an enormous variety of organic compounds. 7. Functional groups influence the characteristics of the mole ...
Chapter 6.4 The Building Blocks of Life
... Proteins can have up to four levels of structures due to the variable groups Number of amino acids in a chain and the order in which they are joined, define the primary ...
... Proteins can have up to four levels of structures due to the variable groups Number of amino acids in a chain and the order in which they are joined, define the primary ...
Document
... All amino acids are identical in the amino and carboxyl groups. Any amino acid can be joined to any other amino acid by a peptide bond formed between these amino and carboxyl groups. Amino acids differ from each other in a side chain called the R-groups, which have a range of different properties. M ...
... All amino acids are identical in the amino and carboxyl groups. Any amino acid can be joined to any other amino acid by a peptide bond formed between these amino and carboxyl groups. Amino acids differ from each other in a side chain called the R-groups, which have a range of different properties. M ...
Ch1_2
... • Expect for water, most of the molecules found in the cell are macromolecules, can be classified into four different categories: – Lipids – Carbohydrates – Proteins – Nucleic acids ...
... • Expect for water, most of the molecules found in the cell are macromolecules, can be classified into four different categories: – Lipids – Carbohydrates – Proteins – Nucleic acids ...
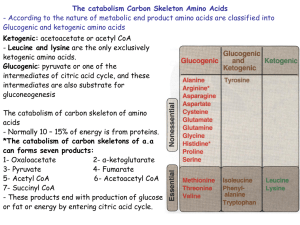
The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...
Macromolecules in Organisms
... oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. The four main classes of organic compounds (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) that are essential to the proper functioning of all living things are known as polymers or macromolecules. All of these compounds are ...
... oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. The four main classes of organic compounds (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) that are essential to the proper functioning of all living things are known as polymers or macromolecules. All of these compounds are ...
Answers - Shelton State
... What are most likely outcomes for the cell if an uncorrected mutation occurs in the DNA? 1. No effect — error in a noncoding region of the DNA; synonym code; code for very similar amino acid. 2. Cell dies — effect is major enough (crucial protein doesn’t function) that the cell cannot survive. 3. Ce ...
... What are most likely outcomes for the cell if an uncorrected mutation occurs in the DNA? 1. No effect — error in a noncoding region of the DNA; synonym code; code for very similar amino acid. 2. Cell dies — effect is major enough (crucial protein doesn’t function) that the cell cannot survive. 3. Ce ...
functional group
... Chitin is a N containing polysaccharide which is found in the exoskeleton of insects and cell wall of fungi. They are not soluble or slightly soluble. ...
... Chitin is a N containing polysaccharide which is found in the exoskeleton of insects and cell wall of fungi. They are not soluble or slightly soluble. ...
Unit 3: Basic Chemistry Content Outline: Carbon Chemistry (3.6
... B. Although there are many types of organic compounds, some containing atoms of Halogens or Oxygen, Sulfur, Nitrogen and Phosphorous, key biochemical compounds (organic compounds found in living things) are divided into 4 categories: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. 1. Carbohydrate ...
... B. Although there are many types of organic compounds, some containing atoms of Halogens or Oxygen, Sulfur, Nitrogen and Phosphorous, key biochemical compounds (organic compounds found in living things) are divided into 4 categories: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. 1. Carbohydrate ...
www.eastpenn.k12.pa.us
... -Amino acids are compounds with an amino group on one end (NH2)and a carboxyl group on the other end (-COOH) -Covalent bonds called peptide bonds link amino acids together to form a polypeptide -Multiple polypeptides join to form a protein -In living things, proteins make up cellular structures. Som ...
... -Amino acids are compounds with an amino group on one end (NH2)and a carboxyl group on the other end (-COOH) -Covalent bonds called peptide bonds link amino acids together to form a polypeptide -Multiple polypeptides join to form a protein -In living things, proteins make up cellular structures. Som ...
BIOMOLECULES
... Remember: Elements are C, H, O, and N “R” groups represent one of the 20 Amino Acids! (so, each amino acid has something different in that spot) ...
... Remember: Elements are C, H, O, and N “R” groups represent one of the 20 Amino Acids! (so, each amino acid has something different in that spot) ...
BIOCHEMISTRY 2.1
... respiration—must be converted into the form our cells can use (“ATP”) •Basic form of “fuel” in living things •Soluble and transported by body fluids to all cells, where is it METABOLIZED to release energy. ...
... respiration—must be converted into the form our cells can use (“ATP”) •Basic form of “fuel” in living things •Soluble and transported by body fluids to all cells, where is it METABOLIZED to release energy. ...
PP Ch_ 2-3 Modified - Maria Regina High School
... Enzymes are substrate specific (One enzyme for a particular reaction will not work with substrates from another particular reaction) Because of the specific fit, the ES Complex is called a LOCK AND KEY COMPLEX ...
... Enzymes are substrate specific (One enzyme for a particular reaction will not work with substrates from another particular reaction) Because of the specific fit, the ES Complex is called a LOCK AND KEY COMPLEX ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.