2.3 Carbon Compounds
... 1.Review- Name four groups of organic compounds found in living things Explain- Describe at least one function of each group of organic compounds Infer- Why are proteins considered polymers but lipids not ...
... 1.Review- Name four groups of organic compounds found in living things Explain- Describe at least one function of each group of organic compounds Infer- Why are proteins considered polymers but lipids not ...
2.3_Carbon_Compounds
... 1.Review- Name four groups of organic compounds found in living things Explain- Describe at least one function of each group of organic compounds Infer- Why are proteins considered polymers but lipids not ...
... 1.Review- Name four groups of organic compounds found in living things Explain- Describe at least one function of each group of organic compounds Infer- Why are proteins considered polymers but lipids not ...
Macromolecules Worksheet
... ____________________ 3. This is the name given to an amino acid added to a dipeptide. ____________________ 4. Of what kind of organic compound are oils, waxes, and fats an example? ____________________ 5. These are the individual subunits that make up DNA and RNA. ____________________ 6. What is a l ...
... ____________________ 3. This is the name given to an amino acid added to a dipeptide. ____________________ 4. Of what kind of organic compound are oils, waxes, and fats an example? ____________________ 5. These are the individual subunits that make up DNA and RNA. ____________________ 6. What is a l ...
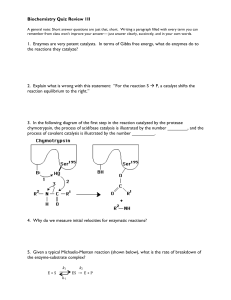
Biochemistry Quiz Review 1II 1. Enzymes are very potent catalysts
... 25. Describe the part of the glycolytic pathway from fructose 6-phosphate to glyceraldehyde 3phosphate. Show structures of intermediates, enzyme names, and indicate where any cofactors participate. ...
... 25. Describe the part of the glycolytic pathway from fructose 6-phosphate to glyceraldehyde 3phosphate. Show structures of intermediates, enzyme names, and indicate where any cofactors participate. ...
Molecules of Life
... Large stores in muscle and liver cells When blood sugar decreases, liver cells ...
... Large stores in muscle and liver cells When blood sugar decreases, liver cells ...
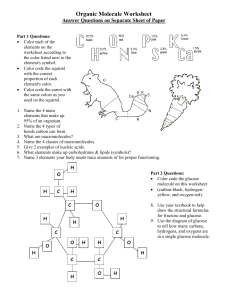
Organic Molecule Worksheet
... and box the carboxyl groups on the drawing to the right. 19. What subunits make up proteins? 20. Amino acids are linked together to make proteins by removing a molecule of ___ in a process called ___. 21. ___ bonds form when water is removed to hold ___ ___ together. ...
... and box the carboxyl groups on the drawing to the right. 19. What subunits make up proteins? 20. Amino acids are linked together to make proteins by removing a molecule of ___ in a process called ___. 21. ___ bonds form when water is removed to hold ___ ___ together. ...
Chapter 3 Review Guide
... C6H12O6 - others include those with 3-8 carbons - monosaccharides (monomers) are joined to make the large polymers Disaccharides - 2 sugars - Joining, for example, glucose, fructose, and galactose in any way. - Dehydration synthesis to make a disaccharide, hydrolysis to break it down - 3 common exam ...
... C6H12O6 - others include those with 3-8 carbons - monosaccharides (monomers) are joined to make the large polymers Disaccharides - 2 sugars - Joining, for example, glucose, fructose, and galactose in any way. - Dehydration synthesis to make a disaccharide, hydrolysis to break it down - 3 common exam ...
9AD Biomolecules
... chemical structures and functions. The building blocks of macromolecules are molecular monomers that include saccharides, fatty acids, amino acids, and nucleotides. Other macromolecules are ATP, hormones, and vitamins. 2. Carbohydrates are polysaccharides that store energy and provide structure for ...
... chemical structures and functions. The building blocks of macromolecules are molecular monomers that include saccharides, fatty acids, amino acids, and nucleotides. Other macromolecules are ATP, hormones, and vitamins. 2. Carbohydrates are polysaccharides that store energy and provide structure for ...
Chemistry of Life notes
... Hydrolysis: a chemical reaction that takes in water (H2O) to break apart polymers monomers - Requires the addition of ONE water molecule. - this same reaction will be used to break down carbs, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids - Hydrolysis is the exact reverse of dehydration synthesis shown above ...
... Hydrolysis: a chemical reaction that takes in water (H2O) to break apart polymers monomers - Requires the addition of ONE water molecule. - this same reaction will be used to break down carbs, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids - Hydrolysis is the exact reverse of dehydration synthesis shown above ...
Biochemistry - Bishop Ireton High School
... • Plants store their excess glucose as starch or cellulose. Cellulose is used to make cell walls. (we can’t digest cellulose) • Animals store their excess glucose as glycogen in the liver and muscle cells ...
... • Plants store their excess glucose as starch or cellulose. Cellulose is used to make cell walls. (we can’t digest cellulose) • Animals store their excess glucose as glycogen in the liver and muscle cells ...
Traffic Lights Biological Cpds
... forming microfibrils (being laid down in different directions). In chitin second carbon –OH groups are replaced by amino groups. 16. The elements which make up lipid molecules are carbon, hydrogen and oxygen plus phosphorus as phosphate in phospholipids. 17. The main types of lipids are described as ...
... forming microfibrils (being laid down in different directions). In chitin second carbon –OH groups are replaced by amino groups. 16. The elements which make up lipid molecules are carbon, hydrogen and oxygen plus phosphorus as phosphate in phospholipids. 17. The main types of lipids are described as ...
Biochemistry
... Unsaturated: at least 1 carbon to carbon bond Polyunsaturated: more than one carbon to carbon bond ...
... Unsaturated: at least 1 carbon to carbon bond Polyunsaturated: more than one carbon to carbon bond ...
Ch.2-3 & 3 Notes - Green Local Schools
... • Water must gain or lose a large amt. of E for its temp. to change • Helps cells maintain homeostasis ...
... • Water must gain or lose a large amt. of E for its temp. to change • Helps cells maintain homeostasis ...
Chapter 2 – Chemical Composition of the Body
... to ketone bodies. – Excess ketone bodies can lower blood pH.. ...
... to ketone bodies. – Excess ketone bodies can lower blood pH.. ...
LS ch 22 part 2 test - Saint Joseph High School
... a. nucleic acids c. proteins b. lipids d. carbohydrates __________2. To make a polymer, complex molecules are formed by joining together of a. macromolecules c. polymers b. micromolecules d. monomers __________3. Most substances in the human body are classified as organic compounds because they cont ...
... a. nucleic acids c. proteins b. lipids d. carbohydrates __________2. To make a polymer, complex molecules are formed by joining together of a. macromolecules c. polymers b. micromolecules d. monomers __________3. Most substances in the human body are classified as organic compounds because they cont ...
Name: :___________Date
... Name:_________________________Period:___________Date:______________ Google: “biology interactive” and choose: “life organization” and view animation. List the steps of organization in order from smallest to largest and an example of each. CELLS ALIVE ...
... Name:_________________________Period:___________Date:______________ Google: “biology interactive” and choose: “life organization” and view animation. List the steps of organization in order from smallest to largest and an example of each. CELLS ALIVE ...
What is Biochemistry ?
... • In 1955,Sanger for the determination of insulin sequence- won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1956 • In 1980, Sanger & Gilbert for first sequencing DNAwon the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1980 • In 1993, Kary B. Mullis for the invention of the PCR method -won the Nobel Prize in Chemis ...
... • In 1955,Sanger for the determination of insulin sequence- won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1956 • In 1980, Sanger & Gilbert for first sequencing DNAwon the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1980 • In 1993, Kary B. Mullis for the invention of the PCR method -won the Nobel Prize in Chemis ...
macromolecules new
... How many types of amino acids are there in living things? • There are about 20 common amino acids that can make literally thousands of proteins. ...
... How many types of amino acids are there in living things? • There are about 20 common amino acids that can make literally thousands of proteins. ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.