* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIOCHEMISTRY
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
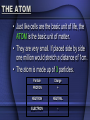
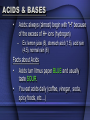
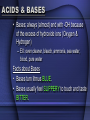
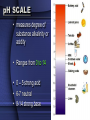
BIOCHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY OF LIFE • Elements: simplest form of a substance - cannot be broken down any further without changing what it is • Atom: the actual basic unit composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons THE ATOM • Just like cells are the basic unit of life, the ATOM is the basic unit of matter. • They are very small. If placed side by side one million would stretch a distance of 1cm. • The atom is made up of 3 particles. Particle Charge PROTON + NEUTRON NEUTRAL ELECTRON - • Electrons are not present within the atom, instead THEY REVOLVE AROUND THE NUCELUS OF THE ATOM & FORM THE ELECTRON CLOUD • Draw a helium atom. Indicate where the protons, neutrons and electrons are. NEUTRONS - ELECTRONS PROTONS + ATOMIC # = 2 (PROTONS) + - ATOMIC MASS = 4 (PROTONS & NEUTRONS) COMPOUNDS • a substance formed by the chemical combination of 2 or more elements in definite proportions – Ex: water, salt, glucose, carbon dioxide TWO TYPES OF COMPOUNDS • Organic - Contain C, H, and O in some ratio (usually referred to as chemicals of life) – • Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, Nucleic Acids Inorganic - usually "support" life - no specific ratio of C, H, and O – Water (H2O), Carbon Dioxide (CO2) CHEMICAL BONDS • Chemical bonds hold the atoms in a molecule together. • There are 2 types of chemical bonds IONIC and COVALENT MIXTURES • Water is not always pure. It is often found as part of a mixture. • A mixture is a material composed of TWO OR MORE ELEMENTS OR COMPOUNDS THAT ARE PHYSICALLY MIXED – Ex: salt & pepper mixed, sugar and sand – can be easily separated SOLUTION Two parts: • SOLUTE – SUBSTANCE THAT IS BEING DISSOLVED (SUGAR / SALT) • SOLVENT - the substance in which the solute dissolves • Materials that do not dissolve are known as SUSPENSIONS. – Blood is the most common example of a suspension. – Cells & other particles remain in suspension. ACIDS & BASES • Acids: always (almost) begin with "H" because of the excess of H+ ions (hydrogen) – Ex: lemon juice (6), stomach acid (1.5), acid rain (4.5), normal rain (6) Facts about Acids • Acids turn litmus paper BLUE and usually taste SOUR. • You eat acids daily (coffee, vinegar, soda, spicy foods, etc…) ACIDS & BASES • Bases: always (almost) end with -OH because of the excess of hydroxide ions (Oxygen & Hydrogen) – EX: oven cleaner, bleach, ammonia, sea water, blood, pure water Facts about Bases • Bases turn litmus BLUE. • Bases usually feel SLIPPERY to touch and taste BITTER. pH SCALE • measures degree of substance alkalinity or acidity • Ranges from 0 to 14 • 0 – 5 strong acid • 6-7 neutral • 8-14 strong base • The goal of the body is to maintain HOMEOSTASIS (neutrality) – to do this when pH is concerned, we add weak acids & bases to prevent sharp changes in pH. • These are called BUFFERS And now for the Biochemistry portion of things…. BIOCHEMISTRY is the chemistry of living organisms and of vital processes. CARBOHYDRATES • Living things use carbohydrates as a key source of ENERGY! • Plants use carbohydrates for structure (CELLULOSE) – include sugars and complex carbohydrates (starches) – contain the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (the hydrogen is in a 2:1 ratio to oxygen) Lipids (Fats) • Fats, oils, waxes, steroids • Chiefly function in energy storage, protection, and insulation • Contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen but the H:O is not in a 2:1 ratio • Tend to be large molecules -- an example of a neutral lipid is below • Neutral lipids are formed from the union of one glycerol molecule and 3 fatty acids • 3 fatty acids + glycerol ----> neutral fat (lipid) • Fats -- found chiefly in animals • Oils and waxes -- found chiefly in plants • Oils are liquid at room temperature, waxes are solids • Lipids along with proteins are key components of cell membranes • Steroids are special lipids used to build many reproductive hormones and cholesterol PROTEINS • contain the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen • composed of MANY amino acid subunits • It is the arrangement of the amino acid that forms the primary structure of proteins. • The basic amino acid form has a carboxyl group on one end, a methyl group that only has one hydrogen in the middle, and a amino group on the other end. • Attached to the methyl group is a R group. Major Protein Functions • • • Growth and repair Energy Buffer -- helps keep body pH constant