* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch.3 Review Using Vocabulary a) A monomer is a simpler, smaller
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
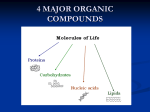
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Ch.3 Review Using Vocabulary 1. a) A monomer is a simpler, smaller molecule while a polymer is composed of monomers. b) A functional group is a cluster of atoms that influence the characteristics of the molecules they compose while macromolecules are large polymers. c) A monosaccharide is a monomer of a carbohydrate, or a simple sugar, while a disaccharide is a double sugar composed of two monosaccharides. d) Polypetides are very long chains of amino acids and proteins are composed of one or more polypeptides. e) A nucleic acid is a very large and complex organic molecule that stores and transfer important information in the cell; DNA and RNA are made p of thousands of linked monomers called nucleotides. 2. a) A triglyceride is composed of three molecules of fatty acid joined to one molecule of glycerol. b) Enzyme reactions depend on a physical fit between the enzyme molecule and its specific substrate, which is the reactant being catalyzed. 3. Monomers link to form polymers in a chemical reaction known as condensation reaction; polymers are broken down by water in a hydrolysis reaction. 4. An organic compound is made primarily of carbon atoms; most matter in living organisms that is not water is made of organic compounds. Understanding Key Concepts 5. Organic compounds are made primarily of carbon atoms while inorganic compound don’t contain carbon atoms. 6. A carbon atom has four electrons in its outermost energy level therefore it readily forms four covalent bonds with the atoms of other elements and it may also bond with itself which results in an enormous variety of organic compounds. 7. Functional groups influence the characteristics of the molecules they compose. 8. Organic compounds are built from smaller, simpler molecules called monomers that link to form polymers or macromolecules in a chemical reaction known as condensation reaction; polymers are broken down by using water in a hydrolysis reaction. 9. Life processes require a constant supply of energy which is available to cells in the form of certain compounds that store a large amount of energy, like adenosine triphosphate or ATP. 10. Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, and Nucleic Acids. 11. Carbohydrates are organic compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of one carbon atom to two hydrogen atoms to one oxygen atom. 12. Isomers are compounds with a single chemical formula but different structural forms. 13. Simple sugars, or monosaccharides, contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of 1:2:1 while a double sugar is a combination of two monosaccharides and a polysaccharide is a complex sugar molecule composed of three or more monosaccharides. 14. There are 20 different amino acids with a similar basic structure but different R groups which give the proteins very different shapes and allow them to carry out many different activities in living things. 15. An amino acid contains a central carbon atom covalently bonded to four other atoms or functional groups. A single hydrogen atom bonds at one site, a carboxyl group at a second site, an amino group at a third site, and a side chain called the R Group bonds at the fourth site. 16. Two amino acids bond to form a dipeptide in a condensation reaction while two monosaccharides combine in a condensation reaction to form a disaccharide. 17. In the induced fit model of enzyme action, the enzyme can attach only to a substrate (reactant) with a specific shape. The enzyme then changes and reduces the activation energy of the reaction so the reactants can become products. 18. Saturated triglycerides are composed of saturated fatty acids; they tend to be hard at room temperature, while unsaturated triglycerides are composed of unsaturated fatty acids and are usually soft or liquid at room temperature. 19. Triglycerides are composed of three molecules of fatty acid joined to one molecule of glycerol, phospholipids have two fatty acids attached to a molecule of glycerol and a phosphate group attached to the third carbon of the glycerol, and steroids are molecules composed of four fused carbon rings with various functional groups attached to them. 20. Steroids are composed of four fused carbon rings with various functional groups attached to them while other lipids are composed of different numbers of fatty acids joined to various functional groups. 21. Waxes are waterproof and they form a protective coating on the outer surfaces of plants and also form protective layers in animals; like ear wax in humans which prevents microorganisms from entering the ear canal. 22. DNA contains information that determines the characteristics of an organism and directs its cell activities while RNA stores and transfers information from DNA that is essential for the manufacturing of proteins. 23. A nucleotide is made of three main components: a phosphate group, a five-carbon sugar, and a ring-shaped nitrogenous base. 24. 25. C3H6O3 26. In a cellulose molecule, thousands of glucose monomers are linked in long, straight chains which tend to form hydrogen bonds with each other. Thus, its structure is strong and can only be broken down by hydrolysis under certain conditions. 27. The organic molecule is alanine, an amino acid composed of one carboxyl group, in green, an amino group, in yellow, and a side chain called the R Group in red. 28. This substance might be the polysaccharide made by plants and called cellulose which is rarely broken down by hydrolysis reactions. 29. We believe lipids would be best suited for the birds’ energy storage because they are the organic molecule that stores the most amount of energy.