* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biochemistry_2011
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
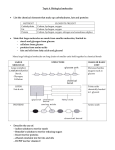
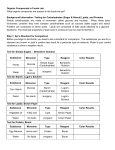
BIOCHEMISTRY Macromolecules - Only one type of element - Cannot be chemically separated - More than one type of element chemically bonded together - Can only be chemically separated into elements Glucose CO2 Fe Pb H2O H2 C6H12O6 ORGANIC COMPOUNDS • Compounds that contain carbon. • Usually associated with living (BIOTIC) things. C INORGANIC COMPOUNDS • Compounds that DO NOT contain carbon. • These are usually linked with non-living (ABIOTIC) things! C POLYMER • A giant molecule made of many smaller molecules (monomers) FOUR GROUPS that make up ALL LIVING THINGS: • Carbohydrates • Lipids • Proteins • Nucleic Acids (DNA and RNA) CARBOHYDRATES • Examples: Sugars, starches, cellulose (fiber) • FUNCTION: break down molecules to release energy & provide shape CARBOHYDRATES • Made up of : –Carbon –Hydrogen –Oxygen CARBOHYDRATES cont. Monomer 1. monosaccharide – single sugar molecules ex. glucose CARBOHYDRATES cont. Polymers Disaccharides – double sugar molecules ex. Fructose (fruit sugar) Polysaccharides – many sugar molecules ex: starch Disaccharide Monosaccharide Cellulose LIPIDS Elements: 1. Carbon 2. Hydrogen 3. Oxygen Monomer: Fatty acid, glycerol Polymer: 3 Fatty acids, 1 glycerol LIPIDS Examples: Fats, waxes, oils, phospholipids, steroids FUNCTION: • Fats & oils – long term energy storage ex: Whales & blubber • Insulate & repel water PROTEIN • Elements… 1. CARBON 2. HYDROGEN 3. OXYGEN 4. NITROGEN Example: Enzymes – proteins that speed up the rate of chemical reactions PROTEIN • Monomers = 1 amino acid • Polymers = made of many amino acids (20). Functions: • Build & repair tissue. • Movement • Structure • Transport • Defense • Regulation Protein NUCLEIC ACIDS • Monomer = nucleotides (a 5carbon sugar + a nitrogenous base + a phosphate group). • Polymer = many nucleotides • Elements = C, H, O, N & P Functions • Contain genetic information-DNA • Control the activities of cells. NUCLEIC ACIDS • Examples: – DNA (carries the instructions to control the activities of a cell) – RNA (carries the instructions to make proteins) Nucleotide Nucleic Acid Testing for Nutrients Benedict Test – a test for monosaccharides; simple sugars like glucose or fructose (fruit sugar). In contact with monosaccharides, the Benedict solution turns from blue to green/orange/red. Testing for Nutrients Benedict Test Testing for Nutrients Biuret Test – uses a solution of potassium hydroxide and copper sulfate to test for protein. The Biuret solution turns pink/purple when proteins are present. Testing for Nutrients Biuret Test Testing for Nutrients Iodine – can be used to test for starch, a polysaccharide (complex sugar). Iodine turns dark purple in the presence of starch. Testing for Nutrients Iodine Test No Starch Starch