AP Chem Test 5-7 Practice Exam - mvhs
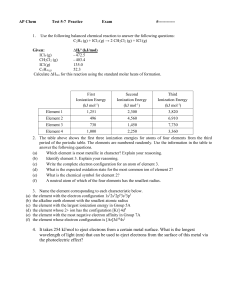
... 2. The ΔH for the exothermic solution process when solid sodium hydroxide dissolves in water is 44.4 kJ/mol. When a 13.9-g sample of NaOH dissolves in 250.0 g of water in a coffee-cup calorimeter, the temperature change is _______. Assume that the solution has the same specific heat as liquid water, ...
... 2. The ΔH for the exothermic solution process when solid sodium hydroxide dissolves in water is 44.4 kJ/mol. When a 13.9-g sample of NaOH dissolves in 250.0 g of water in a coffee-cup calorimeter, the temperature change is _______. Assume that the solution has the same specific heat as liquid water, ...
The History of the Atom Carousel Who-What-When
... ‘airs’ or gasses. In one of his experiments he isolated and ‘discovered’ a new gas – oxygen, in 1772. He visited Antoine Lavoisier in France and explained what he had done. Lavoisier was a noted scientist who used better methodology and measurements in his work. For Priestly’s ‘air’ he ‘invented’ th ...
... ‘airs’ or gasses. In one of his experiments he isolated and ‘discovered’ a new gas – oxygen, in 1772. He visited Antoine Lavoisier in France and explained what he had done. Lavoisier was a noted scientist who used better methodology and measurements in his work. For Priestly’s ‘air’ he ‘invented’ th ...
Biochemistry I (CHE 418 / 5418)
... energy levels as near as possible to the nucleus – Excited state when electrons is pushed into an orbit farther from the nucleus. • When electrons move from an excited state (higher energy level) to the ground state (lower energy level), the energy produced is given off often as light. • Worked well ...
... energy levels as near as possible to the nucleus – Excited state when electrons is pushed into an orbit farther from the nucleus. • When electrons move from an excited state (higher energy level) to the ground state (lower energy level), the energy produced is given off often as light. • Worked well ...
Chapter 5 - Effingham County Schools
... Electrons move around the _________ of the nucleus. Atoms are extremely small. Over a million can fit in the period at the end of this sentence. The identity of an atom is determined by the number of protons in its nucleus, called the ________ ________. For example, a hydrogen atom has 1 proton so i ...
... Electrons move around the _________ of the nucleus. Atoms are extremely small. Over a million can fit in the period at the end of this sentence. The identity of an atom is determined by the number of protons in its nucleus, called the ________ ________. For example, a hydrogen atom has 1 proton so i ...
HONORS CHEMISTRY Quarter 2 Exam Topics Know the following
... o Democritus, Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Chadwick, Bohr, Schrodinger, Heisenberg Know experimental observations and their key contributions to the atomic theory. Be able to draw and label the model of the atom for each scientist mentioned above. Know Dalton’s postulates. Distinguish atoms ba ...
... o Democritus, Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Chadwick, Bohr, Schrodinger, Heisenberg Know experimental observations and their key contributions to the atomic theory. Be able to draw and label the model of the atom for each scientist mentioned above. Know Dalton’s postulates. Distinguish atoms ba ...
Physical Science Notes–Ch. 17-Glencoe
... From this information, he was able to ____________________________________________ of new elements that had not yet been discovered. ...
... From this information, he was able to ____________________________________________ of new elements that had not yet been discovered. ...
Periodic Trends
... Atomic Radius • As the number of protons increases the pull on the electrons increase, which decreases the size of the atom. • As the number of shells increase, the size of the atom increases ...
... Atomic Radius • As the number of protons increases the pull on the electrons increase, which decreases the size of the atom. • As the number of shells increase, the size of the atom increases ...
Atoms and Their Electrons
... number of protons and the neutrons of an atom together. An element must have a certain number of protons but it can have a range of numbers of neutrons i.e. hydrogen can have 0, 1, or 2 neutrons to go with its 1 proton. These are called isotopes of hydrogen In real life there may be a number of diff ...
... number of protons and the neutrons of an atom together. An element must have a certain number of protons but it can have a range of numbers of neutrons i.e. hydrogen can have 0, 1, or 2 neutrons to go with its 1 proton. These are called isotopes of hydrogen In real life there may be a number of diff ...
Vocabulary for Periodic Table
... 6) Atomic mass number: the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus. 7) Isotope: atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons. 8) Ion: when an atom loses or gains electrons. 9) Atomic mass: the average mass of the atoms in an element. 10) Periodic Table: a tabl ...
... 6) Atomic mass number: the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus. 7) Isotope: atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons. 8) Ion: when an atom loses or gains electrons. 9) Atomic mass: the average mass of the atoms in an element. 10) Periodic Table: a tabl ...
Homework – Atoms Instructions
... poster about. Your poster should include the following: The name of your element and its symbol; The number of each subatomic particle (protons, electrons and neutrons); A large atomic structure diagram showing one atom of your element (use the rules below to help you to draw this); The electron con ...
... poster about. Your poster should include the following: The name of your element and its symbol; The number of each subatomic particle (protons, electrons and neutrons); A large atomic structure diagram showing one atom of your element (use the rules below to help you to draw this); The electron con ...
Keypoints of Basic Atomic Structure
... Atomic Number Atomic Radius Electrons Element Isotope Neutrons Periodic Table Protons Subatomic Particles Concepts 1. Be able to describe how protons, neutrons and electrons are arranged in an atom. 2. Be able to list the charges on the subatomic particles that make up and atom, and giv ...
... Atomic Number Atomic Radius Electrons Element Isotope Neutrons Periodic Table Protons Subatomic Particles Concepts 1. Be able to describe how protons, neutrons and electrons are arranged in an atom. 2. Be able to list the charges on the subatomic particles that make up and atom, and giv ...
levels of organization and the atom
... unable to cut”. It has two areas: a nucleus and an electron cloud. It contains subatomic particles that are even smaller. ...
... unable to cut”. It has two areas: a nucleus and an electron cloud. It contains subatomic particles that are even smaller. ...
C1.1 The fundamental ideas in chemistry
... oxygen. Candidates are not required to know of trends within each group in the periodic table, but should be aware of similarities between the elements within a group. The elements in Group 0 of the periodic table are called the noble gases. They are unreactive because their atoms have stable arrang ...
... oxygen. Candidates are not required to know of trends within each group in the periodic table, but should be aware of similarities between the elements within a group. The elements in Group 0 of the periodic table are called the noble gases. They are unreactive because their atoms have stable arrang ...
Chemistry I Lecture Notes – Atomic Structure
... Atoms of different elements can combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. Atoms are simply just rearranged in chemical reactions. Law of Definite Proportions Atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. Law of Multiple Proportions Atoms of the same two (or mo ...
... Atoms of different elements can combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. Atoms are simply just rearranged in chemical reactions. Law of Definite Proportions Atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. Law of Multiple Proportions Atoms of the same two (or mo ...
Atoms - Science with Mrs. Schulte
... Atomic mass The average mass of all the isotopes (different types) of an element ...
... Atomic mass The average mass of all the isotopes (different types) of an element ...
Chapter 3 Chemical Foundations
... Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Nucleus atomic number (Z) = mass number (A) = element symbol (X) = Note: mass number= Therefore …. mass number = ……. A= Z + number of neutrons ….. Number of neutrons = A-Z Note: For any given element on the periodic table: Number of protons = In order to symbolically ...
... Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Nucleus atomic number (Z) = mass number (A) = element symbol (X) = Note: mass number= Therefore …. mass number = ……. A= Z + number of neutrons ….. Number of neutrons = A-Z Note: For any given element on the periodic table: Number of protons = In order to symbolically ...
Science Outline - cloudfront.net
... EX: All Hydrogen has 1 proton in its nucleus. Therefore, its atomic number is always 1. How many protons does an element with an atomic number of 94 have? What is this element? Most matter contains only a few kinds of elements o Ex: hamburgers, gasoline and paper are all made up of: __________ ...
... EX: All Hydrogen has 1 proton in its nucleus. Therefore, its atomic number is always 1. How many protons does an element with an atomic number of 94 have? What is this element? Most matter contains only a few kinds of elements o Ex: hamburgers, gasoline and paper are all made up of: __________ ...
Ch. 18 Notes Atoms and Elements
... electrons occupy 8eThe electron cloud is Up to 18esubdivided into smaller ...
... electrons occupy 8eThe electron cloud is Up to 18esubdivided into smaller ...
Name: Chapter 4 and 5 Study Guide Who was the Greek
... 3. If 2 grams of element X combine with 5 grams of element Y to form a compound, how many grams of element X will react with 15 grams of element Y? ...
... 3. If 2 grams of element X combine with 5 grams of element Y to form a compound, how many grams of element X will react with 15 grams of element Y? ...
Extra Credit Test Review
... 29. How is the bonding of Cl2 different from the bonding in NaCl? Cl2 is a diatomic / covalent bond whereas NaCl is an ionic bond 30. Explain how Helium can be in Group 18, but doesn’t have 8 valence electrons? Helium only has 2 electrons, so they will fill up the first energy level/shell and theref ...
... 29. How is the bonding of Cl2 different from the bonding in NaCl? Cl2 is a diatomic / covalent bond whereas NaCl is an ionic bond 30. Explain how Helium can be in Group 18, but doesn’t have 8 valence electrons? Helium only has 2 electrons, so they will fill up the first energy level/shell and theref ...