Introduction to the Periodic Table
... The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. ...
... The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. ...
Chapter 5
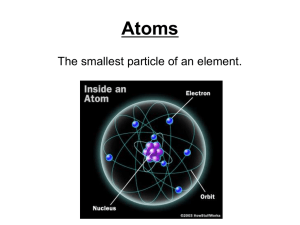
... nucleus, but is still mostly empty. •Electrons are in the cloud but can not be pinpointed at an exact time because they move so quickly. ...
... nucleus, but is still mostly empty. •Electrons are in the cloud but can not be pinpointed at an exact time because they move so quickly. ...
File
... Periodic table: A chart in which elements are arranged by increasing atomic number and by changes in physical and chemical properties. atom: The smallest particles that make up matter. proton: a subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is located in the nucleus of an atom. (The number ...
... Periodic table: A chart in which elements are arranged by increasing atomic number and by changes in physical and chemical properties. atom: The smallest particles that make up matter. proton: a subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is located in the nucleus of an atom. (The number ...
L.O.
... I have some understanding but I need to revise this some more I don’t know this or I need help because I don’t understand it ...
... I have some understanding but I need to revise this some more I don’t know this or I need help because I don’t understand it ...
Chapter 6 Vocabulary crossword puzzle
... 3. Elements in which the highest occupied s and p sublevels are partially filled 6. Measures the ability of an atom to attract electrons when the atom is in a compound; the element named Cesium has the lowest amount, while the element named Fluorine has the highest amount 7. Term that refers to a se ...
... 3. Elements in which the highest occupied s and p sublevels are partially filled 6. Measures the ability of an atom to attract electrons when the atom is in a compound; the element named Cesium has the lowest amount, while the element named Fluorine has the highest amount 7. Term that refers to a se ...
IPC Atoms and Periodic Table
... start with actinium (Ac) at atomic number 89 and finishing up with lawrencium (Lr) at number 103. • They are all radioactive and some are not found in nature. ...
... start with actinium (Ac) at atomic number 89 and finishing up with lawrencium (Lr) at number 103. • They are all radioactive and some are not found in nature. ...
CHEMISTRY TERMS Period: Elements in the same horizontal row
... Period: Elements in the same horizontal row with the same ground state energy level. Periodic Law: Elements list in order of their atomic numbers that fall into reoccurring groups. Ionic Radius: the radius of an atom’s ion, measured by the distance between ions in a crystal lattice. Atomic Radius: o ...
... Period: Elements in the same horizontal row with the same ground state energy level. Periodic Law: Elements list in order of their atomic numbers that fall into reoccurring groups. Ionic Radius: the radius of an atom’s ion, measured by the distance between ions in a crystal lattice. Atomic Radius: o ...
Chapter 6 Review“The Periodic Table”
... Review“The Periodic Table” 1. How is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom calculated? 2. All atoms are neutral, with the number of protons equaling the ___. 3. Isotopes of the same element have different _____. 4. Using the periodic table, determine the number of neutrons in 16O. 5. What ...
... Review“The Periodic Table” 1. How is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom calculated? 2. All atoms are neutral, with the number of protons equaling the ___. 3. Isotopes of the same element have different _____. 4. Using the periodic table, determine the number of neutrons in 16O. 5. What ...
Elements and Atoms - Portola Middle School
... neutron or proton. Protons should have a + or P written on them. Neutrons should be blank or have an N. In a circle around the nucleus are the electrons. Electrons should have a minus sign or an e. ...
... neutron or proton. Protons should have a + or P written on them. Neutrons should be blank or have an N. In a circle around the nucleus are the electrons. Electrons should have a minus sign or an e. ...
C2- Topic 1: Atomic structure and the periodic table. Assessable
... Describe the arrangement of elements in the periodic table such that: - elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, in rows called periods - elements with similar properties are placed in the same vertical column, called groups ...
... Describe the arrangement of elements in the periodic table such that: - elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, in rows called periods - elements with similar properties are placed in the same vertical column, called groups ...
C2 Topic 1 Can Do Sheet
... 1.9 Describe the arrangement of elements in the periodic table such that: a elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, in rows called periods b elements with similar properties are placed in the same vertical column called groups 1.10 Demonstrate an understanding that the existence ...
... 1.9 Describe the arrangement of elements in the periodic table such that: a elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, in rows called periods b elements with similar properties are placed in the same vertical column called groups 1.10 Demonstrate an understanding that the existence ...
Chemical Basis of Life
... Title: The Chemical Basis of Life 1- Introduction: Your body is an elaborate chemical system. Chemical reactions power all of the body’s activities. At the most basic level, life is about chemicals and how they interact with each other. 2- Matter – Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space ...
... Title: The Chemical Basis of Life 1- Introduction: Your body is an elaborate chemical system. Chemical reactions power all of the body’s activities. At the most basic level, life is about chemicals and how they interact with each other. 2- Matter – Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space ...
8.5C Vocabulary
... The columns on a Periodic Table that arrange the elements by the number of electrons that are in the outermost shell (valence electrons) A specific area where electrons (e-) of the same energy level are found Either filled or partially filled last energy level of an atom that determine the chemical ...
... The columns on a Periodic Table that arrange the elements by the number of electrons that are in the outermost shell (valence electrons) A specific area where electrons (e-) of the same energy level are found Either filled or partially filled last energy level of an atom that determine the chemical ...