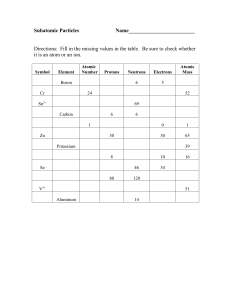
8.P.1.1 Warm-Up Questions for Website
... B.It can be formed through a physical reaction. C.It can be changed into simpler substances through a physical change. D.It is a pure substance containing elements that are chemically combined. ...
... B.It can be formed through a physical reaction. C.It can be changed into simpler substances through a physical change. D.It is a pure substance containing elements that are chemically combined. ...
Chemistry Review: Antoine Lavoisier (1743
... the same number of electrons, their chemical properties will be exactly the same. However, they have different masses due to the different number of neutrons; therefore, they will have slightly different properties that relate to mass. (Ex. Density , melting and boiling point). Also. Since the neutr ...
... the same number of electrons, their chemical properties will be exactly the same. However, they have different masses due to the different number of neutrons; therefore, they will have slightly different properties that relate to mass. (Ex. Density , melting and boiling point). Also. Since the neutr ...
Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry OEQs
... Which rule for “seating” electrons in their orbitals does this notation violate and why? What would happen if the orbital notation had the incorrect number of arrows/symbols? Nuclear energy is both beneficial and potentially harmful to our lives. Give an example of how nuclear energy can be bo ...
... Which rule for “seating” electrons in their orbitals does this notation violate and why? What would happen if the orbital notation had the incorrect number of arrows/symbols? Nuclear energy is both beneficial and potentially harmful to our lives. Give an example of how nuclear energy can be bo ...
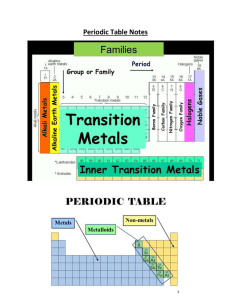
Review for Periodic - Mr-Durands
... 1. Find Scandium (Sc) on the table what is the atomic number? 2. What is the atomic mass of Chromium (Cr)? 3. What is the number of neutrons for Cesium (Cs)? 4. What is the difference between atomic mass and number? 5. How do isotopes affect the atomic mass of an element? 6. What is a group on the p ...
... 1. Find Scandium (Sc) on the table what is the atomic number? 2. What is the atomic mass of Chromium (Cr)? 3. What is the number of neutrons for Cesium (Cs)? 4. What is the difference between atomic mass and number? 5. How do isotopes affect the atomic mass of an element? 6. What is a group on the p ...
Summative Assessment Study Guide Name: Due date: SPS1
... SPS3. Students will distinguish the characteristics and components of radioactivity. a. Differentiate among alpha and beta particles and gamma radiation. b. Differentiate between fission and fusion. c. Explain the process half-life as related to radioactive decay. d. Describe nuclear energy, its pra ...
... SPS3. Students will distinguish the characteristics and components of radioactivity. a. Differentiate among alpha and beta particles and gamma radiation. b. Differentiate between fission and fusion. c. Explain the process half-life as related to radioactive decay. d. Describe nuclear energy, its pra ...
Page 233 - ClassZone
... the world differed because each was made of atoms of different sizes and shapes. How does the modern view of atoms differ from this ancient view? How is it similar? ...
... the world differed because each was made of atoms of different sizes and shapes. How does the modern view of atoms differ from this ancient view? How is it similar? ...
Properties of matter student notes[1]
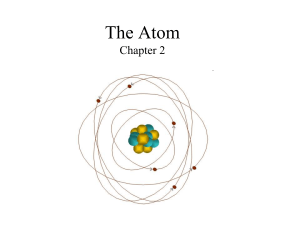
... Nucleus = Positively charged _________________________of an atom Protons = _______________________ charged particles in the nucleus Neutrons = _____________________ particles in the nucleus ...
... Nucleus = Positively charged _________________________of an atom Protons = _______________________ charged particles in the nucleus Neutrons = _____________________ particles in the nucleus ...
Chapter 7 Review Sheet
... 5. It would require more energy to remove an electron from Az than from any other element. 6. Jq has one more valence electron than Dw but one less valence electron than Gt. 7. The sizes of the 3 isoelectronic species are: Cx+ < Hs < By–. 8. Ev and Kp both lose the same number of electrons when they ...
... 5. It would require more energy to remove an electron from Az than from any other element. 6. Jq has one more valence electron than Dw but one less valence electron than Gt. 7. The sizes of the 3 isoelectronic species are: Cx+ < Hs < By–. 8. Ev and Kp both lose the same number of electrons when they ...
Chapter 3: The Structure of Matter
... •Rows in the periodic table are called periods •There are 18 groups/families and 7 periods on the period ...
... •Rows in the periodic table are called periods •There are 18 groups/families and 7 periods on the period ...
File
... • Mixture-a combination of substances that occurs without any chemical reaction. Substances in the mixture retain their own properties and may be physically separated from one another. • Molecule-a chemically bonded cluster of atoms. • Periodic Table of Elements-originally developed by Dimitri Mend ...
... • Mixture-a combination of substances that occurs without any chemical reaction. Substances in the mixture retain their own properties and may be physically separated from one another. • Molecule-a chemically bonded cluster of atoms. • Periodic Table of Elements-originally developed by Dimitri Mend ...
Chap 7: Around the Room Review
... 1. The central part of an atom is called the _____ 2. A proton has a _____ charge. 3. The atomic number tells us __________. 4. Nitrogen’s atomic number is 7. An isotope of nitrogen containing 7 neutrons would be nitrogen_____. 5. How does the size of a negative ion compare to the size of the atom t ...
... 1. The central part of an atom is called the _____ 2. A proton has a _____ charge. 3. The atomic number tells us __________. 4. Nitrogen’s atomic number is 7. An isotope of nitrogen containing 7 neutrons would be nitrogen_____. 5. How does the size of a negative ion compare to the size of the atom t ...
Period Table, valence Electrons and Ion Notes
... Example: Na = 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 Add up the e-‘s found in the last energy level, in this case there is only 1 so Na has 1 valence e**You have to do this for the Transition metal every time** ...
... Example: Na = 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 Add up the e-‘s found in the last energy level, in this case there is only 1 so Na has 1 valence e**You have to do this for the Transition metal every time** ...
Test 2 Review Test 2 Review (15-16)_2
... (18) ____________ How many of these elements are gases at 0 degrees Celsius? (19) ____________ How many of these elements are metalloids? (20) ____________ How many of these elements are NON-metals and solids? (21) ____________ Write the symbol of the element that would have the most similar propert ...
... (18) ____________ How many of these elements are gases at 0 degrees Celsius? (19) ____________ How many of these elements are metalloids? (20) ____________ How many of these elements are NON-metals and solids? (21) ____________ Write the symbol of the element that would have the most similar propert ...
Chemistry Notes
... sodium, magnesium, aluminum, silicon, phosphorous, sulfur, chlorine, argon, potassium, calcium, iron, copper, zinc, bromine, silver, iodine, gold, lead, mercury, radon. Day 3 99% of the atoms mass in the nucleus The energy of the atom in the electron shells Most of an atom empty space ...
... sodium, magnesium, aluminum, silicon, phosphorous, sulfur, chlorine, argon, potassium, calcium, iron, copper, zinc, bromine, silver, iodine, gold, lead, mercury, radon. Day 3 99% of the atoms mass in the nucleus The energy of the atom in the electron shells Most of an atom empty space ...
Periodic Table Vocabulary Periodic Table – a chart that organizes
... nonmetal. Inert – elements and/or compounds that when put together are unable to react chemically. The Law of Conservation of Matter – a scientific law that states that during a chemical reaction, matter cannot be created or destroyed but can be changed into a different form. Period law- The chemica ...
... nonmetal. Inert – elements and/or compounds that when put together are unable to react chemically. The Law of Conservation of Matter – a scientific law that states that during a chemical reaction, matter cannot be created or destroyed but can be changed into a different form. Period law- The chemica ...
Thursday, October 31, 2013 D-day
... • Radioactive Elements- no naturally occurring stable isotope (what is an isotope?). – These elements loose neutrons and protons and emit them as particles. – All manmade elements are radioactive. ...
... • Radioactive Elements- no naturally occurring stable isotope (what is an isotope?). – These elements loose neutrons and protons and emit them as particles. – All manmade elements are radioactive. ...
Chapter 4 Study Guide Physical Science 1. The word atom comes
... 4. Carbon is found in group ______ of the periodic table. 5. Bohr’s model of the atom compares electrons to ____________________. 6. Elements that are found on the “stair case” are known as ___________. 7. The order of elements in the periodic table is based on the number of ____________________ in ...
... 4. Carbon is found in group ______ of the periodic table. 5. Bohr’s model of the atom compares electrons to ____________________. 6. Elements that are found on the “stair case” are known as ___________. 7. The order of elements in the periodic table is based on the number of ____________________ in ...





![Properties of matter student notes[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009076956_1-3293fc3fecf578fd34e3f0f2700d471f-300x300.png)