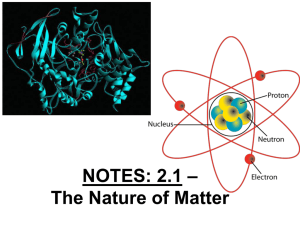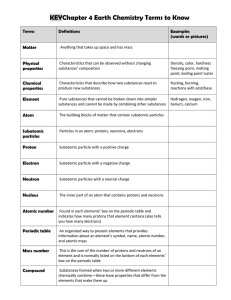
Notes
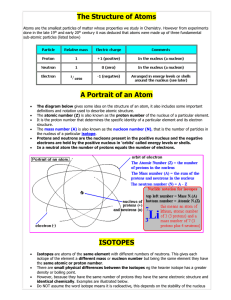
... -the number of protons in an atom of an element •all atoms of an element have the same atomic # •written as a subscript next to the element’s symbol •in a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons (balanced charges). ...
... -the number of protons in an atom of an element •all atoms of an element have the same atomic # •written as a subscript next to the element’s symbol •in a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons (balanced charges). ...
Intro to Element Note Answers
... Alchemists were early chemists whose mean focus was … to turn Pb to Au (change one element into another) Elements are … the building blocks of matter, basic substances that can’t be broken down by ordinary chemical changes ...
... Alchemists were early chemists whose mean focus was … to turn Pb to Au (change one element into another) Elements are … the building blocks of matter, basic substances that can’t be broken down by ordinary chemical changes ...
Elements and Atoms
... More about Elements.. • Elements are the building blocks of all matter. • The periodic table is a list of all of the elements that can build matter. It’s a little like the alphabet of chemistry. • The periodic table tells us several things… ...
... More about Elements.. • Elements are the building blocks of all matter. • The periodic table is a list of all of the elements that can build matter. It’s a little like the alphabet of chemistry. • The periodic table tells us several things… ...
Atoms and Molecules
... and real magic tricks is that in a science magic trick we tell you how we did it • It looks like magic at first, but then you realize there really is no trick. Once you know how it’s done, you can do it too ...
... and real magic tricks is that in a science magic trick we tell you how we did it • It looks like magic at first, but then you realize there really is no trick. Once you know how it’s done, you can do it too ...
VOCABULARY name, date, hour: Fill in the number of each term
... Fill in the number of each term next to its closest definition. ___ positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom ___ stable, orbiting particle of an atom with a negative charge ___ substance that is a mixture of two or more metals ___ columns of the periodic table; also known as group ...
... Fill in the number of each term next to its closest definition. ___ positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom ___ stable, orbiting particle of an atom with a negative charge ___ substance that is a mixture of two or more metals ___ columns of the periodic table; also known as group ...
Chapter 1 D Study Guide
... 1. Charges: protons = positive, electrons = negative, neutrons = non 2. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom. 3. Electrons move around the nucleus in electron rings or shells or energy levels. 4. Atomic number is equal to the number of protons, and is unique to each element 5. Th ...
... 1. Charges: protons = positive, electrons = negative, neutrons = non 2. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom. 3. Electrons move around the nucleus in electron rings or shells or energy levels. 4. Atomic number is equal to the number of protons, and is unique to each element 5. Th ...
Elements Unit Test
... 9. A Dutch scientist by the name of Neils Bohr was the first scientist to figure out that electrons that orbit the nucleus of an atom (sometimes called shells) can only hold a certain number of electrons. Which of the following sets of numbers describe the number of electrons in the first three shel ...
... 9. A Dutch scientist by the name of Neils Bohr was the first scientist to figure out that electrons that orbit the nucleus of an atom (sometimes called shells) can only hold a certain number of electrons. Which of the following sets of numbers describe the number of electrons in the first three shel ...
atoms - Trinity Regional School
... atoms. is anything that has a mass and a volume all matter has a specific density or arrangement of atoms that can be used to identify it. ...
... atoms. is anything that has a mass and a volume all matter has a specific density or arrangement of atoms that can be used to identify it. ...
Atom The smallest piece of matter that still has the properties of the
... A table of the chemical elements arranged in order of atomic number, usually in rows, so that elements with similar atomic structure and similar chemical properties appear in vertical columns. ...
... A table of the chemical elements arranged in order of atomic number, usually in rows, so that elements with similar atomic structure and similar chemical properties appear in vertical columns. ...
atomic structure - IGCSE STUDY BANK
... There are small physical differences between the isotopes eg the heavier isotope has a greater density or boiling point. However, because they have the same number of protons they have the same electronic structure and identical chemically. Examples are illustrated below. Do NOT assume the word isot ...
... There are small physical differences between the isotopes eg the heavier isotope has a greater density or boiling point. However, because they have the same number of protons they have the same electronic structure and identical chemically. Examples are illustrated below. Do NOT assume the word isot ...
RAD 354 Chapt 3 Structure of Matter
... Nuclear model of the atom • 1911 Ernest Rutherford introduced the nuclear model of the atom • 1913 Niels Bohr improved on Rutherford’s • The “mini solar system” model is now know as the Rutherford – Bohr model of the atom ...
... Nuclear model of the atom • 1911 Ernest Rutherford introduced the nuclear model of the atom • 1913 Niels Bohr improved on Rutherford’s • The “mini solar system” model is now know as the Rutherford – Bohr model of the atom ...
introductory chemistry
... Elements are substances that contain only one type of atom. Hydrogen gas is an element as it contains only hydrogen atoms. Compounds contain the atoms of two or more different elements joined together. Water is a compound that consists of hydrogen and oxygen atoms joined together. There are nearly 1 ...
... Elements are substances that contain only one type of atom. Hydrogen gas is an element as it contains only hydrogen atoms. Compounds contain the atoms of two or more different elements joined together. Water is a compound that consists of hydrogen and oxygen atoms joined together. There are nearly 1 ...
Learning Objectives
... of atomic structure. 4. Distinguish between each of the following pairs of terms: a. neutron and proton b. atomic number and mass number c. atomic weight and mass number 5. Explain how the atomic number and mass number of an atom can be used to determine the number of neutrons. 6. Explain how two is ...
... of atomic structure. 4. Distinguish between each of the following pairs of terms: a. neutron and proton b. atomic number and mass number c. atomic weight and mass number 5. Explain how the atomic number and mass number of an atom can be used to determine the number of neutrons. 6. Explain how two is ...
File
... Substances formed when two or more different elements chemically combine—these have properties that differ from the elements that make them up ...
... Substances formed when two or more different elements chemically combine—these have properties that differ from the elements that make them up ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808) (Listed on p 203) 1. Elements are composed of extremely small particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass and chemical properties. 3. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other elements. 4. C ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808) (Listed on p 203) 1. Elements are composed of extremely small particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass and chemical properties. 3. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other elements. 4. C ...
Chapter 2
... • May use latin root of element – higher charge ends in –ic, lower charge in –ous • Polyation ions named as is – change nothing • If covalent compound (2 nonmetals) – need to use prefixes. ...
... • May use latin root of element – higher charge ends in –ic, lower charge in –ous • Polyation ions named as is – change nothing • If covalent compound (2 nonmetals) – need to use prefixes. ...
CH.2
... differentiate between alpha, beta, and gamma radiation with respect to penetrating power, shielding, and composition. (B2) differentiate between the major atom components (proton, neutron and electron) in terms of location, size, and charge. (B2) distinguish between a group and a period. (B2) ...
... differentiate between alpha, beta, and gamma radiation with respect to penetrating power, shielding, and composition. (B2) differentiate between the major atom components (proton, neutron and electron) in terms of location, size, and charge. (B2) distinguish between a group and a period. (B2) ...
Periodic Table Review Key
... 1. Which element has the smallest atomic number? F 2. Which element has the largest atomic number? H 3. Which non-metal has the smallest atomic mass? F 4. Which metal has the largest atomic mass? D 5. Which elements are considered good conductors? C,E,D, 6. Which element is considered semi-conductor ...
... 1. Which element has the smallest atomic number? F 2. Which element has the largest atomic number? H 3. Which non-metal has the smallest atomic mass? F 4. Which metal has the largest atomic mass? D 5. Which elements are considered good conductors? C,E,D, 6. Which element is considered semi-conductor ...
What is Matter? Anything that can be smelled, tasted, touched… Has
... Organized horizontally Indicates # of electron levels of elements Organized vertically Indicates # of electrons in outer cloud (# of P+) (Often from Latin or Greek) (1st letter is upper case, 2nd is lower case) ...
... Organized horizontally Indicates # of electron levels of elements Organized vertically Indicates # of electrons in outer cloud (# of P+) (Often from Latin or Greek) (1st letter is upper case, 2nd is lower case) ...
Name Period _____ Chemistry Review
... ____ 16. A(n) mixture is made of two or more substances—elements, compounds, or both—that are together in the same place but are not chemically combined. _________________________ ____ 32. The elements in a group of the periodic table have similar characteristics. _________________________ ...
... ____ 16. A(n) mixture is made of two or more substances—elements, compounds, or both—that are together in the same place but are not chemically combined. _________________________ ____ 32. The elements in a group of the periodic table have similar characteristics. _________________________ ...
Atom - Sites
... •All compounds are molecules but not all molecules are compounds. (ex. H2O vs. O2) •Molecules can also join together to form larger molecules. •Many, many repeating small molecules joined together form a polymer. http://pslc.ws/macrog/kidsmac/basics.htm ...
... •All compounds are molecules but not all molecules are compounds. (ex. H2O vs. O2) •Molecules can also join together to form larger molecules. •Many, many repeating small molecules joined together form a polymer. http://pslc.ws/macrog/kidsmac/basics.htm ...