Periodic Table
... • Elements in the same group exhibit similar chemical characteristics due to the fact that they all have the same number of __________ . • The most stable number of valence electrons is __________ • This is called an __________ ...
... • Elements in the same group exhibit similar chemical characteristics due to the fact that they all have the same number of __________ . • The most stable number of valence electrons is __________ • This is called an __________ ...
Matter and the Periodic Table
... system of rows and columns on the basis of increasing mass and similar chemical and physical properties. Since the organization exhibited a periodic repetition of similar properties, it became known as the Periodic Table of the Elements. It has become one of modern chemistry's ...
... system of rows and columns on the basis of increasing mass and similar chemical and physical properties. Since the organization exhibited a periodic repetition of similar properties, it became known as the Periodic Table of the Elements. It has become one of modern chemistry's ...
atoms, molecules, and matter (2)
... ELEMENTS – Greek theory of physical world. All earthly objects are a mixture of: 1. EARTH (bottom – center of universe) 2. WATER (water covers earth) 3. AIR (air over water) 4. FIRE (highest – at top) 5. Ether = QUINTESSENCE (Latin) – substance whose natural motion is that most symmetrical and etern ...
... ELEMENTS – Greek theory of physical world. All earthly objects are a mixture of: 1. EARTH (bottom – center of universe) 2. WATER (water covers earth) 3. AIR (air over water) 4. FIRE (highest – at top) 5. Ether = QUINTESSENCE (Latin) – substance whose natural motion is that most symmetrical and etern ...
Comprehensive Science 3 Module 4 Practice Test
... Different elements are made up of different atoms Atoms of different elements combine to make different compounds 5. The elements listed at the far right side of the periodic table are _______. Metalloids Nonmetals Metals Transitional Metals ...
... Different elements are made up of different atoms Atoms of different elements combine to make different compounds 5. The elements listed at the far right side of the periodic table are _______. Metalloids Nonmetals Metals Transitional Metals ...
document
... Alkaline Earth Metals – (Group 2) shiny, ductile and malleable; combine readily with other elements Transition Elements – (Group 3 – 12) most familiar metals because they often occur in nature uncombined Inner Transition Metals – (listed below table) Lanthanide Series – elements with atomic # 58 – ...
... Alkaline Earth Metals – (Group 2) shiny, ductile and malleable; combine readily with other elements Transition Elements – (Group 3 – 12) most familiar metals because they often occur in nature uncombined Inner Transition Metals – (listed below table) Lanthanide Series – elements with atomic # 58 – ...
Chemistry Notes
... Periodic Table 1 • One of a class of substances that cannot be separated into simpler substances by chemical means (Sulfur, Platinum, Iodine) ...
... Periodic Table 1 • One of a class of substances that cannot be separated into simpler substances by chemical means (Sulfur, Platinum, Iodine) ...
Topic 4: Classifying Elements What did the early chemists use to
... • NH3(g) à nitrogen trihydride or ammonia • CH4(g) à carbon tetrahydride or methane • H2O2(l) à dihydrogen monoxide or water A MOLECULAR COMPOUND can contain what two combinations of elements? Non-‐metal + ...
... • NH3(g) à nitrogen trihydride or ammonia • CH4(g) à carbon tetrahydride or methane • H2O2(l) à dihydrogen monoxide or water A MOLECULAR COMPOUND can contain what two combinations of elements? Non-‐metal + ...
Intro to Atoms - Freehold Borough Schools
... Matter: anything that has mass and takes up space. Mass: measurement of how much matter is in an object Element: a substance that cannot be broken down into any other substances by chemical or physical means Compound: a substance of 2 or more elements Mixture: 2 or more substances that are mixed tog ...
... Matter: anything that has mass and takes up space. Mass: measurement of how much matter is in an object Element: a substance that cannot be broken down into any other substances by chemical or physical means Compound: a substance of 2 or more elements Mixture: 2 or more substances that are mixed tog ...
Atoms, Elements, Compounds File
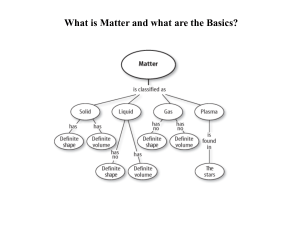
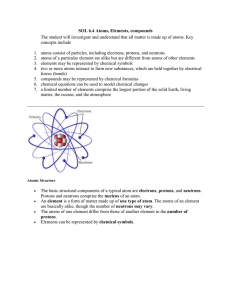
... SOL 6.4 Atoms, Elements, compounds The student will investigate and understand that all matter is made up of atoms. Key concepts include ...
... SOL 6.4 Atoms, Elements, compounds The student will investigate and understand that all matter is made up of atoms. Key concepts include ...
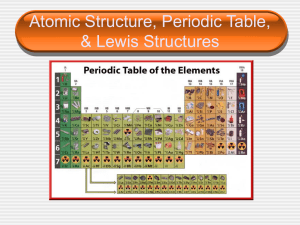
Introduction to the Periodic Table
... Atomic number – number of protons and electrons (number at top of box) Atomic mass – number of protons and neutrons added together (number at bottom of box) ...
... Atomic number – number of protons and electrons (number at top of box) Atomic mass – number of protons and neutrons added together (number at bottom of box) ...
Chapter 2—Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... Dmitri Mendeleev, who first began grouping elements in order of similar chemical properties—and predicted the discovery of elements that were later found ...
... Dmitri Mendeleev, who first began grouping elements in order of similar chemical properties—and predicted the discovery of elements that were later found ...
Atomic Theory
... existence of unknown elements was predicted by Mendeleev on the basis of the blank spaces. When the unknown elements were discovered, it was found that Mendeleev had closely predicted the properties of the ...
... existence of unknown elements was predicted by Mendeleev on the basis of the blank spaces. When the unknown elements were discovered, it was found that Mendeleev had closely predicted the properties of the ...
Setting up Programmable PRS Keypad as Fixed ID Keypads
... Parser06 example6
The identity of an element is determined by the number of…
Q
Protons
Neutrons
Electrons
A molecule may consist of one atom.
Q
True
False
Molybdenum has atomic number 42. Its molar mass is 95.94 grams/mole. How many neutrons does
the most common isotope have?
Q
...
... Parser06 example
File
... of electrons in an atom’s outer shell plays an important role in that atom’s properties determining what other kinds of atoms it can __bond_________ with. Atoms bond together in molecules by either ...
... of electrons in an atom’s outer shell plays an important role in that atom’s properties determining what other kinds of atoms it can __bond_________ with. Atoms bond together in molecules by either ...
The study of biology can help you better understand human
... Which subatomic particle determines chemical properties of an element? ...
... Which subatomic particle determines chemical properties of an element? ...
The History of the Modern Periodic Table
... (atomic number) of the elements*. He rearranged the elements in order of increasing atomic number. *“There is in the atom a fundamental quantity which increases by regular steps as we pass from each element to the next. This quantity can only be the charge on the central positive nucleus.” ...
... (atomic number) of the elements*. He rearranged the elements in order of increasing atomic number. *“There is in the atom a fundamental quantity which increases by regular steps as we pass from each element to the next. This quantity can only be the charge on the central positive nucleus.” ...
Chapter 18
... • Carbon-14 has 6 protons and 8 neutrons Isotopes—atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons Radioactive isotopes—those isotopes that are unstable and become radioactive ...
... • Carbon-14 has 6 protons and 8 neutrons Isotopes—atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons Radioactive isotopes—those isotopes that are unstable and become radioactive ...
PS7aChemistryReviewRevised
... Alcohol boils. Paint dries. A photosynthesizing plant produces sugar. ...
... Alcohol boils. Paint dries. A photosynthesizing plant produces sugar. ...
Chemistry 30A Chapter 2- Atoms and the Periodic Table Laney
... occupies a slightly lower energy than the 3d orbital. Figure 2.6 in the text is a device for figuring out the usual order of filling. Examples will be given in class of two styles of showing the arrangement of the electrons of a particular element. Most of chemistry, and this is a very general state ...
... occupies a slightly lower energy than the 3d orbital. Figure 2.6 in the text is a device for figuring out the usual order of filling. Examples will be given in class of two styles of showing the arrangement of the electrons of a particular element. Most of chemistry, and this is a very general state ...
The_Atoms_Family
... • When the number of neutrons in nuclei vary, you have an isotope • For example, chlorine always has 17 protons, but the number of neutrons could be either 18 or 20. This in turn, changes the atomic mass • The nuclei of some isotopes are unstable and release radiation • During the radioactive decay ...
... • When the number of neutrons in nuclei vary, you have an isotope • For example, chlorine always has 17 protons, but the number of neutrons could be either 18 or 20. This in turn, changes the atomic mass • The nuclei of some isotopes are unstable and release radiation • During the radioactive decay ...