Atoms and Elements
... Every element has its own atomic number or the number of protons in one atom of that element. Only a few kinds of elements are in most matter Molecule = two or more atoms linked together. ...
... Every element has its own atomic number or the number of protons in one atom of that element. Only a few kinds of elements are in most matter Molecule = two or more atoms linked together. ...
Atoms and Elements Notes
... number of valence electrons. (Octet Rule) • Number of valence electrons determines how reactive an element is and what type of bonds they form. ...
... number of valence electrons. (Octet Rule) • Number of valence electrons determines how reactive an element is and what type of bonds they form. ...
Chemistry Timeline
... Joseph John Thomson Polonium) Four elements Invented a good atomic theory (list all points) Matter is made up of “atomos” For each person include in a TYPED paragraph: 1. The name of the scientist with birth and death dates (as known). In other words, WHEN. 2. A complete explanation of their ...
... Joseph John Thomson Polonium) Four elements Invented a good atomic theory (list all points) Matter is made up of “atomos” For each person include in a TYPED paragraph: 1. The name of the scientist with birth and death dates (as known). In other words, WHEN. 2. A complete explanation of their ...
key - Greenslime.info
... From the one’s digit of the group number. For example, elements in group 1 have one valence electron, and elements in group 13 have three valance electrons. The only exception is helium, which only has two valence electrons, even though it is in group 18. ...
... From the one’s digit of the group number. For example, elements in group 1 have one valence electron, and elements in group 13 have three valance electrons. The only exception is helium, which only has two valence electrons, even though it is in group 18. ...
Ions
... particle called an ion. When an atom loses an electron it has more protons therefore becoming positively charged. When an atom gains an electron it has more electrons therefore becoming negatively charged. ...
... particle called an ion. When an atom loses an electron it has more protons therefore becoming positively charged. When an atom gains an electron it has more electrons therefore becoming negatively charged. ...
C2_Chemistry_Summary_Topic_1
... Keywords: proton, neutron, electron, shells, negative, atomic number, mass number ...
... Keywords: proton, neutron, electron, shells, negative, atomic number, mass number ...
PP 04 Atoms_ molecules_ ions
... Groups or Families: Columns which indicate the number of electrons in the outermost energy level determining charge & reactivity ...
... Groups or Families: Columns which indicate the number of electrons in the outermost energy level determining charge & reactivity ...
3-ELEMENTS AND THE ATOMIC MODEL. C4.8A Identify the
... Identify properties of common families of elements. Identify properties of common periods on the periodic table. Explain the history and organization of the periodic table. C4.8e Write the complete electron configuration of elements in the first three rows of the periodic table. C4.8g Predict oxidat ...
... Identify properties of common families of elements. Identify properties of common periods on the periodic table. Explain the history and organization of the periodic table. C4.8e Write the complete electron configuration of elements in the first three rows of the periodic table. C4.8g Predict oxidat ...
Periodic Table
... –Included elements Valence # (bonding power) •How many e- the atom can lose or gain when bonding •Pattern appeared - 1234321 ...
... –Included elements Valence # (bonding power) •How many e- the atom can lose or gain when bonding •Pattern appeared - 1234321 ...
Test Review Answers File
... b. Neutrons = 16 c. Electrons = 15 20. Which part of the atom was discovered as a result of the Gold Foil experiment? ...
... b. Neutrons = 16 c. Electrons = 15 20. Which part of the atom was discovered as a result of the Gold Foil experiment? ...
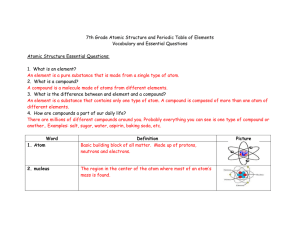
7th Grade Atomic Structure and Periodic Table of Elements
... A compound is a molecule made of atoms from different elements. 3. What is the difference between and element and a compound? An element is a substance that contains only one type of atom. A compound is composed of more than one atom of different elements. 4. How are compounds a part of our daily li ...
... A compound is a molecule made of atoms from different elements. 3. What is the difference between and element and a compound? An element is a substance that contains only one type of atom. A compound is composed of more than one atom of different elements. 4. How are compounds a part of our daily li ...
Metals
... All protons, neutrons, and electrons are the same. What makes elements different is the relative numbers of each. ...
... All protons, neutrons, and electrons are the same. What makes elements different is the relative numbers of each. ...
Chemical Bonding
... • Elements are pure substances that are made of only one type of atom. • Isotopes are elements with different numbers of neutrons. • Because isotopes have the same number electrons, all isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties. ...
... • Elements are pure substances that are made of only one type of atom. • Isotopes are elements with different numbers of neutrons. • Because isotopes have the same number electrons, all isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties. ...
Atomic Theory Outline
... i. Divisions of the electron cloud based on different energy levels ii. Each shell can hold a number of electrons equal to 2n2, where n = the number of the level. iii. Lower level shells are closer to the nucleus and have less energy. iv. Electrons must fill in closer, low energy shells before the f ...
... i. Divisions of the electron cloud based on different energy levels ii. Each shell can hold a number of electrons equal to 2n2, where n = the number of the level. iii. Lower level shells are closer to the nucleus and have less energy. iv. Electrons must fill in closer, low energy shells before the f ...
Part A: Multiple Choice. Circle the letter
... 7. In general, which of the following properties does NOT increase across a row from left to right? a) atomic number b) atomic radius c) nuclear charge d) ionization energy e) electron affinity 8. Which of the following properties decreases from top to bottom in a column? a) ionization energy b) ato ...
... 7. In general, which of the following properties does NOT increase across a row from left to right? a) atomic number b) atomic radius c) nuclear charge d) ionization energy e) electron affinity 8. Which of the following properties decreases from top to bottom in a column? a) ionization energy b) ato ...
Atomic Structure PPT Notes Sheet
... In a neutral atom, the number of ____________= the number of ____________. The atomic mass is equal to the number of __________ and the number of ___________. An __________________ represents the area in an atom where an electron is likely to be found. Each energy levels can hold only a ____________ ...
... In a neutral atom, the number of ____________= the number of ____________. The atomic mass is equal to the number of __________ and the number of ___________. An __________________ represents the area in an atom where an electron is likely to be found. Each energy levels can hold only a ____________ ...
Section 3 The Periodic Table
... arrangement of elements based on their increasing atomic numbers instead of atomic mass. ...
... arrangement of elements based on their increasing atomic numbers instead of atomic mass. ...
a worksheet on C1.1
... atom is called an element. There are about 100 different elements. Elements are shown in the periodic table. The groups contain elements with similar properties. Candidates should understand where metals and non-metals appear in the periodic table. b) Atoms of each element are represented by a chemi ...
... atom is called an element. There are about 100 different elements. Elements are shown in the periodic table. The groups contain elements with similar properties. Candidates should understand where metals and non-metals appear in the periodic table. b) Atoms of each element are represented by a chemi ...
File
... b. How do you know? _____________________________________________________________________ c. Identify the solute: _____________________________________________________________________ d. Identify the solvent: ____________________________________________________________________ 1. List the 4 signs of ...
... b. How do you know? _____________________________________________________________________ c. Identify the solute: _____________________________________________________________________ d. Identify the solvent: ____________________________________________________________________ 1. List the 4 signs of ...
Chapter 4 notes outline
... number of neutrons Elements can have several isotopes 4.3 Modern Atomic Theory Bohr’s Model of the Atom Better description of electrons Electrons orbit around nucleus in energy levels like planets 1st Level = holds up to 2 electrons 2nd Level = holds up to 8 electrons Electrons can move to d ...
... number of neutrons Elements can have several isotopes 4.3 Modern Atomic Theory Bohr’s Model of the Atom Better description of electrons Electrons orbit around nucleus in energy levels like planets 1st Level = holds up to 2 electrons 2nd Level = holds up to 8 electrons Electrons can move to d ...
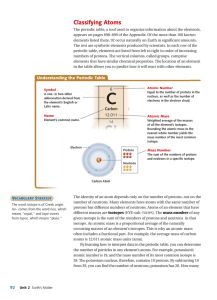
Classifying Atoms
... appears on pages 698–699 of the Appendix. Of the more than 100 known elements listed there, 92 occur naturally on Earth in significant amounts. The rest are synthetic elements produced by scientists. In each row of the periodic table, elements are listed from left to right in order of increasing num ...
... appears on pages 698–699 of the Appendix. Of the more than 100 known elements listed there, 92 occur naturally on Earth in significant amounts. The rest are synthetic elements produced by scientists. In each row of the periodic table, elements are listed from left to right in order of increasing num ...
Atomic Theory- 1. Matter is composed of tiny, indivisible particles
... Atomic Theory1. Matter is composed of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms. 2. An element is composed of one type of atom. Properties of atoms are identical to each other. 3. A compound contains two or more different elements. The relative number of atoms of each element in a compound is the sam ...
... Atomic Theory1. Matter is composed of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms. 2. An element is composed of one type of atom. Properties of atoms are identical to each other. 3. A compound contains two or more different elements. The relative number of atoms of each element in a compound is the sam ...