* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download introductory chemistry
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
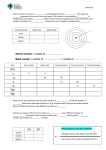
INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Student Worksheet – Week three. Draw electron shells diagrams for various elements. Explain the terms; elements, compounds. Elements and compounds Elements are substances that contain only one type of atom. Hydrogen gas is an element as it contains only hydrogen atoms. Compounds contain the atoms of two or more different elements joined together. Water is a compound that consists of hydrogen and oxygen atoms joined together. There are nearly 100 different, naturally occurring elements. They are arranged into a table called the periodic table. Atoms are made up of electrons, protons and neutrons. A typical atom looks like the one on the right. If you look at a PERIODIC TABLE, you will see that different elements have different ATOMIC NUMBERS. The atomic number is the number of protons in each atom of that element. The number of protons equals the number of electrons for normal atoms. The way that electrons are arranged in atoms is very important. Diagrams can be used to show the arrangement of electrons in atoms. HYDROGEN SODIUM CHLORINE OXYGEN © Peter Adams 2006 MAGNESIUM HELIUM Atoms don’t like to have partially filled shells. They like to be like Neon; having their shells either totally full, or totally empty. Atoms lose or gain electrons to empty or fill the shells. Sodium will lose one electron and become Na+ Oxygen will gain two electrons and become O2Magnesium will ________ _______ electrons and become ______ Chlorine will ________ ________ electron and become ______ Charged atoms, or groups of atoms, like Na+, Mg2+, O2- & Cl- are called IONS. POSITIVE IONS NEGATIVE IONS Name Symbol Name Symbol Hydrogen Mercury (II) Sodium Silver Potassium Ammonium Barium Calcium Lead Copper (I) Copper (II) Magnesium Iron(II) Iron(III) Zinc Aluminium H+ Hg2+ Na+ Ag+ K+ NH4+ Ba2+ Ca2+ Pb2+ Cu+ Cu2+ Mg2+ Fe2+ Fe3+ Zn2+ Al3+ Chloride Sulfide Sulfate Sulfite Hydroxide Oxide Nitrate Nitrite Ethanoate Phosphate Carbonate Bicarbonate Iodide Peroxide Fluoride Bromide ClS2SO42SO32OHO2NO3NO2CH3COOPO43CO32HCO3IO22FBr- © Peter Adams 2006