IMMUNOLOGY 2010™ Poster Symposia Schedule
... Disease Cytokines II: Immunomodulatory Cytokines Effector Cells and Tissue Damage in Autoimmunity Host Defense: Innate Immune Receptors and Signal Transduction Immune Regulation of Host Immunity during Viral Infection Immune System Regulation iTreg, Th17, and CD4 CTL Differentiation Leukocyte Activa ...
... Disease Cytokines II: Immunomodulatory Cytokines Effector Cells and Tissue Damage in Autoimmunity Host Defense: Innate Immune Receptors and Signal Transduction Immune Regulation of Host Immunity during Viral Infection Immune System Regulation iTreg, Th17, and CD4 CTL Differentiation Leukocyte Activa ...
Innate Immune Response
... 20. Where are MHC 1 molecules found? 21. Where are MHC 2 molecules found? 22. What does an MHC molecule present to the immune system? 23. What are the requirements for an effective defence against pathogens? 24. What are the two possible outcomes of a microbial invasion in terms of the innate immune ...
... 20. Where are MHC 1 molecules found? 21. Where are MHC 2 molecules found? 22. What does an MHC molecule present to the immune system? 23. What are the requirements for an effective defence against pathogens? 24. What are the two possible outcomes of a microbial invasion in terms of the innate immune ...
Immune System
... A. Interferon- a substance produced by a virus infected cell that helps other cells resist the virus -The virus turns on the interferon gene- can save the infected cell but diffuses to nearby cells and inhibits viral reproduction there -Host specific-not virus specific -Inteferon may act against can ...
... A. Interferon- a substance produced by a virus infected cell that helps other cells resist the virus -The virus turns on the interferon gene- can save the infected cell but diffuses to nearby cells and inhibits viral reproduction there -Host specific-not virus specific -Inteferon may act against can ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... Basic concepts of tumour immunology • Tumors can be initiated by environmental factors and by viruses. • Transformation involves changes in expression of normal cellular ...
... Basic concepts of tumour immunology • Tumors can be initiated by environmental factors and by viruses. • Transformation involves changes in expression of normal cellular ...
your body`s defense against infection lesson 2
... antibodies Proteins that attach to antigens, keeping them from harming the body ...
... antibodies Proteins that attach to antigens, keeping them from harming the body ...
adaptive immunity
... • Slow during the primary response, but very fast during the secondary responses • memory ...
... • Slow during the primary response, but very fast during the secondary responses • memory ...
Assignment I
... 7. Discuss different features of peptide-MHC interaction. Draw diagram of a MHC class I or II molecule. 8. What are T cell and B cell receptors? Draw a schematic diagram of T cell receptor. 9. Explain the positive and negative selection of lymphocyte. 10. What are co-stimulatory molecules? Explain t ...
... 7. Discuss different features of peptide-MHC interaction. Draw diagram of a MHC class I or II molecule. 8. What are T cell and B cell receptors? Draw a schematic diagram of T cell receptor. 9. Explain the positive and negative selection of lymphocyte. 10. What are co-stimulatory molecules? Explain t ...
Lecture #23 - Suraj @ LUMS
... that increase capillary blood flow into the affected area (causing the areas to become heated and reddened). White Blood Cells can move out of the blood vessels to the site of infection. Phagocytes are a type of White Blood Cell that will recognize and engulf bacteria and other foreign substances, i ...
... that increase capillary blood flow into the affected area (causing the areas to become heated and reddened). White Blood Cells can move out of the blood vessels to the site of infection. Phagocytes are a type of White Blood Cell that will recognize and engulf bacteria and other foreign substances, i ...
1133693644_460426
... Exists at birth Is not pathogen specific Does not require previous exposure Kills invading microbes Begins inflammatory response (redness, swelling, and pain) • Alerts adaptive immune response ...
... Exists at birth Is not pathogen specific Does not require previous exposure Kills invading microbes Begins inflammatory response (redness, swelling, and pain) • Alerts adaptive immune response ...
The Immune System
... 1. Autoimmune disease-body attacks its own cells (multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, Graves’ disease, Type I Diabetes). 2. AIDS is caused by HIV (human immunodeficiency virus). HIV invades helper T cells causing them to produce more virus and then die. – HIV is transmitted through HIV-infecte ...
... 1. Autoimmune disease-body attacks its own cells (multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, Graves’ disease, Type I Diabetes). 2. AIDS is caused by HIV (human immunodeficiency virus). HIV invades helper T cells causing them to produce more virus and then die. – HIV is transmitted through HIV-infecte ...
March 24 (PP)
... Replacement therapy (eg insulin, thyroid hormone) Feeding or oral tolerance (induce tolerance to antigen) – Feed insulin for diabetes – Collagen for rheumatoid arthritis – Cause local intestinal immune response, down regulation of antigen receptors deletion of immune cells ...
... Replacement therapy (eg insulin, thyroid hormone) Feeding or oral tolerance (induce tolerance to antigen) – Feed insulin for diabetes – Collagen for rheumatoid arthritis – Cause local intestinal immune response, down regulation of antigen receptors deletion of immune cells ...
Natural Defence - MedicalBooks.com
... If the infection persists and there are too many organisms for the phagocytes to fight by themselves, the immune system produces proteins called antibodies. Each antibody is designed to combat a particular antigen, or foreign protein. Two types of white blood cells are involved in this process. B ce ...
... If the infection persists and there are too many organisms for the phagocytes to fight by themselves, the immune system produces proteins called antibodies. Each antibody is designed to combat a particular antigen, or foreign protein. Two types of white blood cells are involved in this process. B ce ...
part-3-and-4-immune-system-second-line-of
... o This binding either ____________ pathogen from ____________ a body cell or ____________ the pathogen for ________________ More B cells are produced to help with anti_________ production and attachment Some _______________ will remain in body to protect against further attack (___________) ________ ...
... o This binding either ____________ pathogen from ____________ a body cell or ____________ the pathogen for ________________ More B cells are produced to help with anti_________ production and attachment Some _______________ will remain in body to protect against further attack (___________) ________ ...
The mononuclear phagocyte cell system includes monocytes
... dendritic cells which are important cells in order to recognize, ingest, destroy and also present part of a pathogen to T-lymphocytes in order to activate the adaptive immune system. Dendritic cells (DCs) stand out in their ability to stimulate Tlymphocytes and are also believed to be important to k ...
... dendritic cells which are important cells in order to recognize, ingest, destroy and also present part of a pathogen to T-lymphocytes in order to activate the adaptive immune system. Dendritic cells (DCs) stand out in their ability to stimulate Tlymphocytes and are also believed to be important to k ...
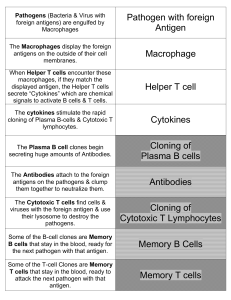
Pathogens (Bacteria with foreign antigens) are
... antigens on the pathogens & clump them together to neutralize them. ...
... antigens on the pathogens & clump them together to neutralize them. ...
presentation
... – Invasion of foreign material causes injured cells to release chemical alarm signals (e.g. histamine) – Chemical alarm signals promote vasodilation – Vasodilation and increased permeability of capillaries causes edema (tissue swelling) – Increased permeability allows macrophages to cross over into ...
... – Invasion of foreign material causes injured cells to release chemical alarm signals (e.g. histamine) – Chemical alarm signals promote vasodilation – Vasodilation and increased permeability of capillaries causes edema (tissue swelling) – Increased permeability allows macrophages to cross over into ...
30_Extracellular bact BA
... - Cytotoxicity of various mechanisms - Inhibition of various cellular functions Endotoxin – released by dying cells ...
... - Cytotoxicity of various mechanisms - Inhibition of various cellular functions Endotoxin – released by dying cells ...
Comic Strip Immunity Project
... Using your knowledge of the function of the immune system and the immune response process create a comic strip or storyboard outlining the basic processes involved with the immune response. Be creative! Use analogies, characters, or stories to help you display your information. It is important that ...
... Using your knowledge of the function of the immune system and the immune response process create a comic strip or storyboard outlining the basic processes involved with the immune response. Be creative! Use analogies, characters, or stories to help you display your information. It is important that ...
Immune system

The immune system is a system of many biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease. To function properly, an immune system must detect a wide variety of agents, known as pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, and distinguish them from the organism's own healthy tissue. In many species, the immune system can be classified into subsystems, such as the innate immune system versus the adaptive immune system, or humoral immunity versus cell-mediated immunity.Pathogens can rapidly evolve and adapt, and thereby avoid detection and neutralization by the immune system; however, multiple defense mechanisms have also evolved to recognize and neutralize pathogens. Even simple unicellular organisms such as bacteria possess a rudimentary immune system, in the form of enzymes that protect against bacteriophage infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient eukaryotes and remain in their modern descendants, such as plants and insects. These mechanisms include phagocytosis, antimicrobial peptides called defensins, and the complement system. Jawed vertebrates, including humans, have even more sophisticated defense mechanisms, including the ability to adapt over time to recognize specific pathogens more efficiently. Adaptive (or acquired) immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, leading to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that same pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination.Disorders of the immune system can result in autoimmune diseases, inflammatory diseases and cancer.Immunodeficiency occurs when the immune system is less active than normal, resulting in recurring and life-threatening infections. In humans, immunodeficiency can either be the result of a genetic disease such as severe combined immunodeficiency, acquired conditions such as HIV/AIDS, or the use of immunosuppressive medication. In contrast, autoimmunity results from a hyperactive immune system attacking normal tissues as if they were foreign organisms. Common autoimmune diseases include Hashimoto's thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes mellitus type 1, and systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunology covers the study of all aspects of the immune system.