Objectives 13
... of T cells • T cell growth is stimulated by the protein displayed on the surface of the macrophage. • Some become active killers others become memory T cells. ...
... of T cells • T cell growth is stimulated by the protein displayed on the surface of the macrophage. • Some become active killers others become memory T cells. ...
The Immune System - Clark Pleasant Community School Corp
... Immune System • Antibodies are made in response to a specific antigen • Takes a while to figure out the exact shape to fit the antigen • Once made, memory cells will be kept for ...
... Immune System • Antibodies are made in response to a specific antigen • Takes a while to figure out the exact shape to fit the antigen • Once made, memory cells will be kept for ...
43 - GEOCITIES.ws
... 3. Contrast the roles of the nonspecific cellular defenses. [2 points] a. Phagocytes engulf and destroy pathogens b. NK cells punch virus-infected and cancerous cells 4. Rationalize the four cardinal signs of an acute inflammatory response. a. Histamine and kinins released b. Increased blood flow ca ...
... 3. Contrast the roles of the nonspecific cellular defenses. [2 points] a. Phagocytes engulf and destroy pathogens b. NK cells punch virus-infected and cancerous cells 4. Rationalize the four cardinal signs of an acute inflammatory response. a. Histamine and kinins released b. Increased blood flow ca ...
Immune Worksheet Session 27- 4/7/11
... 3) What are the dangers of a high fever? 4) What are responsible for resetting the body’s thermostat upward? Where do these come from? ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY (general): 1) What are the 3 key characteristics of the adaptive immune response? 2) Name and define the two overlapping arms of adaptive immunity: ...
... 3) What are the dangers of a high fever? 4) What are responsible for resetting the body’s thermostat upward? Where do these come from? ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY (general): 1) What are the 3 key characteristics of the adaptive immune response? 2) Name and define the two overlapping arms of adaptive immunity: ...
BSC 361
... Muscles work to move irritants out Chemical defenses: Lysozyme Enzyme in tears and mucus that degrades bacterial cell walls Very important for protection of eyes Stomach acid Low pH conditions prevent most bacteria from persisting in stomach Most GI pathogens have temporary means to survive low pH C ...
... Muscles work to move irritants out Chemical defenses: Lysozyme Enzyme in tears and mucus that degrades bacterial cell walls Very important for protection of eyes Stomach acid Low pH conditions prevent most bacteria from persisting in stomach Most GI pathogens have temporary means to survive low pH C ...
Activity 1: Antibodies and the adaptive immune response
... antibodies. B cells and antibodies Antibodies are small, y-shaped glycoproteins produced by B cells. The role of antibodies is to recognize a small part of a pathogen known as an antigen and bind to it. By binding, antibodies can prevent further replication of the pathogen and alert the immune syste ...
... antibodies. B cells and antibodies Antibodies are small, y-shaped glycoproteins produced by B cells. The role of antibodies is to recognize a small part of a pathogen known as an antigen and bind to it. By binding, antibodies can prevent further replication of the pathogen and alert the immune syste ...
Integrated Science 2 Name: Per
... 13. What are some examples of antigens? ______________________________________________ ...
... 13. What are some examples of antigens? ______________________________________________ ...
Antigens and Antibodies, Cell Receptors
... appropriate immune response for a given antigen (recognition of opsonized particles, lysis of cells, and degranulation of mast cells, basophils and eosinophils) ...
... appropriate immune response for a given antigen (recognition of opsonized particles, lysis of cells, and degranulation of mast cells, basophils and eosinophils) ...
Διαφάνεια 1 - Aristotle University of Thessaloniki
... antibodies out of the blood stream -Anti-RhD therapy can also be useful in people with specific blood ...
... antibodies out of the blood stream -Anti-RhD therapy can also be useful in people with specific blood ...
Complexity and the Immune System
... • Genetic variation can lead to B and T cells that cover the entire range of pathogens, and each antibody hits on average one antigen • B cells differentiate into memory cells, which are able to quickly split into lots of effector cells and more memory cells • After an attack, have more memory cells ...
... • Genetic variation can lead to B and T cells that cover the entire range of pathogens, and each antibody hits on average one antigen • B cells differentiate into memory cells, which are able to quickly split into lots of effector cells and more memory cells • After an attack, have more memory cells ...
The Immune System Learning Module | Vaccine Education Center
... Courtesy CDC, Public Health Image Library (PHIL) ...
... Courtesy CDC, Public Health Image Library (PHIL) ...
Notes: Chapter 39 Reading Guide (page 1022
... antibodies against the specific pathogen • Memory B-cells and T-cells hang around in case the pathogen shows up again later – Quick response next time ...
... antibodies against the specific pathogen • Memory B-cells and T-cells hang around in case the pathogen shows up again later – Quick response next time ...
The Immune System Learning Module | Vaccine Education Center
... Courtesy CDC, Public Health Image Library (PHIL) ...
... Courtesy CDC, Public Health Image Library (PHIL) ...
The Immune System - Children`s Hospital of Philadelphia
... Courtesy CDC, Public Health Image Library (PHIL) ...
... Courtesy CDC, Public Health Image Library (PHIL) ...
Chapter 18 Quantitative and Thought Questions 18.1 Both would be
... 18.3 The drug may reduce but would not eliminate the action of complement, because this system destroys cells directly (via the membrane attack complex) as well as by facilitating phagocytosis. 18.4 Antibodies would bind normally to antigen but may not be able to activate complement, act as opsonins ...
... 18.3 The drug may reduce but would not eliminate the action of complement, because this system destroys cells directly (via the membrane attack complex) as well as by facilitating phagocytosis. 18.4 Antibodies would bind normally to antigen but may not be able to activate complement, act as opsonins ...
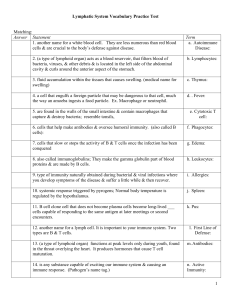
Lymph vocab Test
... 15. fire chemicals secreted by WBC’s exposed to foreign substances in the body which causes the normal body temperature to increase 16. is a mixture of dead or dying neutrophils, broken-down tissue cells, & living ...
... 15. fire chemicals secreted by WBC’s exposed to foreign substances in the body which causes the normal body temperature to increase 16. is a mixture of dead or dying neutrophils, broken-down tissue cells, & living ...
THE PEARLS OF WISDOM - OSW
... B cells (mature in bone marrow, produce antibodies and part of antibody-mediated immunity. T cells(mature in Thymus, coordinate entire immune response and eliminate viruses hiding in infected cells, Attack and destroy, Responsible for cell mediated (cellular) immunity. ...
... B cells (mature in bone marrow, produce antibodies and part of antibody-mediated immunity. T cells(mature in Thymus, coordinate entire immune response and eliminate viruses hiding in infected cells, Attack and destroy, Responsible for cell mediated (cellular) immunity. ...
Reading Guide - Belle Vernon Area School District
... 11. What is the role of cytotoxic T cells and describe their mechanism of action? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 12. What are some of the actions of helper T cells? ________________ ...
... 11. What is the role of cytotoxic T cells and describe their mechanism of action? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 12. What are some of the actions of helper T cells? ________________ ...
Immune system

The immune system is a system of many biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease. To function properly, an immune system must detect a wide variety of agents, known as pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, and distinguish them from the organism's own healthy tissue. In many species, the immune system can be classified into subsystems, such as the innate immune system versus the adaptive immune system, or humoral immunity versus cell-mediated immunity.Pathogens can rapidly evolve and adapt, and thereby avoid detection and neutralization by the immune system; however, multiple defense mechanisms have also evolved to recognize and neutralize pathogens. Even simple unicellular organisms such as bacteria possess a rudimentary immune system, in the form of enzymes that protect against bacteriophage infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient eukaryotes and remain in their modern descendants, such as plants and insects. These mechanisms include phagocytosis, antimicrobial peptides called defensins, and the complement system. Jawed vertebrates, including humans, have even more sophisticated defense mechanisms, including the ability to adapt over time to recognize specific pathogens more efficiently. Adaptive (or acquired) immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, leading to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that same pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination.Disorders of the immune system can result in autoimmune diseases, inflammatory diseases and cancer.Immunodeficiency occurs when the immune system is less active than normal, resulting in recurring and life-threatening infections. In humans, immunodeficiency can either be the result of a genetic disease such as severe combined immunodeficiency, acquired conditions such as HIV/AIDS, or the use of immunosuppressive medication. In contrast, autoimmunity results from a hyperactive immune system attacking normal tissues as if they were foreign organisms. Common autoimmune diseases include Hashimoto's thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes mellitus type 1, and systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunology covers the study of all aspects of the immune system.