Unit Question: What is life and how does it maintain balance? Notes
... into the body • The body produces antibodies which remain in the system in case of another infection by the same pathogen ...
... into the body • The body produces antibodies which remain in the system in case of another infection by the same pathogen ...
ANTIGENS
... Haptens: Small molecules, which are not immunogenic but they induce an immune response when they are attached to a carrier ...
... Haptens: Small molecules, which are not immunogenic but they induce an immune response when they are attached to a carrier ...
specific defenses: the immune system
... the following questions. 1. Label each part of the figure in the spaces provided. a ...
... the following questions. 1. Label each part of the figure in the spaces provided. a ...
The Body Has Methods of Protecting Itself from Diseases
... growth/reproduction of microorganisms Do Not effect viruses Lymphatic System: produces white blood cells and antibodies 2 types of White Blood Cells (1) T cells and (2) B cells ...
... growth/reproduction of microorganisms Do Not effect viruses Lymphatic System: produces white blood cells and antibodies 2 types of White Blood Cells (1) T cells and (2) B cells ...
The Characterization of Myeloid Cell Subsets in Innate and Adaptive
... subsets is still unclear. Furthermore, innate immune responses are not defined well compared to adaptive immune response against Listeria. In particular, immunity in secondary lymphoid organ such as lymph node (LN), there are much more complicated network among immune cells. Therefore I focused on t ...
... subsets is still unclear. Furthermore, innate immune responses are not defined well compared to adaptive immune response against Listeria. In particular, immunity in secondary lymphoid organ such as lymph node (LN), there are much more complicated network among immune cells. Therefore I focused on t ...
3/12 TCOS IO symposium
... material that has penetrated the body’s physical and chemical barriers, are also considered to be part of the innate immune system. The various elements that participate in innate immunity exhibit broad specificity against foreign agents by recognising molecules not found in the host. By contrast, a ...
... material that has penetrated the body’s physical and chemical barriers, are also considered to be part of the innate immune system. The various elements that participate in innate immunity exhibit broad specificity against foreign agents by recognising molecules not found in the host. By contrast, a ...
20150923_koyasu
... The type 2 immune response, characterized by the production of IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13, is a critical immune response against helminths invading cutaneous or mucosal sites. In addition, type 2 immune responses are involved in the pathophysiology of various allergic diseases including asthma. Type 2 cyt ...
... The type 2 immune response, characterized by the production of IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13, is a critical immune response against helminths invading cutaneous or mucosal sites. In addition, type 2 immune responses are involved in the pathophysiology of various allergic diseases including asthma. Type 2 cyt ...
match-up
... invader. Uses a chemical "memory" to remember antigens. this type of acquired immunity uses cytotoxic T cells that are capable of killing other cells. ...
... invader. Uses a chemical "memory" to remember antigens. this type of acquired immunity uses cytotoxic T cells that are capable of killing other cells. ...
Title - Iowa State University
... 13. Write in the name of the mechanism of antibody action next to its corresponding description: Antibodies block specific sites on viruses or bacterial exotoxins, Neutralization preventing antigens from binding to receptors on tissue cells Antibodies bind close together on a cellular antigen, trigg ...
... 13. Write in the name of the mechanism of antibody action next to its corresponding description: Antibodies block specific sites on viruses or bacterial exotoxins, Neutralization preventing antigens from binding to receptors on tissue cells Antibodies bind close together on a cellular antigen, trigg ...
Immune System
... distinguished from foreign substances by the immune system. Autoimmunity- immune reaction against self molecules • Non-self Molecules- recognized as foreign molecules Ex: Antigen (short for antibody generators) Immune System: Responsible for protecting the animal from potentially harmful organisms a ...
... distinguished from foreign substances by the immune system. Autoimmunity- immune reaction against self molecules • Non-self Molecules- recognized as foreign molecules Ex: Antigen (short for antibody generators) Immune System: Responsible for protecting the animal from potentially harmful organisms a ...
How does my immune system react when I puncture my skin on
... Oh no! It’s a bacteria! Humoral Immunity Bacteria is engaged by an Antigen Presenting Cell (APC) which promptly engulphs (phagocytosis) the "bad guy" Inside the APC, the "bad guy" is broken down and a special piece of "bad guy" protein is attached to an MHC II Then, the MHCII/antigen complex moves ...
... Oh no! It’s a bacteria! Humoral Immunity Bacteria is engaged by an Antigen Presenting Cell (APC) which promptly engulphs (phagocytosis) the "bad guy" Inside the APC, the "bad guy" is broken down and a special piece of "bad guy" protein is attached to an MHC II Then, the MHCII/antigen complex moves ...
Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Cancer Therapy: New Insights and
... have shown that CLTA-4 limits T cell proliferation by a cell intrinsic mechanism. However, there is also evidence that anti-CTLA-4 has to engage the target on both effector (Teff) and regulatory (Treg) T cells. Thus anti-CTLA-4 exerts its anti-tumor effects by multiple mechanisms. PD-1, another chec ...
... have shown that CLTA-4 limits T cell proliferation by a cell intrinsic mechanism. However, there is also evidence that anti-CTLA-4 has to engage the target on both effector (Teff) and regulatory (Treg) T cells. Thus anti-CTLA-4 exerts its anti-tumor effects by multiple mechanisms. PD-1, another chec ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
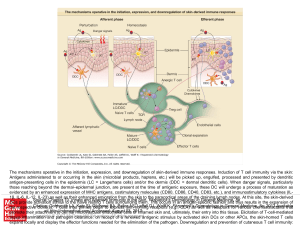
... The mechanisms operative in the initiation, expression, and downregulation of skin-derived immune responses. Induction of T cell immunity via the skin: Antigens administered to or occurring in the skin (microbial products, haptens, etc.) will be picked up, engulfed, processed and presented by dendri ...
... The mechanisms operative in the initiation, expression, and downregulation of skin-derived immune responses. Induction of T cell immunity via the skin: Antigens administered to or occurring in the skin (microbial products, haptens, etc.) will be picked up, engulfed, processed and presented by dendri ...
Q9 Describe how the body defends against infection
... o Skin (prevents bacterial entry and growth) o Normal flora (prevent transient pathogenic organisms from colonizing the skin surface by competing for nutrients or secreting protective enzymes) o Mucous (traps bacteri ...
... o Skin (prevents bacterial entry and growth) o Normal flora (prevent transient pathogenic organisms from colonizing the skin surface by competing for nutrients or secreting protective enzymes) o Mucous (traps bacteri ...
For more information
... Sjögren’s syndrome (SS) is a rheumatic autoimmune disease, with focal lymphocyte infiltration and inflammation in exocrine glands, resulting in destruction of glandular tissue. B cells have an important role in the humoral part of the adaptive immune response where they carry out several functions; ...
... Sjögren’s syndrome (SS) is a rheumatic autoimmune disease, with focal lymphocyte infiltration and inflammation in exocrine glands, resulting in destruction of glandular tissue. B cells have an important role in the humoral part of the adaptive immune response where they carry out several functions; ...
IMMUNE SYSTEM:
... 2. If pathogens get past the barrier of your skin, the inflammatory response helps attack the pathogens. It is called the body’s general defense. 3. A white blood cell that surrounds the pathogen and destroys it is called a phagocyte. 4. If the inflammatory response is not enough to overcome the pat ...
... 2. If pathogens get past the barrier of your skin, the inflammatory response helps attack the pathogens. It is called the body’s general defense. 3. A white blood cell that surrounds the pathogen and destroys it is called a phagocyte. 4. If the inflammatory response is not enough to overcome the pat ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... Describe the structure, characteristics and functions of IgG and IgM. Give an account on the applications of Monoclonal antibodies. Describe the role of cytokines in immunogenic reaction. Explain the immune responses shown to viral, bacterial and parasite infections. Discuss the role of secondary ly ...
... Describe the structure, characteristics and functions of IgG and IgM. Give an account on the applications of Monoclonal antibodies. Describe the role of cytokines in immunogenic reaction. Explain the immune responses shown to viral, bacterial and parasite infections. Discuss the role of secondary ly ...
dr._mather-brown_presentation
... and differentiation – Regulation of immune-mediated inflammation – Stimulation of immature leukocyte growth and ...
... and differentiation – Regulation of immune-mediated inflammation – Stimulation of immature leukocyte growth and ...
Immune system

The immune system is a system of many biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease. To function properly, an immune system must detect a wide variety of agents, known as pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, and distinguish them from the organism's own healthy tissue. In many species, the immune system can be classified into subsystems, such as the innate immune system versus the adaptive immune system, or humoral immunity versus cell-mediated immunity.Pathogens can rapidly evolve and adapt, and thereby avoid detection and neutralization by the immune system; however, multiple defense mechanisms have also evolved to recognize and neutralize pathogens. Even simple unicellular organisms such as bacteria possess a rudimentary immune system, in the form of enzymes that protect against bacteriophage infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient eukaryotes and remain in their modern descendants, such as plants and insects. These mechanisms include phagocytosis, antimicrobial peptides called defensins, and the complement system. Jawed vertebrates, including humans, have even more sophisticated defense mechanisms, including the ability to adapt over time to recognize specific pathogens more efficiently. Adaptive (or acquired) immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, leading to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that same pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination.Disorders of the immune system can result in autoimmune diseases, inflammatory diseases and cancer.Immunodeficiency occurs when the immune system is less active than normal, resulting in recurring and life-threatening infections. In humans, immunodeficiency can either be the result of a genetic disease such as severe combined immunodeficiency, acquired conditions such as HIV/AIDS, or the use of immunosuppressive medication. In contrast, autoimmunity results from a hyperactive immune system attacking normal tissues as if they were foreign organisms. Common autoimmune diseases include Hashimoto's thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes mellitus type 1, and systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunology covers the study of all aspects of the immune system.