Objectives Resistance Nonspecific Defense Inflammatory Response
... Immunity – The body’s ability to protect itself. I. Nonspecific defense – General defense A. Physical Barriers B. Chemicals & Cells II. Specific defense Combats particular strains of diseases ...
... Immunity – The body’s ability to protect itself. I. Nonspecific defense – General defense A. Physical Barriers B. Chemicals & Cells II. Specific defense Combats particular strains of diseases ...
Immunity
... Phagocytes and Granulocytes Phagocytes are large white cells that can engulf and digest foreign invaders. They include monocytes, which circulate in the blood, and macrophages, which are found in tissues throughout the body, as well as neutrophils, cells that circulate in the blood but move into tis ...
... Phagocytes and Granulocytes Phagocytes are large white cells that can engulf and digest foreign invaders. They include monocytes, which circulate in the blood, and macrophages, which are found in tissues throughout the body, as well as neutrophils, cells that circulate in the blood but move into tis ...
35-2 Defense Against Infection Worksheet
... 15. THINK VISUALLY In the space provided, draw an example of each type of lymphocyte indicated to show a basic difference between the two types of cells. B Cell ...
... 15. THINK VISUALLY In the space provided, draw an example of each type of lymphocyte indicated to show a basic difference between the two types of cells. B Cell ...
practice
... mechanisms that defend the host from infection by other organisms in a non-specific manner. Choose TWO different types of innate defenses present in plants and explain how each defense either prevents the entry or prevents establishment of a pathogen. ...
... mechanisms that defend the host from infection by other organisms in a non-specific manner. Choose TWO different types of innate defenses present in plants and explain how each defense either prevents the entry or prevents establishment of a pathogen. ...
Unit 4 Topic 6: Infection, immunity and forensics Revision questions
... 1. How DNA profiling is used for identification and determining genetic relationships between organisms (plants and animals). 2. The role of micro-organisms in the decomposition of organic matter and the recycling of carbon. 3. The major routes pathogens may take when entering the body and explain t ...
... 1. How DNA profiling is used for identification and determining genetic relationships between organisms (plants and animals). 2. The role of micro-organisms in the decomposition of organic matter and the recycling of carbon. 3. The major routes pathogens may take when entering the body and explain t ...
I. Immunity
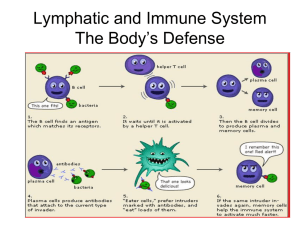
... A. Skin & Mucus: keeps antigens out of the body B. Lymphatic System: produces white blood cells and antibodies 1. White blood cells: two types-T cells and B cells 2. Antibody—protein that disables antigens 3. B cells—makes antibodies 4. T cells—helps make antibodies, kills infected cells 5. Memory B ...
... A. Skin & Mucus: keeps antigens out of the body B. Lymphatic System: produces white blood cells and antibodies 1. White blood cells: two types-T cells and B cells 2. Antibody—protein that disables antigens 3. B cells—makes antibodies 4. T cells—helps make antibodies, kills infected cells 5. Memory B ...
May 13, 2015
... Enhanced-affinity NY-ESO-1-specific T cells exhibit extended functionality without exhaustion in a pattern of effector and memory programming in multiple cancer indications Montreal, Canada – May 13, 2015— Caprion announced today that Adaptimmune will present data at the American Society of Gene and ...
... Enhanced-affinity NY-ESO-1-specific T cells exhibit extended functionality without exhaustion in a pattern of effector and memory programming in multiple cancer indications Montreal, Canada – May 13, 2015— Caprion announced today that Adaptimmune will present data at the American Society of Gene and ...
The Immune System - Holy Angels School
... What is your body’s defense system? • Microscopic organisms and particles can cause sickness. Your body has ways to prevent sickness. • A pathogen is an organism, virus, or protein that causes disease. • The skin provides external protection against pathogens that may enter the body. • Hair, nails, ...
... What is your body’s defense system? • Microscopic organisms and particles can cause sickness. Your body has ways to prevent sickness. • A pathogen is an organism, virus, or protein that causes disease. • The skin provides external protection against pathogens that may enter the body. • Hair, nails, ...
BIOLOGY 212 SI!
... EXPLAIN THE PULSE CHASE EXPERIMENT WHAT ARE THE MAIN DIFFERENCES BETWEEN PROKARYOTIC AND EUKARYOTIC CELLS? ...
... EXPLAIN THE PULSE CHASE EXPERIMENT WHAT ARE THE MAIN DIFFERENCES BETWEEN PROKARYOTIC AND EUKARYOTIC CELLS? ...
Immune System Crossword PARA3002
... 4. A process of controlled cellular suicide; eliminates cells that are unneeded, stressed, or aged. 7. These cells oversee humoral immunity; their descendants differentiate into antibody-producing plasma cells. 10. Acquired immune deficiency syndrome; caused by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV); sy ...
... 4. A process of controlled cellular suicide; eliminates cells that are unneeded, stressed, or aged. 7. These cells oversee humoral immunity; their descendants differentiate into antibody-producing plasma cells. 10. Acquired immune deficiency syndrome; caused by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV); sy ...
MCQs: What cell types can be made tolerant? T
... 8. The autoimmune disease are caused by: (a) a defect in thymus development (b) a defect in the cell mediated immune system (C) a defect in the antibodies mediated immune system (d) an immune response against self-antigens ...
... 8. The autoimmune disease are caused by: (a) a defect in thymus development (b) a defect in the cell mediated immune system (C) a defect in the antibodies mediated immune system (d) an immune response against self-antigens ...
DISEASE - IMMUNE SYSTEM
... These are your first line of defense against pathogens. They guard against all foreign organisms and not just any one specific organism. Two types of non-specific defenses: ...
... These are your first line of defense against pathogens. They guard against all foreign organisms and not just any one specific organism. Two types of non-specific defenses: ...
Immunobiology
... mediates protection against attack by potentially infectious organisms. Malfunctioning of the immune system leads to a number of disorders and diseases. Immunobiology is a comprehensive study of the organization and functioning of the immune system with its network of cells and molecules. Understand ...
... mediates protection against attack by potentially infectious organisms. Malfunctioning of the immune system leads to a number of disorders and diseases. Immunobiology is a comprehensive study of the organization and functioning of the immune system with its network of cells and molecules. Understand ...
Immune Disorders and Imbalances
... Auto immune diseases • The reason why the immune system looses the ability to recognize it’s self is dependent upon a variety of factors. – Lymphocyte programming is ineffective – New proteins appear that the immune system has not had a chance to become acquainted with. – Self antigens look very si ...
... Auto immune diseases • The reason why the immune system looses the ability to recognize it’s self is dependent upon a variety of factors. – Lymphocyte programming is ineffective – New proteins appear that the immune system has not had a chance to become acquainted with. – Self antigens look very si ...
Introduction to Immuno-Oncology
... Mechanisms against cancer development: (1) Cellular immunity- T, NK, & Other innate immune cells (2) Humoral immunity- Cytokines, Abs, etc. ...
... Mechanisms against cancer development: (1) Cellular immunity- T, NK, & Other innate immune cells (2) Humoral immunity- Cytokines, Abs, etc. ...
Lymphatic and Immune System
... the body from all types of pathogens • Protective Chemicals – Acid pH of skin secretions toxic to bacteria – Stomach mucosa secretes HCl to kill pathogens that are ingested – Saliva contains lysozyme to kill bacteria – Mucus traps microorganisms in digestive and respiratory pathways ...
... the body from all types of pathogens • Protective Chemicals – Acid pH of skin secretions toxic to bacteria – Stomach mucosa secretes HCl to kill pathogens that are ingested – Saliva contains lysozyme to kill bacteria – Mucus traps microorganisms in digestive and respiratory pathways ...
Innate immunity against malaria: studies on the mechanisms of Plasmodium -phagocyte interactions and their consequences.
... immunity. The potential for innate immune mechanisms to provide rapid protection against malaria have largely been neglected. Recent studies from animal models, and clinical studies have demonstrated that innate immune cells directed against Plasmodium infected red blood cells contribute to protecti ...
... immunity. The potential for innate immune mechanisms to provide rapid protection against malaria have largely been neglected. Recent studies from animal models, and clinical studies have demonstrated that innate immune cells directed against Plasmodium infected red blood cells contribute to protecti ...
Chapter 18 Answers to Even Numbered Study Questions
... is bound. It also facilitates phagocytosis, as bound antibody acts as an opsonin. And it can interfere sterically with the interaction of viruses or toxins with host cells, preventing their entry. ...
... is bound. It also facilitates phagocytosis, as bound antibody acts as an opsonin. And it can interfere sterically with the interaction of viruses or toxins with host cells, preventing their entry. ...
Matching – Each question is worth 0.5 pt
... Complete the following Diagram of B Cell DNA Gene rearrangement (4 pts) The final Mature B cell will display IgA1 immunoglobulin with V3D1J2 specificity. How many individual rearrangement steps will be required to produce this heavy chain? ...
... Complete the following Diagram of B Cell DNA Gene rearrangement (4 pts) The final Mature B cell will display IgA1 immunoglobulin with V3D1J2 specificity. How many individual rearrangement steps will be required to produce this heavy chain? ...
MICROBIO320 Short Answers – These should be typically 1
... All of the above. Which of the following statements is INCORRECT concerning antigen-specific receptors on B cells? (0.5 pt) A. They are clonally distributed transmembrane molecules. B. They have extensive cytoplasmic domains that interact with intracellular molecules. C. They consist of polypeptides ...
... All of the above. Which of the following statements is INCORRECT concerning antigen-specific receptors on B cells? (0.5 pt) A. They are clonally distributed transmembrane molecules. B. They have extensive cytoplasmic domains that interact with intracellular molecules. C. They consist of polypeptides ...
Lymphatic System - Sizemore's Site
... produced by B cells as a primary immune defense, each molecule and its clones having a unique binding site that can combine with the complementary site of a foreign antigen, as on a virus or bacterium, thereby disabling the antigen and signaling other immune ...
... produced by B cells as a primary immune defense, each molecule and its clones having a unique binding site that can combine with the complementary site of a foreign antigen, as on a virus or bacterium, thereby disabling the antigen and signaling other immune ...
31.5 Overreactions of the Immune System
... • An allergy is a response to a harmless antigen. • Allergies are caused by allergens. – Allergens are antigens that cause an allergic reaction and cause inflammation responses. ...
... • An allergy is a response to a harmless antigen. • Allergies are caused by allergens. – Allergens are antigens that cause an allergic reaction and cause inflammation responses. ...
Immune system

The immune system is a system of many biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease. To function properly, an immune system must detect a wide variety of agents, known as pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, and distinguish them from the organism's own healthy tissue. In many species, the immune system can be classified into subsystems, such as the innate immune system versus the adaptive immune system, or humoral immunity versus cell-mediated immunity.Pathogens can rapidly evolve and adapt, and thereby avoid detection and neutralization by the immune system; however, multiple defense mechanisms have also evolved to recognize and neutralize pathogens. Even simple unicellular organisms such as bacteria possess a rudimentary immune system, in the form of enzymes that protect against bacteriophage infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient eukaryotes and remain in their modern descendants, such as plants and insects. These mechanisms include phagocytosis, antimicrobial peptides called defensins, and the complement system. Jawed vertebrates, including humans, have even more sophisticated defense mechanisms, including the ability to adapt over time to recognize specific pathogens more efficiently. Adaptive (or acquired) immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, leading to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that same pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination.Disorders of the immune system can result in autoimmune diseases, inflammatory diseases and cancer.Immunodeficiency occurs when the immune system is less active than normal, resulting in recurring and life-threatening infections. In humans, immunodeficiency can either be the result of a genetic disease such as severe combined immunodeficiency, acquired conditions such as HIV/AIDS, or the use of immunosuppressive medication. In contrast, autoimmunity results from a hyperactive immune system attacking normal tissues as if they were foreign organisms. Common autoimmune diseases include Hashimoto's thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes mellitus type 1, and systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunology covers the study of all aspects of the immune system.