OPEN UNIVERSITY LIBRARY PROGRAMME SEQUENCE LIST s 100/15 (1972). Tape No. 6HT/70550-
... which students may have had trouble with. He starts by running various solutions through the colorimeter to arrive at a standard curve. This is plotted on a large graph. ...
... which students may have had trouble with. He starts by running various solutions through the colorimeter to arrive at a standard curve. This is plotted on a large graph. ...
Lecture 22 – New HW assignment – Anaerobic metabolism (continued) – Other sugars
... acetyl-CoA) Fatty acids cannot be converted to glucose precursors in animals-degraded completely to acetyl-CoA Plants can convert fatty acids to glucose with the glyoxylate cycle. Glycerol can be converted to to glucose via a DHAP intermediate ...
... acetyl-CoA) Fatty acids cannot be converted to glucose precursors in animals-degraded completely to acetyl-CoA Plants can convert fatty acids to glucose with the glyoxylate cycle. Glycerol can be converted to to glucose via a DHAP intermediate ...
Ketone body metabolism and cardiovascular disease - AJP
... acetyl-CoA to transportable metabolites (see CoA transferasedependent ketogenesis in extrahepatic tissues), inhibits fatty acid oxidation: acetyl-CoA carboxylase catalyzes the conversion of acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA, the lipogenic substrate and an allosteric inhibitor of mitochondrial carnitine palm ...
... acetyl-CoA to transportable metabolites (see CoA transferasedependent ketogenesis in extrahepatic tissues), inhibits fatty acid oxidation: acetyl-CoA carboxylase catalyzes the conversion of acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA, the lipogenic substrate and an allosteric inhibitor of mitochondrial carnitine palm ...
complete
... get them in our diet? • How are proteins digested and absorbed into the blood? How do other tissues and organs get the amino acids out of the blood? • What are plasma proteins and why are they important? Be able to give an example of a plasma protein. • Learn how amino acids can be used in • The syn ...
... get them in our diet? • How are proteins digested and absorbed into the blood? How do other tissues and organs get the amino acids out of the blood? • What are plasma proteins and why are they important? Be able to give an example of a plasma protein. • Learn how amino acids can be used in • The syn ...
Slide 1
... get them in our diet? • How are proteins digested and absorbed into the blood? How do other tissues and organs get the amino acids out of the blood? • What are plasma proteins and why are they important? Be able to give an example of a plasma protein. • Learn how amino acids can be used in • The syn ...
... get them in our diet? • How are proteins digested and absorbed into the blood? How do other tissues and organs get the amino acids out of the blood? • What are plasma proteins and why are they important? Be able to give an example of a plasma protein. • Learn how amino acids can be used in • The syn ...
H - IS MU
... which the body requires, does not result in increased fat oxidation at rest or during exercise in well-nourished individuals; ...
... which the body requires, does not result in increased fat oxidation at rest or during exercise in well-nourished individuals; ...
Fermentation Milos Babic Abstract Fermentation is the process many
... accomplished through conversion of pyruvic acid into CO2 and ethanol. We have examined the process by allowing yeast to ferment glucose, and analyzing the products. Using Benedict’s reagent and Ba(OH)2 test for CO2 , we show that the levels of glucose fall during fermentation, and that carbon dioxid ...
... accomplished through conversion of pyruvic acid into CO2 and ethanol. We have examined the process by allowing yeast to ferment glucose, and analyzing the products. Using Benedict’s reagent and Ba(OH)2 test for CO2 , we show that the levels of glucose fall during fermentation, and that carbon dioxid ...
University of Groningen Interactions between carbohydrate
... organism will solely depend on the production of glucose, mainly by the liver. Glucose can be produced directly through gluconeogenesis from various substrates, such as certain amino acids, lactate and glycerol. The liver is also able to produce glucose indirectly through phosphorylation of glycogen ...
... organism will solely depend on the production of glucose, mainly by the liver. Glucose can be produced directly through gluconeogenesis from various substrates, such as certain amino acids, lactate and glycerol. The liver is also able to produce glucose indirectly through phosphorylation of glycogen ...
The Target of Metformin in Type 2 Diabetes
... agents, the biguanide metformin is the brightest star. Metformin features as first-line pharmacologic treatment for type 2 diabetes in virtually all guidelines and recommendations, its efficacy and tolerability are well tested, and it is safe and cheap. In use in Europe since the late 1950s and rein ...
... agents, the biguanide metformin is the brightest star. Metformin features as first-line pharmacologic treatment for type 2 diabetes in virtually all guidelines and recommendations, its efficacy and tolerability are well tested, and it is safe and cheap. In use in Europe since the late 1950s and rein ...
Toxicology
... o Most useful for sampling o Concentrations of toxins connected to effect on the body ...
... o Most useful for sampling o Concentrations of toxins connected to effect on the body ...
Alpha-Lipoic Acid The Universal Antioxidant
... mitochondria, alpha-lipoic acid is essential for metabolizing carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, and for the conversion of their energy into ATP. Two of these enzyme complexes, PDH (pyruvate dehydrogenase) and alpha-KGDH (alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase) are part of the citric acid cycle (Krebs cy ...
... mitochondria, alpha-lipoic acid is essential for metabolizing carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, and for the conversion of their energy into ATP. Two of these enzyme complexes, PDH (pyruvate dehydrogenase) and alpha-KGDH (alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase) are part of the citric acid cycle (Krebs cy ...
RG 6 - Digestion and Respiration
... 16. Where does the majority of potential energy of glucose reside after fermentation? 17. Under what condition(s) does fermentation occur? 18. Describe what happens during lactic acid fermentation. 19. Why is replenishing NAD+ crucial to cellular metabolism? 20. Summarize the total energy yield from ...
... 16. Where does the majority of potential energy of glucose reside after fermentation? 17. Under what condition(s) does fermentation occur? 18. Describe what happens during lactic acid fermentation. 19. Why is replenishing NAD+ crucial to cellular metabolism? 20. Summarize the total energy yield from ...
IV. Microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA)
... In the 1980’s, ICI (UK) developed a high-density fermentation and downstream process for the production and recovery of Biopol (the trade name used for the range of polymers manufactured by ICI). The process ...
... In the 1980’s, ICI (UK) developed a high-density fermentation and downstream process for the production and recovery of Biopol (the trade name used for the range of polymers manufactured by ICI). The process ...
Document
... of the 3rd phase of Glucose Aerobic oxidation • Stage I The acetyl-CoA is completely oxidized into CO2, with electrons collected by NAD and FAD via a cyclic pathway (tricarboxylic acid cycle) • Stage II Electrons of NADH and FADH2 are transferred to O2 via a series carriers, producing H2O and a H+ g ...
... of the 3rd phase of Glucose Aerobic oxidation • Stage I The acetyl-CoA is completely oxidized into CO2, with electrons collected by NAD and FAD via a cyclic pathway (tricarboxylic acid cycle) • Stage II Electrons of NADH and FADH2 are transferred to O2 via a series carriers, producing H2O and a H+ g ...
Photosynthesis & Respiration
... E absorbing compounds E is transferred to electrons (e-) in matter (chemical bonds) An electron carrier can accept high E e-’s, and transfer them to another compound In Green Plant cells: e- to higher E level in chlorophyll, trapped in two bonds ...
... E absorbing compounds E is transferred to electrons (e-) in matter (chemical bonds) An electron carrier can accept high E e-’s, and transfer them to another compound In Green Plant cells: e- to higher E level in chlorophyll, trapped in two bonds ...
Cellular Respiration Discussion Part 2 Filled In
... For exercise longer than 90 seconds Cellular respiration _____________________ is the only way to make enough ATP. Cellular respiration releases energy more slowly than fermentation. _____________ Well conditioned athletes must pace themselves during a long race. ...
... For exercise longer than 90 seconds Cellular respiration _____________________ is the only way to make enough ATP. Cellular respiration releases energy more slowly than fermentation. _____________ Well conditioned athletes must pace themselves during a long race. ...
檔案下載
... Some fates of glucose •Glycolysis 糖解作用: metabolizes one molecule of glucose to two molecules of pyruvate with the concomitant net production of two molecules of ATP. – The process is anaerobic, O2 is not required – Pyruvate is further processed: •Anarobically through fermentation 發酵作用, two molecule ...
... Some fates of glucose •Glycolysis 糖解作用: metabolizes one molecule of glucose to two molecules of pyruvate with the concomitant net production of two molecules of ATP. – The process is anaerobic, O2 is not required – Pyruvate is further processed: •Anarobically through fermentation 發酵作用, two molecule ...
Slides - Websupport1
... removed from the chain of fatty acid. So after the first round of reaction (as shown in the figure) a fatty acid chain that is 16 carbon long will remain, after the second round of reactions a fatty acid chain that 14 carbon long will ...
... removed from the chain of fatty acid. So after the first round of reaction (as shown in the figure) a fatty acid chain that is 16 carbon long will remain, after the second round of reactions a fatty acid chain that 14 carbon long will ...
CELL RESPIRATION
... of H+ would be highest, and where the concentration would be lowest. 10. Draw a diagram or table that summarizes the ATP yield from the complete breakdown of glucose to carbon dioxide and water. Indicate how many net ATP are formed in glycolysis, how many via the Krebs cycle, and how many are formed ...
... of H+ would be highest, and where the concentration would be lowest. 10. Draw a diagram or table that summarizes the ATP yield from the complete breakdown of glucose to carbon dioxide and water. Indicate how many net ATP are formed in glycolysis, how many via the Krebs cycle, and how many are formed ...
Metabolism 2
... – glycogen breakdown in the liver to release glucose into circulation – lipase in the adipose tissue resulting in release of free fatty acids – gluconeogenesis from amino acids and pyruvate ...
... – glycogen breakdown in the liver to release glucose into circulation – lipase in the adipose tissue resulting in release of free fatty acids – gluconeogenesis from amino acids and pyruvate ...
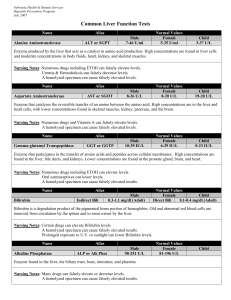
Common Liver Function Tests
... Nursing Notes: Large amounts of IV fluids can cause inaccurate test results. Albumin levels are decreased during pregnancy. Drugs that can increase albumin measurements include anabolic steroids, androgens, growth hormone & insulin ...
... Nursing Notes: Large amounts of IV fluids can cause inaccurate test results. Albumin levels are decreased during pregnancy. Drugs that can increase albumin measurements include anabolic steroids, androgens, growth hormone & insulin ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.