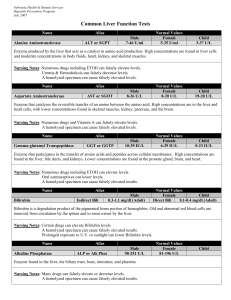
Common Liver Function Tests
... Nursing Notes: Large amounts of IV fluids can cause inaccurate test results. Albumin levels are decreased during pregnancy. Drugs that can increase albumin measurements include anabolic steroids, androgens, growth hormone & insulin ...
... Nursing Notes: Large amounts of IV fluids can cause inaccurate test results. Albumin levels are decreased during pregnancy. Drugs that can increase albumin measurements include anabolic steroids, androgens, growth hormone & insulin ...
Inborn error in metabolism of amino acids
... amino acid.These amino acids serve as an alternate source of fuel for the brain especially under conditions of starvation.metabolism of these amino acid involves loss of the α-amino acid by transamination followed by oxidative decarboxylation of the respective keto acids. . The decarboxylation step ...
... amino acid.These amino acids serve as an alternate source of fuel for the brain especially under conditions of starvation.metabolism of these amino acid involves loss of the α-amino acid by transamination followed by oxidative decarboxylation of the respective keto acids. . The decarboxylation step ...
Energy Systems PPT
... The exercise intensity at which lactic acid begins to accumulate within the blood The point during exercise where the person begins to feel discomfort and burning sensations in their muscles Lactic acid is used to store pyruvate and hydrogen ions until they can be processed by the aerobic system ...
... The exercise intensity at which lactic acid begins to accumulate within the blood The point during exercise where the person begins to feel discomfort and burning sensations in their muscles Lactic acid is used to store pyruvate and hydrogen ions until they can be processed by the aerobic system ...
File
... [4] Cleavage of fumarate from argininosuccinate leads to the proteinogenic amino acid arginine, which is synthesized in this way in animal metabolism. [5] In the final step, urea is released from the guanidinium group of the arginine by hydrolysis , and is immediately rearranged into urea. In addit ...
... [4] Cleavage of fumarate from argininosuccinate leads to the proteinogenic amino acid arginine, which is synthesized in this way in animal metabolism. [5] In the final step, urea is released from the guanidinium group of the arginine by hydrolysis , and is immediately rearranged into urea. In addit ...
(a) (b)
... Citric Acid Cycle Intermediates and Many Amino Acids Are Glucogenic Citrate, isocitrate, -ketoglutarate, succinyl-CoA, succinate, fumarate, and malate—all are citric acid cycle intermediates that can undergo oxidation ...
... Citric Acid Cycle Intermediates and Many Amino Acids Are Glucogenic Citrate, isocitrate, -ketoglutarate, succinyl-CoA, succinate, fumarate, and malate—all are citric acid cycle intermediates that can undergo oxidation ...
The Science of Energy Metabolism
... Energy metabolism involves a symphony of interlinked chemical, hormonal and neurotransmitter cascades, which put in simple terms, provide us with the fuel we need to perform our daily functions. Energy allows the body to perform work and is fundamental for all living organisms. Humans need to obtain ...
... Energy metabolism involves a symphony of interlinked chemical, hormonal and neurotransmitter cascades, which put in simple terms, provide us with the fuel we need to perform our daily functions. Energy allows the body to perform work and is fundamental for all living organisms. Humans need to obtain ...
Preparation for Exam 1
... becomes a major source of reduced coenzymes to drive electron transport. You should be able to determine the number of ATPs that are formed when any compound in glycolysis or the Krebs cycle is broken down to CO2 and H2O. Know how the pentose phosphate pathway provides the cell with NADPH and allows ...
... becomes a major source of reduced coenzymes to drive electron transport. You should be able to determine the number of ATPs that are formed when any compound in glycolysis or the Krebs cycle is broken down to CO2 and H2O. Know how the pentose phosphate pathway provides the cell with NADPH and allows ...
Cell Respiration Key
... 7. Like aerobic respiration, alcoholic fermentation produces CO2 8. The ATP yield of fermentation is much 9. The buildup of lactic acid ...
... 7. Like aerobic respiration, alcoholic fermentation produces CO2 8. The ATP yield of fermentation is much 9. The buildup of lactic acid ...
Pantothenic Acid - Pure Encapsulations
... acid is a precursor of coenzyme A (CoA), an important cofactor and acyl group carrier in cells. One of the main functions for CoA is the formation of acetyl-CoA, vital for cellular respiration and the metabolism of carbohydrates and fatty acids through the Kreb’s cycle. In the first step of the cycl ...
... acid is a precursor of coenzyme A (CoA), an important cofactor and acyl group carrier in cells. One of the main functions for CoA is the formation of acetyl-CoA, vital for cellular respiration and the metabolism of carbohydrates and fatty acids through the Kreb’s cycle. In the first step of the cycl ...
Chemical Elements and water
... enzymes) will have non-polar regions in the active site for hydrophobic, non-polar molecules such as triglycerides to bind. On the other hand, carbohydrates (which digest carbohydrates) will have polar regions in the active site for hydrophilic molecules to bind. Remember, within the active site onl ...
... enzymes) will have non-polar regions in the active site for hydrophobic, non-polar molecules such as triglycerides to bind. On the other hand, carbohydrates (which digest carbohydrates) will have polar regions in the active site for hydrophilic molecules to bind. Remember, within the active site onl ...
CHAPTER OBJECTIVES Topic 1: Introduction 1. Know the
... associated with each level of structure. 3. List the four fundamental bonding interactions found in all proteins. 4. Describe the difference between a structural domain and a subunit. 5. Explain specifically how extreme pH, detergents, heat, high salt concentration, or the addition of a reagent such ...
... associated with each level of structure. 3. List the four fundamental bonding interactions found in all proteins. 4. Describe the difference between a structural domain and a subunit. 5. Explain specifically how extreme pH, detergents, heat, high salt concentration, or the addition of a reagent such ...
TRACE ELEMENTS
... The body contains about 25 mg. of iodine. A small percentage of this is in the muscles, 20 percent is in the thyroid, and the rest is in the skin and bones. Iodine is well absorbed from the stomach into the blood. About 30 percent goes to the thyroid gland, depending on the need. Iodine is eliminate ...
... The body contains about 25 mg. of iodine. A small percentage of this is in the muscles, 20 percent is in the thyroid, and the rest is in the skin and bones. Iodine is well absorbed from the stomach into the blood. About 30 percent goes to the thyroid gland, depending on the need. Iodine is eliminate ...
chapt07_lecture - Globe
... • In ethanol fermentation, which occurs in yeasts, NAD+ and ethanol are produced; this is the source of ethanol for wine and beer • In lactic acid fermentation, carried out in the muscle cells of animals, NAD+ and lactate (lactic acid) are produced ...
... • In ethanol fermentation, which occurs in yeasts, NAD+ and ethanol are produced; this is the source of ethanol for wine and beer • In lactic acid fermentation, carried out in the muscle cells of animals, NAD+ and lactate (lactic acid) are produced ...
Glucose
... one substrate level prosphorylation; • Generation: one FADH2,three NADH+H+,two CO2, one GTP; • Key enzyme:citrate synthase, isocitrate dehydrogenase, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex. ...
... one substrate level prosphorylation; • Generation: one FADH2,three NADH+H+,two CO2, one GTP; • Key enzyme:citrate synthase, isocitrate dehydrogenase, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex. ...
Energy Conversion Pathways 1. Substrate level phosphorylation
... of the CAC reaction steps [succinyl CoA synthetase] that couples GTP synthesis to thioester bond cleavage. Without Pi, this enzyme reaction is inhibited and radioactive carbon would only be found in cycle intermediates that precede this reaction step. 29. The addition of citrate increased the capaci ...
... of the CAC reaction steps [succinyl CoA synthetase] that couples GTP synthesis to thioester bond cleavage. Without Pi, this enzyme reaction is inhibited and radioactive carbon would only be found in cycle intermediates that precede this reaction step. 29. The addition of citrate increased the capaci ...
Dear Notetaker:
... o Whenever it is dephosphorylated it is active o When it is phosphorylated it is inactive Ketone bodies o Other metabolic fuel that the cell can be used o Used under conditions of fasting or starvation o Become relevant when we have moved away from the supply of glucose What can happen to glucose? o ...
... o Whenever it is dephosphorylated it is active o When it is phosphorylated it is inactive Ketone bodies o Other metabolic fuel that the cell can be used o Used under conditions of fasting or starvation o Become relevant when we have moved away from the supply of glucose What can happen to glucose? o ...
CH 2
... 4) In order to control ribose synthesis, a mechanism exists to remove this sugar when it is in excess, by converting it to glycolytic intermediates. A series of three enzymatic steps are carried out, transferring two- and three-carbon fragments from one sugar to another, and all of these steps are ...
... 4) In order to control ribose synthesis, a mechanism exists to remove this sugar when it is in excess, by converting it to glycolytic intermediates. A series of three enzymatic steps are carried out, transferring two- and three-carbon fragments from one sugar to another, and all of these steps are ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.























