Zdroje volných radikál* ROS
... • Hyperglycemia is a major symptom of diabetes- high concentration of glucose – reactive molecule • Covalent bond of aldehyde group glucose to amine group of proteins = glycation (Shiff base) • Non-enzymatic glycation • -early stage-hours-Shiff´s bases – ketomines • -transitional stage-days-Amadori ...
... • Hyperglycemia is a major symptom of diabetes- high concentration of glucose – reactive molecule • Covalent bond of aldehyde group glucose to amine group of proteins = glycation (Shiff base) • Non-enzymatic glycation • -early stage-hours-Shiff´s bases – ketomines • -transitional stage-days-Amadori ...
File
... disease extend well beyond just the obvious hypoglycemia that results from the deficiency in liver being able to deliver free glucose to the blood. The inability to release the phosphate from glucose-6-phopsphate results in diversion into glycolysis and production of pyruvate as well as increased di ...
... disease extend well beyond just the obvious hypoglycemia that results from the deficiency in liver being able to deliver free glucose to the blood. The inability to release the phosphate from glucose-6-phopsphate results in diversion into glycolysis and production of pyruvate as well as increased di ...
Metabolism of pentoses, glycogen, Fru and Gal
... Different role of glycogen stores in the liver and muscles Glycogen synthesis and degradation are separate pathways (regulation) Glycogen storage diseases ...
... Different role of glycogen stores in the liver and muscles Glycogen synthesis and degradation are separate pathways (regulation) Glycogen storage diseases ...
A fatty acid
... One fatty acid replaced by phosphate PO4 Molecule has Hydrophilic head, and long ...
... One fatty acid replaced by phosphate PO4 Molecule has Hydrophilic head, and long ...
NUTRITIONAL INTEREST OF CHEESE FAT A lot of new datas
... Meta-analysis (Siri-Tarino 2010) : 21 cohorts ”Overall, despite the conventional wisdom that reduced dietary saturated fat intake is beneficial for CVD health, there is no significant evidence for concluding that dietary saturated fat is associated with an increased risk of CHD or CVD” ...
... Meta-analysis (Siri-Tarino 2010) : 21 cohorts ”Overall, despite the conventional wisdom that reduced dietary saturated fat intake is beneficial for CVD health, there is no significant evidence for concluding that dietary saturated fat is associated with an increased risk of CHD or CVD” ...
Aminoaciduria
... 1- The disease should not be clinically apparent at the time of screening 2- The disease should have a relatively high incidence in the population screened. 3- The disease should be treatable & so results of screening test must be obtained before irreversible damage is likely to have occurred. 4- Sc ...
... 1- The disease should not be clinically apparent at the time of screening 2- The disease should have a relatively high incidence in the population screened. 3- The disease should be treatable & so results of screening test must be obtained before irreversible damage is likely to have occurred. 4- Sc ...
CHEM 331 Problem Set #6
... the oxidation of β-D-glucose to D-glucono-δ-lactone. This enzyme is highly specific for the β anomer of glucose and does not affect the α anomer. In spite of this specificity, the reaction catalyzed by glucose oxidase is commonly used in a clinical assay for total blood glucose—that is, for solution ...
... the oxidation of β-D-glucose to D-glucono-δ-lactone. This enzyme is highly specific for the β anomer of glucose and does not affect the α anomer. In spite of this specificity, the reaction catalyzed by glucose oxidase is commonly used in a clinical assay for total blood glucose—that is, for solution ...
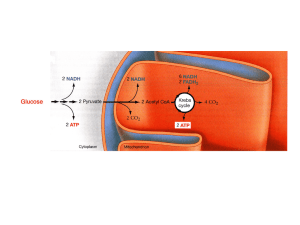
Complete breakdown of Glucose:
... B) Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle): C C - CoA (x 2) Acetyl CoA 3 NAD+ (x 2) 3 NADH ATP ...
... B) Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle): C C - CoA (x 2) Acetyl CoA 3 NAD+ (x 2) 3 NADH ATP ...
Cellular Respiration Activity 9 1. The summary formula for cellular
... If NAD is unavailable, the cell is unable to conduct any processes that involve the conversion of NAD to NADH. Because both glycolysis and the Krebs cycle produce NADH, both of these processes shut down when there is no available.NAD. 5. If the Krebs cycle does not require oxygen, why does cellula ...
... If NAD is unavailable, the cell is unable to conduct any processes that involve the conversion of NAD to NADH. Because both glycolysis and the Krebs cycle produce NADH, both of these processes shut down when there is no available.NAD. 5. If the Krebs cycle does not require oxygen, why does cellula ...
HUMAN BIOCHEMISTRY
... Benefits and Concerns of Genetically Modified Foods Crops and animals can be genetically modified to provide more food, be more resistant to disease, or be more tolerant to heavy metals (among many other characteristics). Genetic engineering involves the process of selecting a single gene for a ...
... Benefits and Concerns of Genetically Modified Foods Crops and animals can be genetically modified to provide more food, be more resistant to disease, or be more tolerant to heavy metals (among many other characteristics). Genetic engineering involves the process of selecting a single gene for a ...
Monogastric Nutrition
... – Hydration, medium for moving wastes into and out of body – Component of milk, lubricates joints, cushions nerves, disperses heat, protects developing fetuses ...
... – Hydration, medium for moving wastes into and out of body – Component of milk, lubricates joints, cushions nerves, disperses heat, protects developing fetuses ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION Fates of Pyruvate from glycolysis (2
... CELLULAR RESPIRATION Metabolism—the sum of all biochemical reactions in an organism or cell. a) anabolic—synthesis of compounds; an example is photosynthesis b) catabolic—breakdown of compounds; an example is cellular respiration Metabolic pathways—are the steps (enzymes, substrates and products) us ...
... CELLULAR RESPIRATION Metabolism—the sum of all biochemical reactions in an organism or cell. a) anabolic—synthesis of compounds; an example is photosynthesis b) catabolic—breakdown of compounds; an example is cellular respiration Metabolic pathways—are the steps (enzymes, substrates and products) us ...
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL
... ent exists in a single homogeneous pool and an awareness of the existence of metabolic pools is essential to an understanding of human metabolism. For example, one might expect that a fasted individual would show a fall in all essential nutrient levels in the plasma pool. In many instances this is n ...
... ent exists in a single homogeneous pool and an awareness of the existence of metabolic pools is essential to an understanding of human metabolism. For example, one might expect that a fasted individual would show a fall in all essential nutrient levels in the plasma pool. In many instances this is n ...
ORGANIC ACIDS – Citric Acid Cycle (urine)
... all nutrients. The complete metabolism for each nutrient must go through the citric acid cycle. This cycle is also an important source of biosynthetic building blocks used in gluconeogenesis, amino acid biosynthesis and fatty acid biosynthesis. The citric cycle takes place in mitochondria where it o ...
... all nutrients. The complete metabolism for each nutrient must go through the citric acid cycle. This cycle is also an important source of biosynthetic building blocks used in gluconeogenesis, amino acid biosynthesis and fatty acid biosynthesis. The citric cycle takes place in mitochondria where it o ...
Anaerobic and Aerobic Glycolysis
... energy is required in the absence of oxygen. It is vital for tissues with high energy requirements, insufficient oxygen supply or absence of oxidative enzymes. Glycolysis produces reduced forms of NAD in the energy generation phase. In an anaerobic environment, lactate dehydrogenase converts pyruvat ...
... energy is required in the absence of oxygen. It is vital for tissues with high energy requirements, insufficient oxygen supply or absence of oxidative enzymes. Glycolysis produces reduced forms of NAD in the energy generation phase. In an anaerobic environment, lactate dehydrogenase converts pyruvat ...
Chemistry 400
... _____ Prolonged deficiency of vitamin D will result in increased density of bone. _____ Vitamin K1 is present in high concentrations in cow’s or breast milk. _____ Water-soluble vitamins are stored in adipose tissue and not easily excreted. _____ Fat-soluble vitamins are isoprenoids. _____ Vitamin E ...
... _____ Prolonged deficiency of vitamin D will result in increased density of bone. _____ Vitamin K1 is present in high concentrations in cow’s or breast milk. _____ Water-soluble vitamins are stored in adipose tissue and not easily excreted. _____ Fat-soluble vitamins are isoprenoids. _____ Vitamin E ...
Biological Molecules Review Questions 2015
... 40. A lipid molecule is produced when A. fatty acids bond to glycerol. B. amino acids bond to glycerol. C. monosaccharides bond to glycogen. D. dehydration occurs between fatty acids and glycogen. 41. Lipids are composed of A. nucleotides. B. amino acids. C. monosaccharides. D. glycerol and fatty ac ...
... 40. A lipid molecule is produced when A. fatty acids bond to glycerol. B. amino acids bond to glycerol. C. monosaccharides bond to glycogen. D. dehydration occurs between fatty acids and glycogen. 41. Lipids are composed of A. nucleotides. B. amino acids. C. monosaccharides. D. glycerol and fatty ac ...
Integration of Metabolism
... b. A 100m sprint takes about 10s and is powered mainly by ATP stored in the muscle, creatine phosphate, and some anaerobic glycolysis c. A whole kilometer takes longer, you can’t run as fast, and you rapidly deplete creatine phosphate i. Anaerobic glycolysis starts becoming a problem because you sta ...
... b. A 100m sprint takes about 10s and is powered mainly by ATP stored in the muscle, creatine phosphate, and some anaerobic glycolysis c. A whole kilometer takes longer, you can’t run as fast, and you rapidly deplete creatine phosphate i. Anaerobic glycolysis starts becoming a problem because you sta ...
Cells and Energy Cellular Respiration Chapter 2 Lesson 4 Part 1
... environments that do not have oxygen available. Many bacteria in the lower layers of swamps, lakes, or the ocean do not have oxygen. ...
... environments that do not have oxygen available. Many bacteria in the lower layers of swamps, lakes, or the ocean do not have oxygen. ...
Glycolysis and the Catabolism of Hexoses
... wasteful “futile cycling” • Gluconeogenesis: The pathway converting simpler precursors (e.g., pyruvate and lactate) to glucose, mainly occurring in the liver of mammals. • Gluconeogenesis uses most of the same enzymes of glycolysis, but the three exergonic irreversible reactions (catalyzed by the th ...
... wasteful “futile cycling” • Gluconeogenesis: The pathway converting simpler precursors (e.g., pyruvate and lactate) to glucose, mainly occurring in the liver of mammals. • Gluconeogenesis uses most of the same enzymes of glycolysis, but the three exergonic irreversible reactions (catalyzed by the th ...
Glycogen Metabolism
... The transferase transfers 3 glucose residues from a 4-residue limit branch to the end of another branch, reducing the limit branch to a single glucose residue. ...
... The transferase transfers 3 glucose residues from a 4-residue limit branch to the end of another branch, reducing the limit branch to a single glucose residue. ...
Cellular Respiration - Labs - Department of Plant Biology, Cornell
... fermentation as a simple breaking up of sugar into alcohol and carbonic acid! Undeceive yourselves…. Ah! So you are bound to ignore the yeast in this phenomenon, or at the most will concede to it only the role of initiator! Very well! Learn that this yeast always borrows something from the sugar, an ...
... fermentation as a simple breaking up of sugar into alcohol and carbonic acid! Undeceive yourselves…. Ah! So you are bound to ignore the yeast in this phenomenon, or at the most will concede to it only the role of initiator! Very well! Learn that this yeast always borrows something from the sugar, an ...
Fatty Acid Synthesis
... De novo synthesis of FAs In mammals fatty acid synthesis occurs primarily in the cytosol of the liver and adipose tissues .It also occurs in mammary glands during lactation. Acetyl-CoA is the starting material for FA synthesis. However, most acetyl-CoA in mitochondria(from the breakdown of suga ...
... De novo synthesis of FAs In mammals fatty acid synthesis occurs primarily in the cytosol of the liver and adipose tissues .It also occurs in mammary glands during lactation. Acetyl-CoA is the starting material for FA synthesis. However, most acetyl-CoA in mitochondria(from the breakdown of suga ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.