Document
... The brain problem… Most energy stored as fatty acids Brain only uses Glc Fatty acids Glc? How does brain function during starvation? ...
... The brain problem… Most energy stored as fatty acids Brain only uses Glc Fatty acids Glc? How does brain function during starvation? ...
KETONE BODY METABOLISM - Qassim College of Medicine
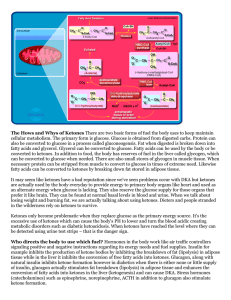
... release H+ ions, which lowers the pH. This decrease in blood pH as a result of severe ketosis is called as Ketoacidosis. ...
... release H+ ions, which lowers the pH. This decrease in blood pH as a result of severe ketosis is called as Ketoacidosis. ...
Concepts in Biochemistry 3/e
... G6P can be degraded via pentose phosphate pathway (to generate NADPH required for f.acids biosynthesis and liver’s many other biosynthetic functions) ...
... G6P can be degraded via pentose phosphate pathway (to generate NADPH required for f.acids biosynthesis and liver’s many other biosynthetic functions) ...
KetoVie Peptide Letter of Medical Necessity (PDCD)
... Ketosis occurs when the body is utilizing fat as a primary fuel source in the place of glucose. Ketones are able to be metabolized as an alternative fuel source and avoids the damaging build-up of lactic acid occurring from the impaired carbohydrate metabolism. KetoVie Peptide 4:1 is a specialized k ...
... Ketosis occurs when the body is utilizing fat as a primary fuel source in the place of glucose. Ketones are able to be metabolized as an alternative fuel source and avoids the damaging build-up of lactic acid occurring from the impaired carbohydrate metabolism. KetoVie Peptide 4:1 is a specialized k ...
2015FallNSC408
... 2. In which of the following tissue does gluconeogenesis take place? a. Muscle b. Liver c. Adipose 3. Gluconeogenesis produces glucose from amino acids. a. True b. False 4. When an amino acid is metabolized to Acetyl CoA, how many net carbons are contributed for the synthesis of glucose via gluconeo ...
... 2. In which of the following tissue does gluconeogenesis take place? a. Muscle b. Liver c. Adipose 3. Gluconeogenesis produces glucose from amino acids. a. True b. False 4. When an amino acid is metabolized to Acetyl CoA, how many net carbons are contributed for the synthesis of glucose via gluconeo ...
What is Ketosis
... OOC-CH2-C-CH3 O CO2 NADH + H+ NAD+ CH3-C-CH3 OOC-CH2-CH-CH3 O Acetone OH -hydroxybutyrate ...
... OOC-CH2-C-CH3 O CO2 NADH + H+ NAD+ CH3-C-CH3 OOC-CH2-CH-CH3 O Acetone OH -hydroxybutyrate ...
Acetyl CoA
... yields D-bhydroxybutyrate (do not confuse with L- bhydroxybutyrate of the boxidation pathway). 5. Acetoacetate is easily decarboxylated (may be spontaneously or enzymatically) to acetone and CO2. ...
... yields D-bhydroxybutyrate (do not confuse with L- bhydroxybutyrate of the boxidation pathway). 5. Acetoacetate is easily decarboxylated (may be spontaneously or enzymatically) to acetone and CO2. ...
NME2.29 - Fat and Carbohydrate Metabolism 2
... Fatty acid oxidation produces acetyl-CoA that allosterically activates pyruvate carboxylase Pyruvate carboxylase is a crucial enzymes in gluconeogenesis Defects in fatty acid oxidation may reduce production of acetyl-CoA and hence inhibit gluconeogenesis If the body cannot synthesise glucose ‘on dem ...
... Fatty acid oxidation produces acetyl-CoA that allosterically activates pyruvate carboxylase Pyruvate carboxylase is a crucial enzymes in gluconeogenesis Defects in fatty acid oxidation may reduce production of acetyl-CoA and hence inhibit gluconeogenesis If the body cannot synthesise glucose ‘on dem ...
Pertubation of metabolism in IDD Q3-5 Joe - PBL-J-2015
... pathways of fatty acid metabolism that are up regulated The oversupply of fatty acids in the liver cells (in the absence of insulin) leads to the up regulation of the β-oxidation of these fatty acids in the mitochondrial cells of the liver. This is initiated when excess supply of fatty acids trigger ...
... pathways of fatty acid metabolism that are up regulated The oversupply of fatty acids in the liver cells (in the absence of insulin) leads to the up regulation of the β-oxidation of these fatty acids in the mitochondrial cells of the liver. This is initiated when excess supply of fatty acids trigger ...
Slide 1
... After 48 hours in ketosis, the brain increases its use of ketone bodies and reduces its reliance on glucose, thus reducing the degree of muscle wasting necessary to support ketosis. ...
... After 48 hours in ketosis, the brain increases its use of ketone bodies and reduces its reliance on glucose, thus reducing the degree of muscle wasting necessary to support ketosis. ...
Pathology Ketone bodies are created at moderate
... excessive use of ketones which can cause the body's PH to lower and turn the blood acidic creating metabolic disorders such as diabetic ketoacidosis. When ketones have reached the level where they can be detected using urine test strips – that is the danger sign. Who directs the body to use which fu ...
... excessive use of ketones which can cause the body's PH to lower and turn the blood acidic creating metabolic disorders such as diabetic ketoacidosis. When ketones have reached the level where they can be detected using urine test strips – that is the danger sign. Who directs the body to use which fu ...
ketone bodies
... gluconeogensis, it is less available for citrate synthase and AcCoA accumulates. As concentration of AcCoA increases it inhibits PDH and stimulates pyruvate carboxylase, further favoring the diversion of pyruvate for gluconeogenesis (pyr OAA PEP). In addition, as the concentration of AcCoA increases ...
... gluconeogensis, it is less available for citrate synthase and AcCoA accumulates. As concentration of AcCoA increases it inhibits PDH and stimulates pyruvate carboxylase, further favoring the diversion of pyruvate for gluconeogenesis (pyr OAA PEP). In addition, as the concentration of AcCoA increases ...
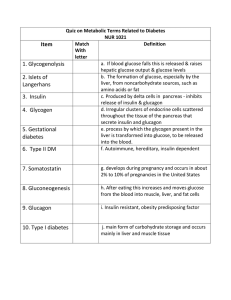
Quiz on Metabolic Terms Related to Diabetes NUR 1021 Item Match
... a. If blood glucose falls this is released & raises 1. Glycogenolysis hepatic glucose output & glucose levels b. The formation of glucose, especially by the 2. Islets of liver, from noncarbohydrate sources, such as Langerhans amino acids or fat c. Produced by delta cells in pancreas - inhibits 3. In ...
... a. If blood glucose falls this is released & raises 1. Glycogenolysis hepatic glucose output & glucose levels b. The formation of glucose, especially by the 2. Islets of liver, from noncarbohydrate sources, such as Langerhans amino acids or fat c. Produced by delta cells in pancreas - inhibits 3. In ...
The ketogenic diet
... the liver converts fat into fatty acids and ketone bodies. The ketone bodies pass into the brain and replace glucose as an energy source. ...
... the liver converts fat into fatty acids and ketone bodies. The ketone bodies pass into the brain and replace glucose as an energy source. ...
Metabolism of the whole organism
... • uses keto acids for fuel • Kidney: needs energy for active transport • uses FA, KB, glucose, amino acids, • gluneogenic tissue ...
... • uses keto acids for fuel • Kidney: needs energy for active transport • uses FA, KB, glucose, amino acids, • gluneogenic tissue ...
Acyl-CoA synthetases : Fatty acid +CoA + ATP → fatty acyl
... • Ketone bodies in the blood and urine of untreated diabetics can reach extraordinary levels, a condition called ketosis. • In individuals on every low-calorie diets, using the fats stored in adipose tissue as their major energy source, levels of ketone bodies in the blood and urine must be monitor ...
... • Ketone bodies in the blood and urine of untreated diabetics can reach extraordinary levels, a condition called ketosis. • In individuals on every low-calorie diets, using the fats stored in adipose tissue as their major energy source, levels of ketone bodies in the blood and urine must be monitor ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.