Proseminar 3: Questions and Answers
... student) Can ganglia take up and utilise fatty acids from the blood? Answer: FK: In fact, free fatty acids are taken up by the brain (so-called lipid-mediated transport), but this is not sufficient for complete energy supply. So the question is, why there is no specific carrier or receptor to pass t ...
... student) Can ganglia take up and utilise fatty acids from the blood? Answer: FK: In fact, free fatty acids are taken up by the brain (so-called lipid-mediated transport), but this is not sufficient for complete energy supply. So the question is, why there is no specific carrier or receptor to pass t ...
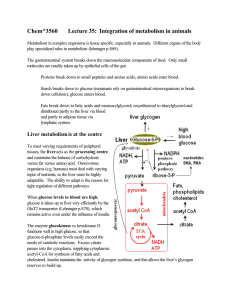
Chem*3560 Lecture 35: Integration of metabolism in animals
... at least a part of their carbon skeleton available either as pyruvate or as TCA cycle intermediates such as succinate, fumarate or oxaloacetate (Lehninger p. 872). ...
... at least a part of their carbon skeleton available either as pyruvate or as TCA cycle intermediates such as succinate, fumarate or oxaloacetate (Lehninger p. 872). ...
MAKEUP: Briefly discuss functions of the liver
... o CHO: glycogenesis ↑glucose trapping (hepatocytes) 2° ↑glucokinase activity o Fat: Fatty acid formation • Once maximal glycogen stores → glucose metabolised to pyruvate → AcetylCoA → fatty acid Cholesterol / phospholipid formation o Protein synthesis Lipoproteins - Catabolic Functions: o CH ...
... o CHO: glycogenesis ↑glucose trapping (hepatocytes) 2° ↑glucokinase activity o Fat: Fatty acid formation • Once maximal glycogen stores → glucose metabolised to pyruvate → AcetylCoA → fatty acid Cholesterol / phospholipid formation o Protein synthesis Lipoproteins - Catabolic Functions: o CH ...
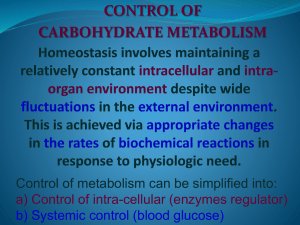
Control of intra-cellular (enzyme regulator)
... Fatty acid biosynthesis occurs in the cytosol, whereas fatty acid oxidation takes place within mitochondria Segregation of certain metabolic pathways within specialized cell types can provide further physical compartmentation. ...
... Fatty acid biosynthesis occurs in the cytosol, whereas fatty acid oxidation takes place within mitochondria Segregation of certain metabolic pathways within specialized cell types can provide further physical compartmentation. ...
Substrate Metabolism – Rest vs Stress
... SP Notes Primary Notes - rest = basal metabolic rate + minimal exercise - major stress = 50% burn - aim = to preserve plasma glucose levels for brain metabolism. REST - least expensive form of energy production utilized: carbohydrate -> fat -> protein in decreasing ratios. Carbohydrate Sources ...
... SP Notes Primary Notes - rest = basal metabolic rate + minimal exercise - major stress = 50% burn - aim = to preserve plasma glucose levels for brain metabolism. REST - least expensive form of energy production utilized: carbohydrate -> fat -> protein in decreasing ratios. Carbohydrate Sources ...
Learning Objectives Chapter 2 Biochem [10-30
... Muscle: use glucose from the blood or from own glycogen stores; convert glucose to lactate through glycolysis or oxidize it to CO2 and H2O. Muscle also uses other fuels from the blood like fatty acids Adipose tissue: Insulin stimulates transport of glucose into adipose cells. Adipocytes oxidize gluc ...
... Muscle: use glucose from the blood or from own glycogen stores; convert glucose to lactate through glycolysis or oxidize it to CO2 and H2O. Muscle also uses other fuels from the blood like fatty acids Adipose tissue: Insulin stimulates transport of glucose into adipose cells. Adipocytes oxidize gluc ...
BDS Ist YEAR EXAMINATION 2008-09
... Cyanide is toxic because it: a) Inhibits cytochrome C oxidase b) Forms cyanmethaemoglobin c) Inhibits ATP carrier in mitochondria d) Inhibits Na+-K+ ATPase ...
... Cyanide is toxic because it: a) Inhibits cytochrome C oxidase b) Forms cyanmethaemoglobin c) Inhibits ATP carrier in mitochondria d) Inhibits Na+-K+ ATPase ...
Assimilation vs Absorption
... blood stream reaches the liver. Here, the excess glucose is stored as glycogen to be used in times of need. The cells take the glucose they need from the blood directly for respiration. The amino acids are used to form new proteins. ...
... blood stream reaches the liver. Here, the excess glucose is stored as glycogen to be used in times of need. The cells take the glucose they need from the blood directly for respiration. The amino acids are used to form new proteins. ...
幻灯片 1
... the fatty acids from which they are derived but they make up for this deficiency by serving as “water-soluble lipids” that can be more readily transported in the blood plasma. During starvation, ketone bodies are produced in large amounts becoming substitutes for glucose as the principal fuel for br ...
... the fatty acids from which they are derived but they make up for this deficiency by serving as “water-soluble lipids” that can be more readily transported in the blood plasma. During starvation, ketone bodies are produced in large amounts becoming substitutes for glucose as the principal fuel for br ...
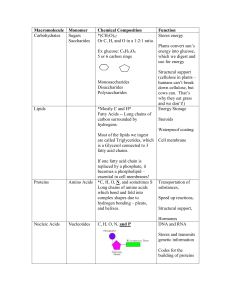
Macromolecule
... Stores energy Or C, H, and O in a 1:2:1 ratio. Plants convert sun’s Ex glucose: C6H12O6 energy into glucose, 5 or 6 carbon rings which we digest and use for energy ...
... Stores energy Or C, H, and O in a 1:2:1 ratio. Plants convert sun’s Ex glucose: C6H12O6 energy into glucose, 5 or 6 carbon rings which we digest and use for energy ...
nutritional terminology
... A polysaccharide; the main storage form of carbohydrate, mainly stored in the liver and muscles. ...
... A polysaccharide; the main storage form of carbohydrate, mainly stored in the liver and muscles. ...
2008b(12): Detail the protective and regulatory roles of the liver
... - the actions of these macrophages are an example of innate immunity - Kupffer Cell activitation initiates a chain of events: o phagocytosis → complement activation → recruitment of other cells - can function as a blood reservoir: o 450mL in the liver at resting state o can ↑ to 1500mL in fluid over ...
... - the actions of these macrophages are an example of innate immunity - Kupffer Cell activitation initiates a chain of events: o phagocytosis → complement activation → recruitment of other cells - can function as a blood reservoir: o 450mL in the liver at resting state o can ↑ to 1500mL in fluid over ...
classsssssss
... abnormal in these enzymes. The patient is most likely to have which of the following findings? • A. citrullinemia • B. Methylmalonic aciduria • C. homocystinuria • D. orotic aciduria • E. lactic acidosis ...
... abnormal in these enzymes. The patient is most likely to have which of the following findings? • A. citrullinemia • B. Methylmalonic aciduria • C. homocystinuria • D. orotic aciduria • E. lactic acidosis ...
Organ Integration and Control
... breakdown fat to extract the glycerol and fatty acids. The glycerol is used to make glucose but the fatty acids are used directly by many organs as a source of energy (not brain or RBC). As fatty acid metabolism increases the liver begins to convert some of the acetyl-CoA in so-called ketone bodies. ...
... breakdown fat to extract the glycerol and fatty acids. The glycerol is used to make glucose but the fatty acids are used directly by many organs as a source of energy (not brain or RBC). As fatty acid metabolism increases the liver begins to convert some of the acetyl-CoA in so-called ketone bodies. ...
Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
... Ketone bodies are exported from the liver to other tissues to be used as fuel. ...
... Ketone bodies are exported from the liver to other tissues to be used as fuel. ...
Powerpoint Slides for Chapter Seven
... Fatty acids leave small intestine via lymph Lymph converges with blood stream Fatty acids taken directly to fat cells and stored as fat (triglyceride) No metabolism involved ...
... Fatty acids leave small intestine via lymph Lymph converges with blood stream Fatty acids taken directly to fat cells and stored as fat (triglyceride) No metabolism involved ...
Document
... considerably depending on lipolysis rates > uptake: free diffusion across the plasma membrane > rate of uptake is proportional to plasma concentration • Fatty acid utilization is governed by demand, ensuring fuel economy > FAD and NAD are necessary for b-oxidation > these factors are limiting in cel ...
... considerably depending on lipolysis rates > uptake: free diffusion across the plasma membrane > rate of uptake is proportional to plasma concentration • Fatty acid utilization is governed by demand, ensuring fuel economy > FAD and NAD are necessary for b-oxidation > these factors are limiting in cel ...
Q1 Describe the physiological consequences that
... Upregulates Pyruvate Dehydrogenase, Lipoprotein Lipase and Fatty Acid Synthase to facilitate the breakdown of TAGs to fatty acids for uptake by adipose tissue cells Inhibits Hormone Sensitive lipase to decrease ...
... Upregulates Pyruvate Dehydrogenase, Lipoprotein Lipase and Fatty Acid Synthase to facilitate the breakdown of TAGs to fatty acids for uptake by adipose tissue cells Inhibits Hormone Sensitive lipase to decrease ...
Reading Guide
... glycogen degradation and turning on glycogen synthesis. 16. Liver cells respond to glucagon by _________________________. 17. Muscle does not respond to glucagon, but does respond to ______________________ by releasing stored fuel. 18. How do glucagon and epinephrine stimulate the breakdown of fats? ...
... glycogen degradation and turning on glycogen synthesis. 16. Liver cells respond to glucagon by _________________________. 17. Muscle does not respond to glucagon, but does respond to ______________________ by releasing stored fuel. 18. How do glucagon and epinephrine stimulate the breakdown of fats? ...
Energy metabolism
... possible mechanism(s) were further explored in the present study. In a 4-week experiment, rats were fed a low-fat (70 g/kg) or a high-fat (300 g/kg) diet with or without BM (7.5 g/kg or 0.75%). BM-supplemented rats had lower energy efficiency, visceral fat mass, plasma glucose and hepatic triacylgly ...
... possible mechanism(s) were further explored in the present study. In a 4-week experiment, rats were fed a low-fat (70 g/kg) or a high-fat (300 g/kg) diet with or without BM (7.5 g/kg or 0.75%). BM-supplemented rats had lower energy efficiency, visceral fat mass, plasma glucose and hepatic triacylgly ...
`Keto-adapt` your clients in 3 months in 8 easy steps
... in fat-free mass in individuals following a ketogenic diet. However, some confounding factors exist, such as the use of aggressive weight loss diets and potential concerns with fat-free mass measurement. A limited number of studies have examined combining resistance training with ketogenic diets, an ...
... in fat-free mass in individuals following a ketogenic diet. However, some confounding factors exist, such as the use of aggressive weight loss diets and potential concerns with fat-free mass measurement. A limited number of studies have examined combining resistance training with ketogenic diets, an ...
Ketone bodies
... Ketone bodies Ketone bodies are three water-soluble compounds that are produced as by-products when fatty acids are broken down for energy in the liver and kidney. Two of the three are used as a source of energy in the heart and brain while the third is a waste product excreted from the body. In the ...
... Ketone bodies Ketone bodies are three water-soluble compounds that are produced as by-products when fatty acids are broken down for energy in the liver and kidney. Two of the three are used as a source of energy in the heart and brain while the third is a waste product excreted from the body. In the ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.