Instructor`s Answer Key
... the intestine and thus raise the blood calcium levels, taking vitamin D may help people with osteoporosis raise their blood calcium levels and promote the deposition of bone calcium. 6. Insulin resistance refers to abnormally low tissue sensitivity to the hormone, insulin. Insulin resistance is comp ...
... the intestine and thus raise the blood calcium levels, taking vitamin D may help people with osteoporosis raise their blood calcium levels and promote the deposition of bone calcium. 6. Insulin resistance refers to abnormally low tissue sensitivity to the hormone, insulin. Insulin resistance is comp ...
ENERGY METABOLISM
... The surplus amino acids ARE NOT STORED, but are either: a. released into the blood for all tissues to use in protein synthesis, b. they are with the resulting carbon skeletons being degraded by the liver pyruvate, acetyl CoA, or TCA cycle intermediates, these metabolites can be oxidized for energy o ...
... The surplus amino acids ARE NOT STORED, but are either: a. released into the blood for all tissues to use in protein synthesis, b. they are with the resulting carbon skeletons being degraded by the liver pyruvate, acetyl CoA, or TCA cycle intermediates, these metabolites can be oxidized for energy o ...
Biochemistry Jeopardy
... What is atherosclerosis? Hardening of the arteries, also called atherosclerosis, is a common disorder. It occurs when fat, cholesterol, and other substances build up in the walls of arteries and form ...
... What is atherosclerosis? Hardening of the arteries, also called atherosclerosis, is a common disorder. It occurs when fat, cholesterol, and other substances build up in the walls of arteries and form ...
Biology 12 - Biologically Important Molecules – Review Worksheet
... a fatty acid whose carbons are all joined to the maximum number of hydrogens a fatty acid that has a "kink" in it due to a double bond between carbon atoms a disaccharide consisting of two glucose molecules a class of molecules that includes neutral fats and steroids a chemical that resists changes ...
... a fatty acid whose carbons are all joined to the maximum number of hydrogens a fatty acid that has a "kink" in it due to a double bond between carbon atoms a disaccharide consisting of two glucose molecules a class of molecules that includes neutral fats and steroids a chemical that resists changes ...
BIOL 103 Ch5-2 for Students
... Carbohydrates in the Body • Glucose is your primary fuel (cont.) – Sparing Body Protein • Order of Energy usage by body: _________________ ____________ ____________________ • Adequate carbohydrates prevent body from breaking down proteins to make glucose. ...
... Carbohydrates in the Body • Glucose is your primary fuel (cont.) – Sparing Body Protein • Order of Energy usage by body: _________________ ____________ ____________________ • Adequate carbohydrates prevent body from breaking down proteins to make glucose. ...
Regulation of glycolysis ang glycogen metabolism
... Reaction 1 – The amount of glucose entering the glycolysis pathway decreases when high levels of glucose-6phosphate are present in the cell. Reaction 3 – The enzyme here is inhibited by high levels of ATP (when ATP is plentiful) and activated by high levels of ADP and AMP (the cell has used up much ...
... Reaction 1 – The amount of glucose entering the glycolysis pathway decreases when high levels of glucose-6phosphate are present in the cell. Reaction 3 – The enzyme here is inhibited by high levels of ATP (when ATP is plentiful) and activated by high levels of ADP and AMP (the cell has used up much ...
1 - Chiropractic National Board Review Questions
... 35. Which of the following bonds are found in secondary protein structures? A. Peptide B. H C. S D. Ester 36. Which of the following is a pentose? A. Glucose B. Ribose C. Fructose D. Galactose 37. Which of the following bonds are found in lipids? A. Peptide B. Disulfate C. Ester D. H 38. Decarboxyla ...
... 35. Which of the following bonds are found in secondary protein structures? A. Peptide B. H C. S D. Ester 36. Which of the following is a pentose? A. Glucose B. Ribose C. Fructose D. Galactose 37. Which of the following bonds are found in lipids? A. Peptide B. Disulfate C. Ester D. H 38. Decarboxyla ...
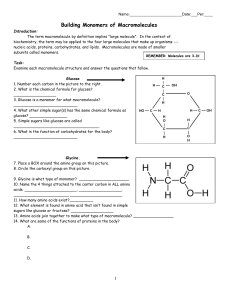
Building Monomers of Macromolecules
... Building Monomers of Macromolecules Introduction: The term macromolecule by definition implies "large molecule". In the context of biochemistry, the term may be applied to the four large molecules that make up organisms --nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. Macromolecules are made of ...
... Building Monomers of Macromolecules Introduction: The term macromolecule by definition implies "large molecule". In the context of biochemistry, the term may be applied to the four large molecules that make up organisms --nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. Macromolecules are made of ...
2.3 Outline
... • Simple sugars such as glucose are a major source of energy in cells. • _________________________ are double sugars formed when two _________________________ are joined. • Sucrose, or common table sugar, is a disaccharide that consists of both glucose and fructose. • _________________________ such ...
... • Simple sugars such as glucose are a major source of energy in cells. • _________________________ are double sugars formed when two _________________________ are joined. • Sucrose, or common table sugar, is a disaccharide that consists of both glucose and fructose. • _________________________ such ...
Integration of Mammalian Metabolism
... • With low intensity work, lactate is cleared from the bloodstream as fast as it is made. • As work increases, there is a point when lactate is produced too fast for the body to ...
... • With low intensity work, lactate is cleared from the bloodstream as fast as it is made. • As work increases, there is a point when lactate is produced too fast for the body to ...
Presentation - MD Anderson Cancer Center
... • Most studies of ketogenic diet are in fact studies of calorie restricted ketogenic diet and evidence for CRKD antitumor effects strong whereas mixed for ad libitum ...
... • Most studies of ketogenic diet are in fact studies of calorie restricted ketogenic diet and evidence for CRKD antitumor effects strong whereas mixed for ad libitum ...
annotated slides Power Point
... • A variant of TCA for plants and bacteria • Acetate-based growth - net synthesis of carbohydrates and other intermediates from acetate - is not possible with TCA • Glyoxylate cycle offers a solution for plants and some bacteria and algae • The CO2-evolving steps are bypassed and an extra acetate is ...
... • A variant of TCA for plants and bacteria • Acetate-based growth - net synthesis of carbohydrates and other intermediates from acetate - is not possible with TCA • Glyoxylate cycle offers a solution for plants and some bacteria and algae • The CO2-evolving steps are bypassed and an extra acetate is ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Ch. 6 Cellular Respiration
... Fats hydrolyzed to glycerol & fatty acids. How are carbohydrates stored? Stored as a polysaccharide, such as glycogen, in our liver & muscle cells. How is glycogen used between meals? Glycogen is hydrolyzed to glucose to serve as fuel between meals. ...
... Fats hydrolyzed to glycerol & fatty acids. How are carbohydrates stored? Stored as a polysaccharide, such as glycogen, in our liver & muscle cells. How is glycogen used between meals? Glycogen is hydrolyzed to glucose to serve as fuel between meals. ...
Gluconeogenesis
... Gluconeogenesis and starch/glycogen synthesis • In animals, lactate formed anaerobically in muscles is converted to glucose in liver and kidney and stored as glycogen or released as blood glucose. • In plants, G3P product of photosynthesis is converted to starch and stored in chloroplasts or conver ...
... Gluconeogenesis and starch/glycogen synthesis • In animals, lactate formed anaerobically in muscles is converted to glucose in liver and kidney and stored as glycogen or released as blood glucose. • In plants, G3P product of photosynthesis is converted to starch and stored in chloroplasts or conver ...
Carbohydrates are
... bonds in the carbon chain are said to be unsaturated Most plant fats are unsaturated oils. Corn oil, olive oil, and other vegetable oils are unsaturated fats. ...
... bonds in the carbon chain are said to be unsaturated Most plant fats are unsaturated oils. Corn oil, olive oil, and other vegetable oils are unsaturated fats. ...
Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in
... and an oxidizable substrate, such as NADH, to convert an alkane to a primary alcohol. Studies show that three additional reactions are required for the primary alcohol to under bg oxidation. Propose a pathway for the conversion of a long-chain primary alcohol to a substrate that can undergo b oxidat ...
... and an oxidizable substrate, such as NADH, to convert an alkane to a primary alcohol. Studies show that three additional reactions are required for the primary alcohol to under bg oxidation. Propose a pathway for the conversion of a long-chain primary alcohol to a substrate that can undergo b oxidat ...
Respiratory Substrates
... • Number of hydrogen atoms per mole accepted by NAD then used in electron transport chain is slightly more than the number of hydrogen atoms per mole of glucose, so proteins release slightly more energy than equivalent masses of glucose ...
... • Number of hydrogen atoms per mole accepted by NAD then used in electron transport chain is slightly more than the number of hydrogen atoms per mole of glucose, so proteins release slightly more energy than equivalent masses of glucose ...
BHS 150.1 – Biochemistry II Date: 2/1/2013, 2sndhalf Notetaker: Kim
... Most fats are put into storage in adipose tissue ...
... Most fats are put into storage in adipose tissue ...
peptides - WordPress.com
... provided for the brain and red blood cells; in the early fasting state, this is supplied from glycogen reserves. In order to spare glucose, muscle and other tissues do not take up glucose when insulin secretion is low; they utilize fatty acids (and later ketone bodies) as their preferred fuel. ...
... provided for the brain and red blood cells; in the early fasting state, this is supplied from glycogen reserves. In order to spare glucose, muscle and other tissues do not take up glucose when insulin secretion is low; they utilize fatty acids (and later ketone bodies) as their preferred fuel. ...
Objectives 7
... - Energy is stored as glycogen (carbohydrates), protein (amino acids) or triacylglyercols (fatty acids) - The four circulating fuels are glucose (most important), lactate, free fatty acids, and ketone bodies; these provide fuel in response to specific physiological conditions - In fed and early star ...
... - Energy is stored as glycogen (carbohydrates), protein (amino acids) or triacylglyercols (fatty acids) - The four circulating fuels are glucose (most important), lactate, free fatty acids, and ketone bodies; these provide fuel in response to specific physiological conditions - In fed and early star ...
pbl – night starvation - UQMBBS-2013
... highly branched glycogen state. In adipose tissue it is converted into acetyl-CoA and then stored as FA's and TAGS. ...
... highly branched glycogen state. In adipose tissue it is converted into acetyl-CoA and then stored as FA's and TAGS. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Ch. 6 Cellular Respiration
... Cells use many kinds of organic molecules as fuel for cellular respiration ...
... Cells use many kinds of organic molecules as fuel for cellular respiration ...
L20_StvnWAT
... • BUT liver can do b-oxidation on FA even if there is no need for ATP – In the liver, CoA can be regenerated in a pathway other than the Krebs cycle ...
... • BUT liver can do b-oxidation on FA even if there is no need for ATP – In the liver, CoA can be regenerated in a pathway other than the Krebs cycle ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.