Metabolism of ketonе bodies
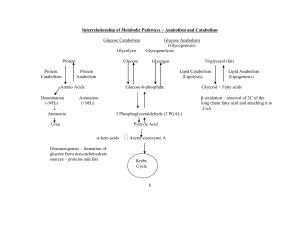
... The entry of acetyl CoA into the citric acid cycle depends on the availability of oxaloacetate. The concentration of oxaloacetate is lowered if carbohydrate is unavailable (starvation) or improperly utilized (diabetes). Oxaloacetate is normally formed from pyruvate by pyruvate carboxylase (anaplerot ...
... The entry of acetyl CoA into the citric acid cycle depends on the availability of oxaloacetate. The concentration of oxaloacetate is lowered if carbohydrate is unavailable (starvation) or improperly utilized (diabetes). Oxaloacetate is normally formed from pyruvate by pyruvate carboxylase (anaplerot ...
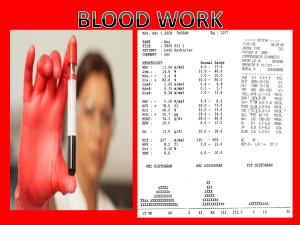
Blood Work - Mr. Lesiuk
... • Fasting blood sugar level tests are used to diagnose diabetes. • Blood work is collected first thing in the morning after 8 hours of fasting • Fasting, as the name suggests, means refraining from eating of drinking any liquids other than water for eight hours. It is used as a test for diabetes. I ...
... • Fasting blood sugar level tests are used to diagnose diabetes. • Blood work is collected first thing in the morning after 8 hours of fasting • Fasting, as the name suggests, means refraining from eating of drinking any liquids other than water for eight hours. It is used as a test for diabetes. I ...
Spotlight on Metabolism
... •Recurrent episodes of binge eating characterized by both: • Eating, in a discrete period of time (within a 2-hr period), an amount of food definitely larger than most people would eat during a similar period of time under similar circumstances • A sense of lack of control over eating during the epi ...
... •Recurrent episodes of binge eating characterized by both: • Eating, in a discrete period of time (within a 2-hr period), an amount of food definitely larger than most people would eat during a similar period of time under similar circumstances • A sense of lack of control over eating during the epi ...
Q43to47
... need fatty acids to make ketone bodies Blood glucose concentration would rise if alternate fuels not used, glucose will rapidly fall Blood fatty acid concentration would rise lipolysis releases fatty acids into the blood There would be fewer substrates for gluconeogenesis in the liver less glycerol, ...
... need fatty acids to make ketone bodies Blood glucose concentration would rise if alternate fuels not used, glucose will rapidly fall Blood fatty acid concentration would rise lipolysis releases fatty acids into the blood There would be fewer substrates for gluconeogenesis in the liver less glycerol, ...
Document
... = vitamins and minerals. RDAs (recommended daily allowances) have been long determined. Recent recommendations refine diet to prevent chronic disease. Essential nutrients must be in diet, cannot be created in body. (F) Carbohydrates should comprise ~ 50% of Calories. Most becomes glucose. For energy ...
... = vitamins and minerals. RDAs (recommended daily allowances) have been long determined. Recent recommendations refine diet to prevent chronic disease. Essential nutrients must be in diet, cannot be created in body. (F) Carbohydrates should comprise ~ 50% of Calories. Most becomes glucose. For energy ...
Document
... b. It increases the utilization of glucose for energy. c. It increase glycogen storage in cells. d. It increases the conversion of glucose into fat to be stored in adipose tissues. e. So it is the only Hypoglycemic Agent of body. ...
... b. It increases the utilization of glucose for energy. c. It increase glycogen storage in cells. d. It increases the conversion of glucose into fat to be stored in adipose tissues. e. So it is the only Hypoglycemic Agent of body. ...
Ketoacidosis - Wellington ICU
... of ketone bodies (keto-anions). - ketone bodies (acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate, acetone) are released into the blood from the liver when hepatic lipid metabolism has changed to a state of increased ketogenesis. - a relative or absolute insulin deficiency is present in all cases. CAUSES The thre ...
... of ketone bodies (keto-anions). - ketone bodies (acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate, acetone) are released into the blood from the liver when hepatic lipid metabolism has changed to a state of increased ketogenesis. - a relative or absolute insulin deficiency is present in all cases. CAUSES The thre ...
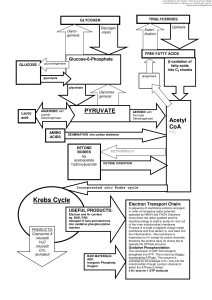
Regulation on Cellular respiration
... acid. Each cleavage requires one ATP, but produces 1 NADH and 1 FADH2. • The result is that Palmitic Acid, a 16-carbon fatty acid, produces 131 ATP molecules, whereas 2 glucose molecules produce 73 ATPs. • By mass, lipids produce about twice the energy yield of carbohydrates ...
... acid. Each cleavage requires one ATP, but produces 1 NADH and 1 FADH2. • The result is that Palmitic Acid, a 16-carbon fatty acid, produces 131 ATP molecules, whereas 2 glucose molecules produce 73 ATPs. • By mass, lipids produce about twice the energy yield of carbohydrates ...
BioN08 Metabolism of lipids Summer 2015
... increased urine flow, labored breathing because acidic blood is a poor oxygen carrier, and depression. • Ultimately, if untreated, the condition leads to coma and death. ...
... increased urine flow, labored breathing because acidic blood is a poor oxygen carrier, and depression. • Ultimately, if untreated, the condition leads to coma and death. ...
PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX
... b) Anaerobic glycolysis can not be accelerated enough to compensate its inefficient ATP production. ...
... b) Anaerobic glycolysis can not be accelerated enough to compensate its inefficient ATP production. ...
Selected Solutions to End of Chapter 17 Problems
... This is an underestimate because we did not include glycerol oxidation of which would produce a small quantity of water and we did not include longer chain fatty acids. But, it is also an overestimate because less water would be produced from each point of unsaturation. See problem 26 below. ...
... This is an underestimate because we did not include glycerol oxidation of which would produce a small quantity of water and we did not include longer chain fatty acids. But, it is also an overestimate because less water would be produced from each point of unsaturation. See problem 26 below. ...
the effect of deleting or inverting the 132 base pair repeats in a
... Obesity is epidemic, in part because Americans are eating more fat and more simple carbohydrates than ever, including sugar, high fructose corn syrup, white flour, white rice, and alcohol. Because simple carbohydrates are so low in fiber, large quantities can be consumed without getting full. Also, ...
... Obesity is epidemic, in part because Americans are eating more fat and more simple carbohydrates than ever, including sugar, high fructose corn syrup, white flour, white rice, and alcohol. Because simple carbohydrates are so low in fiber, large quantities can be consumed without getting full. Also, ...
Slide 1
... Subjective feelings of fatigue appear to coincide with an increase in glucagon and cortisol levels. These increased glucogenic hormones are often associated with a decline in serum glucose - resulting predominantly from glycogen depletion in the liver (and muscles) or associated with stress; result ...
... Subjective feelings of fatigue appear to coincide with an increase in glucagon and cortisol levels. These increased glucogenic hormones are often associated with a decline in serum glucose - resulting predominantly from glycogen depletion in the liver (and muscles) or associated with stress; result ...
Metabolism08
... breaks triglycerides into glycerol and fatty acids Most of the energy is stored in the fatty acids (glycerol can be converted to glucose or pyruvate) Fatty acids usually produce substantially more ATP than glucose (16 carbon fatty acid = 129 ATP) ...
... breaks triglycerides into glycerol and fatty acids Most of the energy is stored in the fatty acids (glycerol can be converted to glucose or pyruvate) Fatty acids usually produce substantially more ATP than glucose (16 carbon fatty acid = 129 ATP) ...
Chap 23 –Nutrition, Part III
... When we eat carbs they are basically converted into __________ (blood sugar) for our cells to use. Sometimes, when we eat too much carbohydrate (more than our bodies need at the present time), the reserve is stored as either: - ___ (*fats account for 80-85% stored energy) - _________ (*accounts for ...
... When we eat carbs they are basically converted into __________ (blood sugar) for our cells to use. Sometimes, when we eat too much carbohydrate (more than our bodies need at the present time), the reserve is stored as either: - ___ (*fats account for 80-85% stored energy) - _________ (*accounts for ...
Ketogenesis (Biosynthesis of ketone bodies)
... b. Enzymatic condensation of two molecules of acetylCoA, which catalyzed by thiolase (the reversal of thiolase reaction of fatty acid oxidation). 2- The acetoacetyl-CoA, condenses with 3rd molecule of acetyl-CoA to form β -hydroxy- β -methylglutarylCoA (HMG-CoA) catalyzed by HMG-CoA synthase (the ra ...
... b. Enzymatic condensation of two molecules of acetylCoA, which catalyzed by thiolase (the reversal of thiolase reaction of fatty acid oxidation). 2- The acetoacetyl-CoA, condenses with 3rd molecule of acetyl-CoA to form β -hydroxy- β -methylglutarylCoA (HMG-CoA) catalyzed by HMG-CoA synthase (the ra ...
3 Chemistry
... “Ketone” comes from the word “acetone”. A ketone is an oxygen atom joined to a carbon atom by a double bond, and the carbon is also bonded to two other carbon atoms. Many ketones are of great importance in industry and in biology. Examples include many sugars (ketoses) and the industrial solvent ace ...
... “Ketone” comes from the word “acetone”. A ketone is an oxygen atom joined to a carbon atom by a double bond, and the carbon is also bonded to two other carbon atoms. Many ketones are of great importance in industry and in biology. Examples include many sugars (ketoses) and the industrial solvent ace ...
A1981LY47200002
... development of understanding of the "As a graduate student at Camprocess of fuel selection in mammalian bridge, I had worked on the rat muscle. I hope that it adequately diaphragm assay for insulin and anti-inrepresented and acknowledged the sulin factors in blood plasma. This excontribution of coll ...
... development of understanding of the "As a graduate student at Camprocess of fuel selection in mammalian bridge, I had worked on the rat muscle. I hope that it adequately diaphragm assay for insulin and anti-inrepresented and acknowledged the sulin factors in blood plasma. This excontribution of coll ...
Slide 1
... – Energy yield depends on length of carbon chain (ex. 16C palmitic acid results in 129 ATPs, ~3.5x more than glucose) – Ketoacidosis: results if oxaloacetate in short supply; acetyl-CoA converted into ketones, which are weak acids; can occur due to starvation, low-carbohydrate diet, or by uncontroll ...
... – Energy yield depends on length of carbon chain (ex. 16C palmitic acid results in 129 ATPs, ~3.5x more than glucose) – Ketoacidosis: results if oxaloacetate in short supply; acetyl-CoA converted into ketones, which are weak acids; can occur due to starvation, low-carbohydrate diet, or by uncontroll ...
Digestive System
... Aids in formation of glycogen Aids in transfer of peptide monomer amino acids into cells ...
... Aids in formation of glycogen Aids in transfer of peptide monomer amino acids into cells ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.