Carbs and Lipids Review
... 16. Which involves food storage in animals? _______________________________________ a. Where is it found? _____________________________________________________ 17. What is cellulose used for? ___________________________________________________ a. Where is it found? __________________________________ ...
... 16. Which involves food storage in animals? _______________________________________ a. Where is it found? _____________________________________________________ 17. What is cellulose used for? ___________________________________________________ a. Where is it found? __________________________________ ...
Biomolecule exam review
... 16. Which involves food storage in animals? _______________________________________ a. Where is it found? _____________________________________________________ 17. What is cellulose used for? ___________________________________________________ a. Where is it found? __________________________________ ...
... 16. Which involves food storage in animals? _______________________________________ a. Where is it found? _____________________________________________________ 17. What is cellulose used for? ___________________________________________________ a. Where is it found? __________________________________ ...
Cellular Respiration
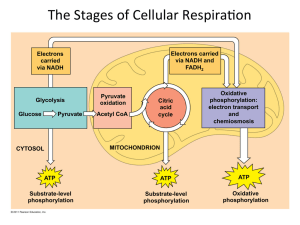
... Glycolysis – always occurs in the cytoplasm/cytosol of the cell & produces 2 ATP’s (Four molecules of ATP are produced during glycolysis, but 2 molecules are consumed in activating the glucose.); glycolysis is an anaerobic process and does NOT need oxygen. All living organisms go through glycolysi ...
... Glycolysis – always occurs in the cytoplasm/cytosol of the cell & produces 2 ATP’s (Four molecules of ATP are produced during glycolysis, but 2 molecules are consumed in activating the glucose.); glycolysis is an anaerobic process and does NOT need oxygen. All living organisms go through glycolysi ...
RESPIRATION
... • (b) Sucrose:- It is the principal soluble disaccharide which is converted into the glucose and fructose by the action of enzyme invertase. • (C) Glucose:- A monosaccharide hexose molecule which act as chief respiratory substrate. • (d)Fructose:- It is directly converted into fructose-6-phosphate ...
... • (b) Sucrose:- It is the principal soluble disaccharide which is converted into the glucose and fructose by the action of enzyme invertase. • (C) Glucose:- A monosaccharide hexose molecule which act as chief respiratory substrate. • (d)Fructose:- It is directly converted into fructose-6-phosphate ...
Nutrition
... very lucrative business venture as well. Still, practices are reluctant to include this service simply because of the time-management issue and the uncertainty that it will yield any positive acceptance. The first obstacle to overcome is to establish a need to provide the service within your pract ...
... very lucrative business venture as well. Still, practices are reluctant to include this service simply because of the time-management issue and the uncertainty that it will yield any positive acceptance. The first obstacle to overcome is to establish a need to provide the service within your pract ...
Disorders of phenylalanine and tyrosine metabolism
... further catabolised via cysteine sulphinate (precursor of the amino acid taurine, a component of the bile acids) to sulphite which is oxidised to sulphate by the molybdenum-containing enzyme sulphite oxidase (SO) and excreted in the urine. ...
... further catabolised via cysteine sulphinate (precursor of the amino acid taurine, a component of the bile acids) to sulphite which is oxidised to sulphate by the molybdenum-containing enzyme sulphite oxidase (SO) and excreted in the urine. ...
Principles of Metabolic Regulation
... Under resting conditions, [ATP] is high and [AMP] low because the total adenine nucleotide pool is constant. [Citrate] and [acetyl-CoA] are intermediate because O2 is not limiting and the citric acid cycle is functioning. Under conditions of active exertion (running), O2 becomes limiting and ATP syn ...
... Under resting conditions, [ATP] is high and [AMP] low because the total adenine nucleotide pool is constant. [Citrate] and [acetyl-CoA] are intermediate because O2 is not limiting and the citric acid cycle is functioning. Under conditions of active exertion (running), O2 becomes limiting and ATP syn ...
Mitochondria
... synthesized from a smaller one, it uses up the energy from another ATP. So we eat food to acquire ATP from catabolism, but since we don’t eat constantly, we need to synthesize and store glycogen and fat, anabolic processes that require ATP. These stored molecules can then be broken down later for ox ...
... synthesized from a smaller one, it uses up the energy from another ATP. So we eat food to acquire ATP from catabolism, but since we don’t eat constantly, we need to synthesize and store glycogen and fat, anabolic processes that require ATP. These stored molecules can then be broken down later for ox ...
03-232 Biochemistry
... key intermediates and their products. Feel free to draw a well-labeled diagram. Choice B: When cellular levels of O2 are limiting during strenuous exercise, glycolysis becomes the main source of energy. Describe what additional step(s) in either yeast or mammalian cells is (are) needed to allow cont ...
... key intermediates and their products. Feel free to draw a well-labeled diagram. Choice B: When cellular levels of O2 are limiting during strenuous exercise, glycolysis becomes the main source of energy. Describe what additional step(s) in either yeast or mammalian cells is (are) needed to allow cont ...
to DIABETES MELLITUS ppt
... and absorption from the digestive tract into the blood, thus reducing the glucose surge seen after a meal. E.g: Precose. • Byetta (Glucagon-like peptide 1 mimic) mimics the incretin GLP-1. It suppresses glucagon secretion and slows gastric emptying. By promoting satiety, it decreases food intake and ...
... and absorption from the digestive tract into the blood, thus reducing the glucose surge seen after a meal. E.g: Precose. • Byetta (Glucagon-like peptide 1 mimic) mimics the incretin GLP-1. It suppresses glucagon secretion and slows gastric emptying. By promoting satiety, it decreases food intake and ...
Intermediary Metabolism-II SECTION A What are ketogenic amino
... Discuss the role of carnitine. What are chylomicrons? How are water insoluble triacylglycerol and cholesterol transported in the aqueous medium of blood? Expalin fatty acid synthetase enzyme complex components. What is the effect of dietary cholesterol on the cholesterol biosynthesis? When does acet ...
... Discuss the role of carnitine. What are chylomicrons? How are water insoluble triacylglycerol and cholesterol transported in the aqueous medium of blood? Expalin fatty acid synthetase enzyme complex components. What is the effect of dietary cholesterol on the cholesterol biosynthesis? When does acet ...
Name 1 Bio 451 17th November 2000 EXAM III KEY
... A. Explain why individuals with a hereditary deficiency of carnitine palmitoyl transferase I have muscle weakness. Why are these symptoms more severe during fasting? This enzyme is required for transport of fatty acids into the mitochondrion so that they can yield energy. FA are particularly importa ...
... A. Explain why individuals with a hereditary deficiency of carnitine palmitoyl transferase I have muscle weakness. Why are these symptoms more severe during fasting? This enzyme is required for transport of fatty acids into the mitochondrion so that they can yield energy. FA are particularly importa ...
Chapter 6
... • Ketones are by-products of fat catabolism • Ketosis occurs when ketones (acidic) inappropriately lower blood pH • Ketoacidosis occurs when blood pH falls, further resulting in severe dehydration ...
... • Ketones are by-products of fat catabolism • Ketosis occurs when ketones (acidic) inappropriately lower blood pH • Ketoacidosis occurs when blood pH falls, further resulting in severe dehydration ...
Chemistry of Fats and Carbohydrates
... All living things are composed of many different kinds of chemical molecules. Two very important chemical molecules are fats and proteins. Both make up parts of living cells. Fats are a part of all cellular membranes. They also may be stored within a cell as an energy source. Proteins form part of a ...
... All living things are composed of many different kinds of chemical molecules. Two very important chemical molecules are fats and proteins. Both make up parts of living cells. Fats are a part of all cellular membranes. They also may be stored within a cell as an energy source. Proteins form part of a ...
Protein Metabolism - Morning By Morning!
... Produce glutamate – may be deaminated to yield ammonia for urea cycle. Can be converted to glucose (alanine-glucose cycle) – transport N to liver for conversion to urea while also generating needed substrate. Occurs in low CHO stores (liver glycogen) to maintain blood glucose; eExcessive use for glu ...
... Produce glutamate – may be deaminated to yield ammonia for urea cycle. Can be converted to glucose (alanine-glucose cycle) – transport N to liver for conversion to urea while also generating needed substrate. Occurs in low CHO stores (liver glycogen) to maintain blood glucose; eExcessive use for glu ...
LIPID MOBILIZATION
... • Roles of FABPs – Promote cellular uptake of FA – Facilitate targeted transport of FA to specific ...
... • Roles of FABPs – Promote cellular uptake of FA – Facilitate targeted transport of FA to specific ...
Energy Metabolism and Mitochondria
... The process of glycolysis and citric acid cycle generates high-energy electrons that are carried by the NADH and FADH2 molecules. The NADH (and FADH2) molecules transfer their electrons via multiple electron carriers that are components of the electron transport chain. These are located in the mitoc ...
... The process of glycolysis and citric acid cycle generates high-energy electrons that are carried by the NADH and FADH2 molecules. The NADH (and FADH2) molecules transfer their electrons via multiple electron carriers that are components of the electron transport chain. These are located in the mitoc ...
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
... Fates of Pyruvate Under aerobic conditions In most aerobic organisms, pyruvate continues in the formation of Acetyl CoA and NADH that follows into the Krebs cycle and ETC ...
... Fates of Pyruvate Under aerobic conditions In most aerobic organisms, pyruvate continues in the formation of Acetyl CoA and NADH that follows into the Krebs cycle and ETC ...
Milk products
... (bacteria) added to milk and incubated for 8 hours to let fermentation occur. Lactose changes to lactic acid. The acid coagulates milk protein thickens the yoghurt and gives the flavour Cooled, other ingredients added Packaged ...
... (bacteria) added to milk and incubated for 8 hours to let fermentation occur. Lactose changes to lactic acid. The acid coagulates milk protein thickens the yoghurt and gives the flavour Cooled, other ingredients added Packaged ...
November 6th
... -oxidation yields n-2/2 NADH n-2/2 FADH2 You make n/2 Acetyl-CoA, which enter TCA cycle to yield 3n/2 NADH n/2 FADH2 n/2 ATP 3ATP per NADH Lost in activation 2ATP per FADH2 ...
... -oxidation yields n-2/2 NADH n-2/2 FADH2 You make n/2 Acetyl-CoA, which enter TCA cycle to yield 3n/2 NADH n/2 FADH2 n/2 ATP 3ATP per NADH Lost in activation 2ATP per FADH2 ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.