* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download endocrine system - Coach Frei Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Gynecomastia wikipedia , lookup
Vasopressin wikipedia , lookup
Sex reassignment therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (female-to-male) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Hypothyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Pituitary apoplexy wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
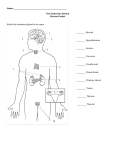
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM A ____________ is any organ __________________________________________. Endocrine glands are groups of tissues ____________________________________ from materials already present in the blood or lymph. Hormones act as ____________________________. They coordinate and direct activities of target cells and organs throughout the body. Negative Feedback A mechanism that regulates homeostasis within the body. A drop in the level of a hormone will trigger a cascade of events that will result in an increase of that hormone. The opposite can also occur, too much of a hormone will send a signal to stop or decrease the production of that hormone. The Pituitary Gland Divided into ______________ and ______________ lobes. Known as the _________________________ because of its major influence in body’s activities The Anterior Pituitary Lobe 1. Growth Hormone (_____) Is responsible for ______________ and _____________________of ____________ and ________________. Also helps ________ to be used for energy; this ____________________________________. 2. Prolactin hormone (_____) _____________________________________________ and stimulates the production of __________ after childbirth. The function in males is _______________. 3. Thyroid stimulating hormone (_____) Stimulates the _____________ and secretion of the ___________________________ 4. Adrenocorticotropic hormone (______) Stimulates the ____________ and secretion of the ____________________________ The Posterior Pituitary Lobe: ______________ 2 hormones made by the _______________________: 1. Oxytocin Released during ______________________. Causes strong ____________________ of the _________________. 2. Vasopressin Changes into _______________________ hormone (ADH) as soon as it enters the bloodstream. Maintains a _______________________________ by increasing the amount of water that is absorbed by the kidneys. Results in _______________________________ output and _______________________________ volume. Thyroid Gland Secretes 3 hormones: 1. Triiodothyronine (T3) 2. Thyroxine (T4) 3. Calcitonin Iodine hormones These hormones are produced when thyroid stimulating hormone triggers the thyroid to become active. 1. and 2. The first 2 hormones (T3 and T4) _____________________________ to work properly. The iodine for these hormones comes _____________________________ it combines with the amino acid _________________ to form T3 and T4 T 3 and T4 control the rate of _______________________________________ throughout the body. 3. Calcitonin controls the ________________________________________________ in the bloodstream. _____________ levels of calcium ions in the blood stimulate the ______________________ of calcitonin. Calcium is then stored in _____________ and calcium concentrations in the blood stream _________________ Parathyroid Glands Secretes a hormone called _______________________ (PTH). Extracts calcium from bones to ____________________________________________________ levels. The hormone causes an increase in number and size of ___________________ (bone-demineralizing cells) which _______________________________ from the bones. Thymus The major hormone is ____________________ Stimulates the lymphoid cells which are responsible for the production of __________ an important part of the _____________________________. Adrenal Glands Epinephrine (adrenalin) Released in response to _______________. _________________ the _________________________ and helps the __________________________ _______________ for energy needs. Considered the “fight or flight” hormone Gonads (sex organs) 1. Ovaries – the __________________ sex organs, found at the end of each Fallopian tube; produces: estrogen for __________________________________________ and progesterone which prepares the ___________________ for implantation. 2. Testes – the ___________ sex organ; found in the scrotum sac; produces: testosterone for __________________________________. Pancreas Pancreas as an endocrine gland produces: 1. insulin - a hormone that promotes the _____________________________________ by cells 2. glucagon - a hormone that causes the liver to ___________________________________ ______________ and release it as glucose into the bloodstream Pineal Gland Produces the hormone _____________________ Amount of light entering the eye affects the amount of melatonin secreted The ______________ it is, the ____________________________ produced. The ________________ it is, the ___________________________ produced. Causes low body temperature & ______________________.