* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 7-2.5 Summarize how genetic information is passed from parent to
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
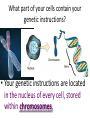
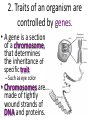
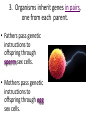
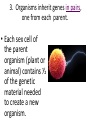
The Basics of Genetics 7-2.5 Summarize how genetic information is passed from parent to offspring by using the terms genes, chromosomes, inherited traits, genotype, phenotype, dominant traits, and recessive traits. 7-2.6 Use Punnett squares to predict inherited monohybrid traits. 1. Physical characteristics (traits) are passed or inherited from parent to offspring through sexual reproduction. What part of your cells contain your genetic instructions? • Your genetic instructions are located in the nucleus of every cell, stored within chromosomes. 2. Traits of an organism are controlled by genes. • Genes are responsible for the inherited characteristics that distinguish one individual from another. 2. Traits of an organism are controlled by genes. • A gene is a section of a chromosome, that determines the inheritance of a specific trait. – Such as eye color • Chromosomes are made of tightly wound strands of DNA and proteins. 3. Organisms inherit genes in pairs, one from each parent. • Fathers pass genetic instructions to offspring through sperm sex cells. • Mothers pass genetic instructions to offspring through egg sex cells. 3. Organisms inherit genes in pairs, one from each parent. • Each sex cell of the parent organism (plant or animal) contains ½ of the genetic material needed to create a new organism. 3. Organisms inherit genes in pairs, one from each parent. • A human body cell contains 46 Chromosomes, which are stored inside every cell’s nucleus. • Human sex cells (sperm or egg) contain 23 chromosomes each. Sexual Reproduction (2 parents) creates unique offspring. • In plants, male chromosomes are passed through pollen grains to female egg cells. Once fertilized, these eggs will develop into seeds. • The new plants will receive a combination of traits from both parents. 3. Organisms inherit genes in pairs, one from each parent. • One gene from the pair is called an allele. 4. Genes may be expressed in two different forms. • Genotype –Set of genes carried by the organism –“genetic” make-up • Phenotype –Physical expression of the genes –The way the trait shows 5. Some traits are dominant, while others are recessive. • Dominant trait will always be expressed in the phenotype (mask or cover) • Recessive trait can be masked/covered by the dominant trait. • Geneticists use symbols (letters) to represent the different forms of a gene (alleles) Alleles for dominant traits are represented by a capital letter. Yellow seeds are dominant……. Y Alleles for a recessive trait (for the same gene) are represented by THE SAME lower case letter. Green seeds are recessive………. y Dominant (yellow) = Y Recessive (green) = y • In pea plants, tall is dominant over short. The letter used to represent the tall gene is T. • The short gene is represented by t. Tall =T Short = t In humans, brown eyes are dominant over blue. Brown = B Blue = b 6. Dominant genes cover recessive genes when both are inherited by an organism. • Y + y = yellow seeds (yellow is dominant) • T + t = tall plant (tall is dominant) • B+ b = brown eyes (brown is dominant) A PUREBRED organism has two of the same genes for a trait. TT = purebred TALL tt = purebred SHORT A HYBRID organism has two different alleles for a trait. Tt = hybrid TALL (tall is dominant.) Bb = hybrid for black feathers (black is dominant.) Will a hybrid human with the genes Bb have brown or blue eyes? • Bb = Brown eyes • The dominant gene (brown), will be expressed in a hybrid. Why must all blue eyed people be PUREBRED for that trait? • If the dominant gene is present, it will always be expressed. • The only possible gene combination for blue eyes is bb. These basic laws of inheritance control the traits of all living organisms on Earth.